 Leading Blog | Posts by Category |
 Leading Blog | Posts by Category |
12.04.23

Society Needs a Leadership Paradigm Shift
THE contemplation of character has engaged great minds reaching back to Confucius, Aristotle, and Plato. Building on the shoulders of such philosophical giants and the subsequent research over millennia, science has further defined, assessed, and developed the concept of character to apply findings to organizational leadership. But what has become abundantly clear is that disregarding the science of leaders’ character has led to incredible dysfunction for organizations and society as a whole. In countless cases, leaders have missed opportunities to tap into the enormous potential associated with the development of character to create innovation and excellence. What the Science of Leadership Character Reveals In Fred Kiel’s groundbreaking book, Return on Character, he discussed the seven-year study of 84 CEOS, their executive staffs, and their employees, which found that CEOs with strength of character brought in nearly five times greater return on assets and enjoyed a 26 percent higher level of workforce engagement. Further research at the Ivey Business School has revealed the following benefits of leaders moving from weak to strong character:
Taking into consideration two of these benefits — employee voice (18%) and psychological safety (16%) — alone gives all the evidence needed to show that you can’t turn a blind eye to the development of character. These metrics relate to judgment and decision-making in organizations, and it’s easy to see that if the leader doesn’t allow employees to feel psychologically safe, they won’t voice their concerns, nor will they engage in risk-taking needed for innovation for fear of reprisal. Let’s take a look at the anatomy of character, how it establishes itself, and what leaders can do about it. Our research reveals a consistent overweighting of the character dimensions of drive, accountability, and integrity and an associated under-weighting of temperance, transcendence, humility, and humanity. However, when the traits associated with integrity — being authentic, candid, transparent, principled, and consistent — are overweighted without being counterbalanced by the under-weighted dimensions — self-awareness, vulnerability, empathy, compassion, patience, and calm, a person can end up being a bully, abrasive, dogmatic, and toxic. In terms of psychological safety, how safe do employees feel when their leaders are bullies, abrasive, dogmatic, and toxic? How likely are employees going to speak up under these conditions? The anatomy of character explains the persistence of toxicity in organizations — and these are matters of character, not matters of competence. Now consider what enables high performance in organizations. The space for innovation and growth relies on dimensions of character that are often in short supply, like transcendence — being appreciative, inspired, purposive, optimistic, creative, and future-oriented. The beauty associated with the science of character development is that investments made to develop character underpin all key metrics of the organization. The Underlying Problem Among thousands of leaders with whom we’ve worked, few would describe themselves as ineffective or toxic leaders until they see themselves through others’ eyes. We tend to judge ourselves on our intentions and others on their behavior, and the gap between them is significant. This is compounded by the fact that self-awareness — a behavior associated with humility — is exceptionally weak. Research reveals that although 85 percent of people believe they’re self-aware, only 10 percent actually are. We’ve constructed an “anatomy of leader character” based on a set of 11 dimensions and associated behaviors. This is only the starting point, but that starting point provides an exceptionally solid research base to support the paradigm shift to elevate character alongside competence. A key part of the science shows that character and competence are like apples and oranges in terms of what they are, how they need to be developed, and how they can be applied. Too often in organizations, the notion of competency drifts into that of character, missing the fundamental tenet that character is a habit of being that permeates a person’s personal and professional life, and, importantly, that the dimensions of character are interconnected. The conditions that we thought of as a strength are actually operating like a vice. Making the Necessary Course Correction Although it won’t happen overnight, these key steps will promote the needed paradigm shift to develop positive dimensions of character: 1. Cultivate awareness: The paradigm shift starts with a clear understanding of what character is and how it operates. Extensive research and analysis concerning this can equip leaders with the necessary means to scale it in their own organizations. It is critical to understand that character is not just about morals and ethics but, in its fullest form, about human flourishing through better judgments and well-being. It’s this more complete formulation and habit of character that we look to import into leaders’ lives. This step is straightforward and quite doable. 2. Attend to your character development: Again, many resources are available to start this journey, including an app to develop character. The more you apply yourself toward character development, the better able you are to observe it in yourself and in others. It tends to snowball; it’s contagious. You begin to understand the ways in which your organization enables or inhibits the development of character and where the overweighting and underweighting are occurring. 3. Work on the organization: Organizations are hard-wired around competence. Simply put, wherever competence resides, character belongs. This is a more difficult part of the journey, and for leaders to take on an organizational paradigm shift, it needs to course correct throughout. For example, all facets of selection, promotion, and rewards must be undertaken through the lens of character. This may sound daunting, but many organizations are embarking on the journey — from nonprofits, to professional sports teams, to healthcare organizations, to financial institutions, and more. The science surrounding character provides the critical compass for the path forward.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:48 AM
11.27.23

5 Leadership Development Practices to Kick to the Curb
IN MY THIRTY YEARS as an executive coach, I have seen a lot of change — the complete digital transformation of the workplace, increased diversity of the labor market, the shifting role of employers. But one thing that has largely remained unchanged has been the approach to leadership development. Even though the world looks nothing like it did 30 years ago, organizations still cling to strategies and methodologies developed in the 20th century. Here are five outdated practices that organizations need to kick to the curb immediately: 1. Limiting the definition of leadership Many have asked me how to define a leader, but I have refused. There is no one way to be a leader. Effective leadership does not rely upon a standard set of characteristics like charisma or aggressiveness. Narrowly defining leadership restricts innovation by excluding countless points of view and modes of operating. Yet, many learning and development strategies are built towards forcing leaders to fit themselves into a restrictive mold. When leaders are pressured into leadership styles that go against their natural way of operating, they are set up for failure. It’s like wearing a set of clothes that don’t fit. Leaders feel self-conscious and uncomfortable. They end up focusing on themselves instead of the people and organization they are leading. Opening the definition of leadership empowers leaders to play to their strengths rather than confining them to operate within a set style. And it opens the door to greater diversity in the leadership ranks and pipeline. 2. Focusing solely on skill development Early in my career, I worked as a corporate trainer. Sessions were standardized training with 30 or more participants working on building skills or horizontal development. After the sessions, there was time for questions, and often, I would be asked, “This is great, but how do I actually use this in my day-to-day?” Vertical development answers that question by building a leader’s capabilities and capacities. Capabilities are sets of skills and the ability to apply these within the context of the moment. Capacity is a leader’s ability to contain, manage, or affect change in the evolving circumstances within their role. Traditional training and skill development are needed, but without vertical development to contextualize the use of these skills, leaders will fail to transfer these skills into their daily routines. In short, without vertical development, training dollars are wasted. 3. Using standard 360 assessment tools Most assessment tools — like most leadership development models — were created in the last century and no longer accurately reflect a leader’s developmental needs. The typical 360 assessment is too linear and only provides a snapshot of the leader at a single point in time. They provide limited value in our current fast-paced, complex, constantly changing, non-binary business environment. Organizations need a way to measure and track a leader’s development over time rather than a one-and-done assessment. Assessments should rely on a feedback loop from leaders, managers, and coaches to evaluate and track progress. Insights could then be used to develop new goals, creating a continuous learning experience. 4. Relying on ranked or traditional performance evaluations In the early 2000s, companies were beginning to abandon performance evaluations because they provided very little helpful information regarding talent decisions and development. Typically, evaluation scores are determined subjectively, which can often lead to disagreements between managers and direct reports on whether expectations are being met. Performance evaluations are also a massive drain on manpower and resources. Yet, having no alternative, performance evaluations have once again become popular because organizations feel they must “do something” to evaluate workers. Our company has decided to leave performance evaluations in the past where they belong. We have opted for manager/employee alignment tools. Instead of relying on a once-a-year subjective evaluation, our leaders work regularly with direct reports to ensure that everyone on the team is aligned to the same priorities, goals, and objectives. 5. Manually managing leadership development programs I recently hosted a webinar and polled the audience on how they managed their programs, and more than half of the respondents said they either used spreadsheets or manually tracked everything. When programs are manually managed, the cost and labor associated with development programs become unsustainable. Worse, manual management opens the door to human errors like coach or mentor mismatches, mis-scheduling, and loss of data. With today’s technology, there is absolutely no excuse to manage leadership development programs manually. A well-designed leadership development platform can eliminate the pitfalls associated with manual management, while also increasing engagement among leaders. Technology can eliminate the guesswork when matching coaches and coachees, scheduling, and tracking development. The right platform will provide a throughline between development and return on investment. Is your organization guilty of clinging to these outdated practices? If so, it’s time to finally get your company’s leadership development into the 21st century. Failing to do so will guarantee a weak leadership bench that is unprepared to adapt and thrive within today’s ever-changing economic environment.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:45 AM
06.26.23

The One Truth: Moving From Separateness to Oneness to Elevate Your State of Mind
WHY do we feel anxious, disconnected, insecure, cluttered, and chronically stressed? Moments when we feel stuck with no way out. As counterintuitive as it sounds, it’s not your circumstances that make you feel that way. Jon Gordon explains in The One Truth that it’s always your state of mind that determines your performance. We are either in a low state of mind or a high state of mind. A low state of mind is characterized by a lot of thought, a lot of clutter, fear, anxiety, worry, insecurity, and/or doubt. A high state of mind consists of a lot of clarity, focus, belief, and confidence. He says that if you make a mistake in a low state of mind, you begin to question and doubt yourself. “But if you make the same mistake while you are in a high state of mind, you just brush it off and move forward. You have a next-play, next-moment mindset and look forward to the next opportunity.” Of course, we all go through high and low states for various lengths of time. It’s part of being human and how our thoughts work. When we experience a low state of mind, we need to stay in the game, understanding that this happens to all of us, and not let it get the better of us. Gordon identifies the Five D’s that sabotage us: The first is Doubt. Doubt breaks us down, and we begin to question ourselves and begin to feel weak and powerless. The second D is Distortion. These are the lies we tell ourselves about ourselves that lead to discouragement. The third D is Discouragement. “This happens when the doubt and distortion (negative thoughts) overpower your mind, seep into your soul, and cause pessimism, apathy, and hopelessness. We don’t give up because life is hard. We give up because we get discouraged.” The fourth D is Distraction. Distractions keep us from what matters most. “Distractions are the emeny of greatness and a soul-nourishing life.” The fifth D is Division. This is what happens “when you experience doubt, believe in distortions, get discouraged, and find yourself distracted. You feel divided.” We spiral downward. Gordon says it is important to realize that these negative thoughts are not coming from us initially. How do we counteract them? “The answer to doubt is trust. When doubt comes in, choose trust.” If you see negative thoughts for what they are—lies—the antidote is truth. (Truth: “You are here for a reason. There is a plan for your life.”) You can elevate your mind through gratitude. (Appreciate to elevate.”) Learn to encourage yourself. When you become distracted, stop and focus on what matters most. You defeat division through love because love connects. “Anytime you start to feel fearful and anxious and divided, if you respond with love, the fear will dissipate and you will feel united.” The path to a high state of mind is love. The solution comes from the inside—inside you. “When you fear that a circumstance has power over you, this lowers your state of mind. But when you know that you and your love are more powerful than your circumstance, this elevates your state of mind.” Fear complicates things. Love clarifies. The One Truth is that our state of mind, the thoughts we think, the words we say, the life we live, the power we have, and everything we experience is ultimately influenced by oneness and separateness. There is a battle being waged for your mind. “Life and other forces are always driving you to look outside and cause you to feel separate and weaken you.” While growing up, my parents would tell me that two wavelengths are being broadcasted all of the time: a positive one and a negative one. We are receptive to both but must choose which one we will listen to. Our first instinct is to listen to the negative. Connecting and tuning in to the positive is a developed state of being. We must overcome our instincts. Gordon put the concept this way: He thinks of the brain as an antenna that tunes into both positive and negative frequencies. “The more we tune into negative thoughts, such as fear, worry, doubt, jealousy, anger, or unworthiness, these thoughts negatively affect our antenna, which causes us to tune into and receive more negative thoughts.” There’s wholeness and there are forces constantly trying to tear you apart and create holes that lead to every dysfunction and weakness. Evil exists in the space between humans and God. With oneness there is no space for evil to exist. But if you can be divided, then evil has space to tear you and the world apart. This is not a business fable as we have come to expect from Gordon, but a heartfelt treatise on an issue of singular importance to him and to us. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:13 PM
04.17.23

Grace Under Pressure
REMAINING clam in moments of urgency when things are coming apart at the seams is the subject of Grace Under Pressure: Leading Through Change and Crisis by John Baldoni. Good leaders do three things, writes Baldoni. One, they take care of their people. Two, they take care of themselves. And three, they prepare for the future. What pulls them all together is grace. Grace is the “catalyst for the greater good.” Grace is critical to creating a connection with others that leads to positive forward movement. “When it comes to dealing with change and crisis, grace becomes evident in how we treat one another.” Baldoni looks at the three characteristics of good leaders through the lens of grace. In all three areas, Baldoni stresses the importance of community. It’s good for the organization, it’s good for you, and it’s good moving forward into the future and whatever it may bring. “Communities by nature are places where people feel they belong.” But it’s more than that, says Baldoni. “It is more than a place to work; it becomes a place to be.” We seek to create community where individuals feel empowered to lead with conviction rooted in wisdom, compassion gained from suffering, and good examples learned from experience. Three lessons regarding community:
Grace makes this possible. “Grace facilitates our ability to connect with ourselves more genuinely so that we can contribute more humanly with others. Such connections are essential to keep oneself together when everything around seems to be falling apart.” Here are some thoughts in brief from each of the three sections on how to demonstrate grace under pressure: Good Leaders Take Care of Their People Build resilience through divergent thinking throughout your organization. Become a better listener. Be direct and honest but inspire hope in the face of uncertainty and crisis. How can I make things better for others? How can I find humor in the situation? Good Leaders Take Care of Themselves Anchor yourself on the values that are most important to you. Even in a changing world, they will not change. Prioritize what is most important. Be intentional. Confront your biases and be willing to change. Assume the best in others. Good Leaders Prepare for the Future A crisis often elicits innovation. It is important that we are open to it and encourage it by listening to others. Be patient. “Having patience gives us the space to learn and enables the heart to direct and our character to rise to the fore.” Baldoni advises, “Speed to the chase, but wait for the opportunity.” Grace is more than a thought. It is a practice. It is something we do. In the final section of the book, Baldoni presents pithy and practical chapters for practicing grace under pressure. He highlights the many and sometimes subtle mindsets that motivate grace into action. At the end of the book, Baldoni summarizes his thoughts in a handbook and challenges us with a Grace Under Pressure Self-Assessment. Grace Under Pressure means meeting: 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:42 PM
01.24.23

Intentional Leadership: The Big 8 Capabilities for Leading Well
THE context of leadership has changed. It is more complex, and values that must be addressed have shifted. What we once glossed over now requires our attention and action. Mostly it requires that we be more intentional about relationships. Rose Patten puts it this way in Intentional Leadership: “The spotlight on leadership has moved to how people lead in challenging and changing circumstances. Innovative models, digitalization, technologies—these are all important. But what matters more is how leaders lead other people.” Good leadership happens when someone, by intention, has a positive impact—whether through empathy, inspiration, or wisdom. While some people seem to do this naturally, most of us—if we have the will—can learn it and continue to do it better. We must begin with our mindset. Our mindsets have consequences. This is where we begin to improve our influence and impact. Patten identifies four common beliefs that impede our success as a leader:
If these false beliefs are part of our mindset, then we will not take the steps necessary to respond to our leadership environment with the renewed capabilities that are required of us. They can become blind spots—unspoken beliefs that control our behavior—that, on a conscious level, we would never admit to. So, there is a need to examine ourselves to see where our behaviors don’t line up with what we say we believe. Leaders are dependent upon, and guided by, their own individual level of self-awareness, gained from self-reflection and feedback from others. This enables them to take deliberate, intentional action to check and adjust their mindset. The Big 8 The Big 8 capabilities have been created to address the needs of the changing leadership environment and to counter the false beliefs that can creep into our thinking. A healthy self-awareness is the sine qua non for all of the Big 8. They are not a definitive list of desired traits but a roadmap to self-reflection and intentional renewal for the leadership context we face today. It does not address all the skills that leaders are expected to have. Rather, the Big 8 offers the solution for leaders to become more effective and better balanced in their leading.
The Big 8 #1: Personal Adaptability Adaptability is the capacity that matters most. “Adaptability, open-mindedness, and renewal are overlapping, one leading to another. Open-mindedness enables adaptability to occur; with adaptability, the hope of renewal is possible.” It is what it means to be a lifelong learner. Adaptability requires accepting diverse views and the willingness to be uncomfortable. The Big 8 #2: Strategic Agility In a consistently changing environment, strategies are short-lived. Success depends on commitment and our ability to be adaptable and creative. It is a mindset issue. Can we adapt to the “reality that strategies do have a shelf life no matter how successful they were in the past?” The leader needs the mindset of what Patten calls the three A’s: Appraising constantly, adjusting courageously, and acting urgently. “The leader needs strategic agility, beginning with personal adaptability and overlaid with critical thinking.” The Big 8 #3: Self-Renewal Teachability—discovering what you do not know. Arrogance leads to regret. Patten reflects, “In my own leadership experiences, learning does come from mistakes and from admitting to not having all the answers. Becoming teachable and open and being around other great insightful people, including mentors, has helped me tremendously. Having a need to know things and a continuing curiosity also feed teachability. Whether it comes from innate curiosity or through intentionality – either is welcome and impactful in becoming a better leader.” The Big 8 #4: Certainty of Character “Character is not a victim of circumstances; it survives in spite of them.” Character is doing the right thing in spite of circumstances. Patten offers five checks to guide leaders: Keeping your word (Integrity), Looking to self for cause (Responsibility), Sticking your neck out (Courage), Letting go of others’ mistakes (Forgiveness), and Putting self in others’ shoes (Empathy). The Big 8 #5: Empathy Quite naturally, empathy helps you to connect with others. Not only understanding others but understanding your impact on them—putting yourself in their shoes. It allows you to adjust your behavior to the situation. The Big 8 #6: Contextual Communication Leaders must explain not just the what but the why—the context. “Communicating without “the why,” without the purpose, but with just ‘the what’ doesn’t do it in today’s workforce. More than an expression of respect, communicating ‘the why’ engenders trust.” Leaders must go beyond the analytical mindset to consider emotions and understand others’ states of mind by recognizing preconceived mindsets. The Big 8 #7: Spirited Collaboration Patten calls it spirited collaboration because it enables and encourages “dissent, with the ultimate objective of arriving at a better outcome. A harmonious group of like minds becomes an echo chamber of agreement. A leader who doesn’t allow diverse opinions and ideas for improvement will perform suboptimally.” Collaboration means listening well, understanding motivations, and depersonalizing ideas. The Big 8 #8: Developing Other Leaders—Not Only Followers “Shifting the way in which we lead from command and control to connect and collaborate means that leaders move more to empowerment and distributed leadership in the workplace.” Developing leaders is not just a matter of time and experience. It is more than just teaching technical skills. A development approach of 70-20-10 is recommended: 70% is real-time apprentice-like learning, 20% is mentoring, and 10% is classroom-type resources. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:43 AM
12.28.22

How Important Is Coaching in Professional Development?
AS A LIFELONG communication skills coach, I was asked recently by one of my colleagues how important individual coaching attention is for a person to learn and grow at any stage of their career. Of course, this is sort of like asking a baker if bread is worth baking. I’ve seen many breakthrough moments when people from all walks of life set their sights on developing new thoughts, actions, and habits. So, I’m going to say coaching is pretty important, both when we’re kids and when we’re adults. Here’s why: none of us can see ourselves as others do. We often look right past our beautiful, natural gifts (and every one of us has them, although we haven’t all become aware of them). We also might gloss over some weaker points we’d benefit from addressing sooner rather than later. Looking outward from inside our bodies, we see out into the world but can’t observe the effects of our own energy and behaviors on others as easily as those who are paying attention can see us. In my book Communicate with Courage: Taking Risks to Overcome the Four Hidden Challenges, I illuminate obstacles that hold most of us back at some point in our lives and present methods of overcoming them. The “big four” in my experience include:
It’s often useful to ask others where they see us compensating in communication or in life rather than stretching to reach our potential. We can choose to open ourselves up to others and invite them to share their observations, feelings, and opinions about us and the way we interact as we move through the world. Sometimes that feedback comes from a mentor or in a formal coaching relationship, and other times it’s family, friends, or co-workers who can shine a light on a path forward if we make them feel safe to do so. One-on-one coaching (or executive coaching) is tricky territory. Some folks who want to share advice or questions for us to ponder don’t have our best interests at heart. It’s possible they may care more about themselves and what they get from the interaction than what we receive from the communication. Some people would have us believe they’re able to guide us fairly and capably, but they’re not qualified to do so or might be blind to their own limitations. So, buyer beware. Don’t be too quick to believe praise OR criticism unless you’ve thought through the coach’s skill and motivations. Choose someone to trust – which involves risk – and who you believe is:
I mentor many adults who didn’t have a role model in their youth and many who did. It is possible to nurture one’s own learning at any age and possible to find mentors if one is willing to do a few hard things, such as:
You asked for a sample goal. Here are a few that people in jobs ranging from nursing home administrator to mechanical engineer are working on this week: For a client who’s finding their voice – participate in every meeting you attend for one month; for one who finds it hard to focus – document and prioritize a task list, then share it with your boss to become more aligned. For the client who feels overwhelmed – create a self-care menu and use one entry daily; for one who manages a large team, document what wows you about your employees and where they need to improve to make giving feedback easier at performance review time. Some coaching clients receive recipes to try to help them give more resonant praise, apply more skillful delegation, or approach a conflict constructively. We all have different growth needs. We’ll always have growth needs. As long as we’re breathing and learning, it’s never too late to make positive change.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:52 AM
11.22.22

Executive Presence: Why it Matters. How to Get it.
HOW IMPORTANT is executive presence? “No one can realize their full potential without executive presence,” says Joel Garfinkle. Seventy-eight percent of business leaders state that a low level of executive presence paralyzes career advancement. Executive presence is another way of saying leadership presence and should be a part of our personal leadership development agenda. “Practicing the skills that support a strong executive presence will lay the groundwork for becoming the best leader possible.” Executive Presence by Joel Garfinkle will show you the right qualities to be practicing and the specific behaviors that will highlight your strengths and increase your contribution as a leader. It is possible for the self-absorbed person to come across with the appearance of executive presence, but as Abraham Lincoln is often credited as saying, “You can fool all the people some of the time and some of the people all the time, but you cannot fool all the people all the time.” Garfinkle says: They can talk a good game and may even rise up through the ranks because some leaders perceive their arrogance as confidence. However, they lack essential qualities of executive presence that will make them truly a great leader, and most experienced leaders will see through them. Great leaders are committed to nurturing others, leveraging all of their executive presence qualities for the good of the team rather than just personal gain. And this is really what the endgame of executive presence is. Your confidence is people-centered. Executive presence is about lifting other people up, not dominating them. So, as you practice these behaviors, it is helpful to understand the why of building executive presence. Garfinkle has created the 3x3 Executive Presence Model—as shown below—to guide you in developing your executive presence. It sets up three domains, each containing three core competencies. “To cultivate executive presence, you need to look closely at how you show up at work, how you speak, and how you make decisions.”
What holds us back more than anything else is self-doubt. It is our internal beliefs that limit us. By examining the 3x3 Model, we can more easily see what internal thinking may be controlling the behaviors that hold us back from being as effective as we could be. The competencies that have been identified in the Model need to be in balance. “When a person has a great deal of one quality but not complementary ones, it can undermine their overall executive presence.” For instance, a leader who comes across as always in command but who hasn’t cultivated charisma probably won’t seem approachable. Such people tend to intimidate others and seem domineering, which negatively affects their ability to lead. Similarly, leaders who are extremely decisive but can’t vocalize the reason behind their decisions will have trouble gaining buy-in. To have executive presence, you need to develop the overall package, not just a few select characteristics. Many of us have some of these core competencies, but not all. The Model will help us to find the balance we need by filling in the gaps. What is particularly useful are the chapters discussing in depth the specific behaviors associated with each of the nine core competencies. There are questions, evaluations, and exercises throughout the book to guide you step-by-step and keep you on the right path. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:01 AM
11.18.22

Tears from Bordeaux: Leadership Lessons from a Failure to Win Gold
HOW COULD I be spending 10 days in Bordeaux, the premium wine district in France, yet feel unhappy? I had no work to do, was surrounded by beautiful scenery, and found amazing French cuisine around every corner. Yet, there I was, feeling sorry for myself. Was I somehow looking at circumstances the wrong way? Sure, I was honored to be representing Canada at the Senior World Water Ski Championships. But when I didn’t ski as well as expected, I suddenly lost my equilibrium. Friends and family tried to cheer me up, but a pat on the back from well-meaning supporters didn’t help much, especially when my expectations were linked to either a gold, silver, or bronze medal. Most would expect a rational, logical response to this situation from a 67-year-old who had for many years been CEO of a major construction and real estate enterprise. Yet I was letting my emotions take over. I didn’t throw my ski or swear a blue streak, but I found it hard to enjoy the beauty and bounty around me. Where did these feelings of despair come from? Shouldn’t I be able to lift myself out of the pit I’d fallen into? Couldn’t I replace the feelings of discouragement with different thoughts so I could I be happy in France in spite of how I had skied? Could cultivating more emotional intelligence have helped? I believe so. Surprisingly, when we become more curious, more patient, and more humble, we can cope with challenges and disappointments much more effectively as leaders — and competitive athletes. Permit me to explain: Curiosity: In essence, curiosity is a hunger to know more and have a greater understanding. It’s a drive to discover and to expand our horizons. Instead of focusing on what I hadn’t accomplished, I would have been wise to remain curious. I could have asked myself, “What can I learn from this? How can I get better?” Had I done this, I could have remained grounded and grateful rather than so self-focused and critical of my performance. Many executives, early in their careers, possess unbridled curiosity. But as time goes on and they achieve greater success, they allow their curiosity to fall to the wayside and therefore constrict their potential to learn. This is true in both business and in sports. As the great former UCLA basketball coach John Wooden said, “A leader who is through learning is through.” Humility: I arrived in France full of optimism, believing I had a good chance of finishing on the podium in my division. Although belief in our own abilities is important, confidence is overrated. What’s more, relying on ourselves puts a lot of weight squarely on our own shoulders. This burden can weigh us down and prevent us from performing at our best. In contrast, humility helps us to achieve more than we ever thought possible. Rather than trying to cultivate confidence, we should focus on cultivating humility. Instead of believing or trusting in ourselves, we’d be wise to trust in our training. As most athletes will admit, confidence is hard to conjure up and to sustain. However, putting our faith in the process can be liberating. Doing so takes the pressure off our performance and puts it where it belongs — on the process. With this approach, we can do the hard work required to hone our craft, and then when it’s time to perform we can be more relaxed and trust that we’ve put in the work required to excel. Former New York Yankee superstar Alex Rodriguez famously quipped that he was paid as a baseball player “to get hits.” However, instead of trying to get hits, he focused on trying to get four good “at-bats” each game. If he could do that, he said, “the hits would always come.” Humility begins with introspection and an honest appraisal of oneself. Just like looking in the mirror, humility gives us an accurate picture of ourselves. Patience: Warren Buffet recently noted, “The key to everything is patience. You get the chicken by hatching the egg, not by smashing it.” After my disappointing result in France, I felt like quitting as a competitive skier. Thankfully, my wife talked some sense into me, encouraging me to remember how far I’d come. She re-focused my attention on preparing for the next World Championships in two years. Patience comes from the Latin word “Pati,” which means to suffer. Therefore, patience can be understood as a willingness to suffer (or tolerate) delay without getting all bent out of shape. Raphael Nadal, the legendary tennis star with more Grand Slam victories than any male tennis player in history, emphasizes that in order to win, he needs to be “willing to suffer.” We can all learn from his example. Yet, in a culture geared to rapid or instantaneous responses to almost everything, we’re not accustomed to being patient. In our world, waiting is rarely required, and that’s made us unwilling to exercise patience. Rather than accepting that many circumstances are beyond our control, we plan our days and our lives around the mistaken expectation that traffic always runs smoothly, parking spots are always available, and flights are always on time. It would be nice if those expectations were met, but the reality is usually very different. We’ll continue to be frustrated and impatient unless we come to accept that life doesn’t always unfold as we hoped or planned. To retain or recover our emotional bearings when things don’t go as planned, cultivating our emotional intelligence and working to become more curious, more humble, and more patient will improve our attitude. These tips will help leaders and athletes alike to develop these soft skills. Cultivating Curiosity:
Developing Humility:
Learning Patience:
My trip to Bordeaux was a major disappointment. But it wasn’t just because I didn’t win a medal. It was disappointing because I’d been looking at life the wrong way. Instead of being grateful for the opportunity and enjoying the experience, I’d been caught up in the quest to win. In hindsight, I missed out on what could have been a great vacation. The next time, in addition to taking my ski equipment, I plan to also bring along curiosity, humility, and patience. Not only do I think they’ll be good traveling companions, they might also help me to perform better.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:00 AM
02.18.22

Impact Players
MOST people are contributors and do quite well at it. Then there are the few that are Impact Players. Which one are you? Could you have greater influence and impact? The difference between the two is in the way they work, and that determines their level of contribution, influence, and thus their impact. If we are just doing what we are told to do and looking out for ourselves, we are living beneath our potential. In business and in life, how we approach everything we do makes a huge difference regarding the impact we have on others. Liz Wiseman’s book Multipliers focused on the impact leaders have on someone’s ability to contribute. But that’s only part of the equation when it comes to making an impactful contribution. The other part is the contributor’s role. How does one become a top contributor—an impact player? We all want to contribute in meaningful ways and make an impact. To do this, we must have the right mindset. In Impact Players, Liz Wiseman shows us how. Impact Players are those who “make a significant contribution individually but who also have an enormously positive effect on the entire team. There’s also their mental game: how they view their role, work with their managers, and deal with adversity and ambiguity, and how willing they are to improve.” The fundamental difference between contributors and Impact Players is the way they respond to ambiguity and uncertainty and the everyday struggles in the workplace like problems without clear owners, unclear roles, unforeseen obstacles, moving targets, and unrealistic workloads. The Five Practices of Impact Players There are five practices that set Impact Players apart from contributors, as summarized in the chart below.
1. Do the Job That’s Needed. While others do their job, Impact Players do the job that needs to be done. Contributors see themselves as position holders. They do the work they’re given and stay within the boundaries of their role but risk becoming so myopic that they lose sight of the overall strategy and veer off the agenda. Impact Players have an awareness to see what needs to be done without being asked. They know what is valued by the organization and know what it takes for the organization to succeed. Having an overall view, they fulfill their role but play outside it too. Wiseman recommends, “Don’t just update others on your work; find out how their priorities are shifting so you can stay on top of the agenda.” 2. Step Up, Step Back. While others wait for direction, Impact Players step up and lead. Leadership is needed at all levels of an organization. Impact Players practice on-demand leadership. They step up when needed and step back when the task is completed. Impact Players take charge of situations that lack leadership. When they see an opportunity for improvement, they don’t wait for permission to act. They step up, volunteering to lead long before higher-ups in the organization ask them to do so. They are disruptors of the status quo who choose to lead rather than let things be. They offer a higher value proposition; instead of just carrying out the boss’s direction, they can also rally others. Wiseman adds, “The real key to not overstepping our authority or stepping on toes is to be willing to step back when our work is done and showing our colleagues that we can get behind them when it’s their turn to step up and lead.” 3. Finish Stronger. While others escalate problems, Impact Players move things across the finish line and build strength along the way. Impact Players offer a low-maintenance, high-accountability proposition: they take ownership, anticipate and wrestle down problems, and do what it takes to complete the job. Persistence allows you to move forward even in the face of ambiguity. When they need help, they call on reinforcements without relinquishing accountability. And they deliver—every time. 4. Ask and Adjust. While others attempt to manage and minimize change, Impact Players are learning and adapting to change. Small adjustments are always needed to stay on track. “The most valuable players are never finished. They are continually adapting, adjusting to hit the mark. When targets are continually moving, you need continual feedback, guidance, and correction so you can adjust your aim.” Feedback as information, not criticism. “The critical skill isn’t what you know but how fast you can learn.” Impact Players were able to adapt because they were confident in their ability to learn. But they were also comfortable enough with themselves that the prospect of failure—and inherent risk of learning—didn’t compromise their self-worth. It is a posture of confidence—the belief that I have value that can grow and evolve. 5. Make Work Light. While others add to the load, Impact Players make heavy demand feel lighter. Impact Players create a positive and productive work environment for anyone on the team—including themselves. Impact Players are quick to lend a hand and bring levity to stressful situations. Importantly, each one of these practices come with Safety Tips—emotional intelligence, if you will—that are valuable as you begin to develop these practices. The many examples found in the book help to see how others perform as Impact Players. You don’t need to master all five, Most Impact Players in their study usually exhibited three or four of the five practices. Where Do We Start? Becoming an Impact Player is a matter of adopting a new mindset. We begin by focusing on two master skills that all Impact Players seem to possess. First, we learn to see situations and issues through the eyes of the people that are served by our work—seeing the needs of others. And secondly, we view ambiguity and uncertainty as an opportunity, not a threat. We change the lens through which we see the world. When we use a threat lens, we become myopic: we look inward, consider the situational aspects, and tend to see ourselves as standing alone, lacking control or organizational backing. Wiseman writes about how to create a team of Impact Players and what behaviors and beliefs are the most and least coachable. Valuable information. Finding Meaning in Your Work If you are looking to find meaning in your work, the path to becoming an Impact Player that Wiseman lays out here is your answer. Being an Impact Player is about having an other-awareness. Along the way, some people have gotten the impression that meaning is something a leader gives you or an organization fills you with because of their mission. Meaning has become a right and someone else’s responsibility. Certainly, leaders can create a nurturing environment that facilitates the individual’s creation of meaning, but meaning comes from inside you. It’s personal. Working with initiative and enthusiasm is a decision you make regardless of the events unfolding around you. Ironically, while meaning is developed on the inside, it is not present in the self-absorbed mind. Meaning is derived from your impact and influence with the people around you. To do that, you need to think outside yourself. It doesn’t matter—and it has never mattered—where you work or what you do. If you apply the mindset of an Impact Player at work or in your personal life, you will find meaning in your life. Impact Players was a 2021 Best Leadershp Book of the Year for a good reason. The ideas presented here are critically important for leadership and influence. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:21 AM
01.14.22

The Eight Paradoxes of Great Leadership
LIFE is full of paradoxes. Sometimes we move forward by backing off, performing while being reflective, being an extrovert and an introvert, leading and following, confident and humble. Paradoxes are not to be solved but managed. It is a continuum to move along. It requires a heightened level of awareness. Leaders bring clarity to these paradoxes. In The Eight Paradoxes of Great Leadership by Tim Elmore, he covers eight such paradoxes of uncommon leaders. In such volatile times, embracing these paradoxes is critical for effective leadership. Leadership is seldom easy, but today it affords us the challenge of collaborating with a more educated, more entitled, more savvy population that has greater expectations of satisfaction and rewards than in past generations. Uncommon leaders stand out because they are able to juggle seemingly contradictory traits to lead such people. Emore introduces many great concepts and (sometimes very moving) stories to illuminate these paradoxes. He gets into the nitty-gritty of what these paradoxes look like or how they are practiced in everyday situations. I’ll just give you a flavor of each, so you get the idea of where Elmore is headed with these paradoxes and how you might begin to recognize them in your own leadership. Paradox #1: Uncommon Leaders Balance Both Confidence and Humility Leading today requires combining these two attributes—confidence and humility. Reality changes so quickly, leaders cannot become arrogant, but remain in a learning posture. At the same time, team members long for their leaders to inspire them with confidence. Paradox #2: Uncommon Leaders Leverage Both Their Vision and Their Blind Spots Vision gives leaders (and teams) a direction, but blind spots are often the very motivator that enables them to approach an idea in an unconventional way—and believe they can pull it off. Most new ventures require a leader to possess a clear target they want to hit. At the same time, their inability to see all the obstacles or challenges ahead of time helps them to maintain their energy as they try to hit their target. In short, leaders usually have to see something and fail to see something to reach their goal. When Elmore talks about blind spots, he’s talking about rookie smarts. He’s not talking about the blind spots of character that lead us to the wrong choices. Regarding these kinds of blind spots, he notes, “Our blind spots are often found conspicuously close to ur strengths.” Paradox #3: Uncommon Leaders Embrace Both Visibility and Invisibility In the beginning of any mission, most people need a visible leader, demonstrating what to do and clarifying the goal. Over time, however, these people need the leader to step aside to let them realize their potential. Paradox #4: Uncommon Leaders Are Both Stubborn and Open-Minded Leaders will never reach a goal without being strong-willed. Without a stubborn will, obstacles will stop them. At the same time, they’d be naïve to think they have all the answers at the beginning of a venture. They must be open to voices of counsel; to flex and to adapt to changing realities. Paradox #5: Uncommon Leaders Are Both Deeply Personal and Inherently Collective People need big-picture vision from their leader, someone who grasps the gravity of what’s happened, and the steps required to respond to it. At the same time, people need a leader who empathizes with their personal journey; someone who understands how the struggle feels to individuals, and who articulates the vision with a personal touch. Elmore adds, “Wise leaders seemed to understand their people and offered three gifts:” context to problems, applications (practical action steps), and belief (hope for a better future). Paradox #6: Uncommon Leaders Are Both Teachers and Learners In our day of unceasing change, leaders are forced to be teachers, and organizations are forced to adapt. To do this, however, these leaders must first and foremost be lifelong learners, always adapting and never resting on what they know. Leaders are both receptacles of information and libraries of information. Paradox #7: Uncommon Leaders Model Both High Standards and Gracious Forgiveness The paradox of this uncommon leader is their propensity to forgive people. It’s not that they lower their standards. It’s simply that they’re able to absolve a team member who acknowledges they failed to meet the standard and chooses to improve. Forgiveness isn’t approving what happened. It’s choosing to rise above it. Forgiveness does not remove the past, but it does expand the future. Paradox #8: Uncommon Leaders Are Both Timely and Timeless Uncommon leaders in the twenty-first century must balance this very difficult paradox. First, they must embrace and advance timeless principles that make for lasting success, values that have stood the test of time and worked in all generations and in every context. At the same time, these leaders must leverage culturally relevant methods and futuristic resources. Elmore says that leadership approaches have changed over the last seventy years. And so they have. He says we are now in the time of the Poet-Gardener. The Poet-Gardener possesses these ten characteristics:
They are very aware leaders and read situations before they lead them. As a result, they practice paradoxical leadership as a norm. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:52 AM
01.10.22

Smart Leadership: Four Simple Choices to Scale Your Impact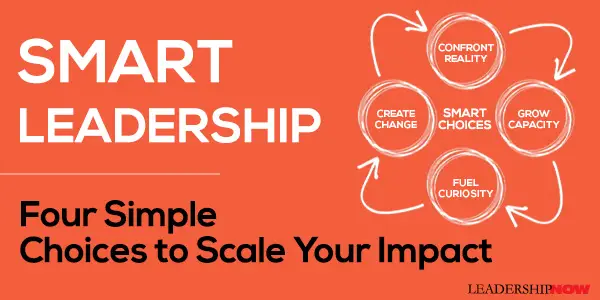
THERE’S power in choices. Yet we often don’t think about them. We operate on autopilot. Of course, not all choices are equal. Some matter more than others. Some are trivial or routine, but then there are those that change course for you, your team, or your organization. In Smart Leadership, author Mark Miller calls these Smart Choices—those that have high impact and require the most from us and most influence our futures. Assuming you have the character and skills to lead, there is one more crucial ingredient required for you to reach your full potential: Your choices. Your choices determine your impact. Smart Choices make Smart Leaders. Many factors come into play when making Smart Choices, so it is helpful to have a default way of considering them. To this end, Miller has outlined four Smart Choices to apply when faced with high-impact decisions.
Notice each choice, successfully made, leads to another choice—a virtuous cycle. The individual choices have inherent value, but the real power is released, and your impact multiplied, when you make all four choices. For each of these choices, Miller gives an overview and then goes deeper with specific practices in a couple of follow-up chapters for each question. Smart Choice #1: Confront Reality
Without the truth, you have no place to begin. You could end up anywhere. Seeking the truth is not a one-time event but a continuous process. Reality is always changing, and we must know where we are in relation to it. Your current reality is not your destination—it is only the starting point. Never be fearful of your current reality—embrace it, learn from it, and get ready to take action. What is true today does not have to define your tomorrow. It is only where you must begin. To begin to define your current reality, Miller suggest that you first define the universe. “Make a list of all of the areas in your life where it would be really good for you to have a crystal clear picture of your current reality.” Then start with the person in the mirror—“a hard look at your performance and the way you lead.” Smart Choice #2: Grow Capacity
Growing your capacity is how you bridge the gap between the reality of where you are and what you need to do to get there. Expanding your capacity is the path to your maximum potential. You must make time to lead. “Margin is not natural.” You need to create it. Margin—the time and space needed to reflect, assess, think, create, and plan. Do you have time and space for these critical activities? Without them, you will forever be reacting, like a ship without an anchor or a rudder. Capacity includes not just skills but your mental, physical, and emotional energy. Miller challenges us to “pick one of the energy boosting strategies (hydration, sleep, relationships, recreation, etc.) and make a commitment to yourself to incorporate the practice into your daily routine for thirty days.” Smart Choice #3: Fuel Curiosity
Curiosity fuels learning and your relevance. Miller suggests to rediscover your creativity, ask more and better questions, spend time with diverse and talented people (strangers), experiment, and read. Asking questions is your best tool. “Questions to a leader are like a pickaxe to a frontier miner. They can serve as your primary tool to unearth the nuggets of truth and insight you seek.” “Curiosity is rarely welcomed, particularly in a season of success. ‘If it’s not broken, don’t fix it,’ is a popular refrain from the many short-sighted, ‘successful’ leaders.” We have to avoid the success trap. Smart Choice #4: Create Change
Change puts all of these choices together. Change takes your vision and makes it a reality. Miller writes about the ability to “see the unseen.” “If you are a leader, you need a vision. You should always have a preferred picture of what you are trying to create.” Keeping a vision alive means backing up from the daily challenges of your job. Leaders mired in distractions and encumbrances of any sort cannot effectively and efficiently Create Change. How could they? They are just trying to survive. Acknowledging that change is hard, Miller reminds us of the tools of change we have at our disposal. Tools include passion (“it is the kindling to start the fires of change”), accountability, goals and measurement, values (they drive behavior), planning (must have credible plans), communication (we under-communicate the vision perhaps by a factor of ten), and recognition. As leaders, we have the opportunity to choose. Looking at our choices through the lens of these four questions will help us to choose wisely. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:37 PM
01.03.22

The Edge: How 10 CEOs Learned to Lead—and the Lessons for Us All
GIVEN that we live in a radically changing world, what got you here won’t get you there. In Michael Useem’s words, “The best capacities of an earlier time remain informative but also incomplete for the challenges we face ahead.” Therefore, “what’s required is a mixture of traditional capacities, fresh capabilities, and a learning bridge for combining the two.” In The Edge: How 10 CEOs Learned to Lead—and the Lessons for Us All, Michael Useem asks what gave ten CEOs the edge. The edge is that “place or point or period where your past skills are serving you, but you need to bring new skills online as well.” He explains: It can feel like a cliff edge because your comfort zone, the solid ground you navigated to get you where you are, is behind you. What lies beyond the edge is the opposite, an unfamiliar landscape barely coming into focus. Your task is now to acquire the skills you need in this new territory before your career or your enterprise falters as a result of your personal limitations. Useem has identified ten principles or capacities that will be called for to supplement traditional leadership capacities.
He chose ten CEOs that became what they needed to be when the situation called for it and incorporated at least one of these ten new capacities. “In finding their own ways forward, sometimes over years, our exemplars taken together provide us with an instructive roadmap for designing our own ways forward. We learn:

Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:28 AM
08.23.21

Timeless Leadership Lessons I Learned from My First Job as a Swim Instructor
THERE’S something about our first jobs that stick with us. They teach us things we didn’t expect to learn and shape the person we become later in our professional lives. This phenomenon happens even when that first job has absolutely nothing to do with the career you ultimately end up pursuing, which is exactly what happened to me. I was 14 when I first started as a lifeguard and swim instructor at my hometown pool in Canton, Connecticut. I got the position despite an awkward first interview: an inexperienced teenager – I simply wasn’t prepared for the questions they asked. What would you say are your greatest strengths and weaknesses? Where do you see yourself in five years? I didn’t know. But they gave me the job anyway. And in the months that followed, I learned some important lessons that guide me in my work life even to this day as a healthcare executive. Here are three of the most important ones: Lesson 1: Don’t Force It As a swim instructor, I quickly learned that moving at the student’s pace - moving into the pool one step at a time, taking small steps - or strokes - instead of telling them to jump into the deep end right off the bat, or worse yet forcing them into the water when they were not ready, creates much better results. Using the baby step approach develops students who are comfortable and who, instead of being so paralyzed with fear that they can’t move, feel ready to learn. Breaking lessons into smaller, more manageable goals - like reaching underwater for the penny on the stairs first and then submerging their heads in the shallow end second - actually increased my students’ rates of improvement because they could move to the next level with confidence. While each staff member may learn at a different pace, slow and steady progression in their individual roles is beneficial to all. Creating manageable and immediate goals - all of which may lead to the accomplishment of a larger goal - makes for a confident worker who enjoys learning new things and growing and tends to stay in their job or at the company longer. Lesson 2: Making it Fun Makes a Difference In swimming class, making lessons fun is easy: “Let’s see who can splash the most water out of the pool by kicking their legs as straight as possible!” almost always works with kids. And while they are busy having fun, they’re also improving an essential skill for their swimming. Not everything can be fun all the time – we call it work for a reason – but finding ways to turn trainings into games, holding a competition for the best way to improve a work process, or giving monthly employee of the month awards are all ways to reward staff for a job well done. No matter our age, we all enjoy playing, and making training enjoyable can create professionals who have perfected skills that will be essential for more serious situations. Lesson 3: Persistence Pays Off Anyone who has ever coached or taught knows the incredible satisfaction that comes from watching a student or athlete achieve a goal. As a swim instructor, watching the child who was scared to even step into the shallow end of the pool finally jump off the diving board was as rewarding for me as it was for the swimmer. One of my greatest managerial joys is seeing a LinkedIn posting about a new position or reading a healthcare publication article about some new company’s success and realizing that I am reading about one of my former employees. Our greatest success as managers is seeing those we mentored succeed themselves.  A lot has changed in the world of work since that summer, but the leadership lessons I learned giving swim classes at the pool in 1977 are as timeless as that vintage magazine cover. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:10 AM
07.02.21

Three Secrets to Building Strong Leaders
TOO many leaders are stuck in mediocrity. A Ketchum study found that only 23% of the 25,000 surveyed believe their leaders are leading well. Only 31% believe leaders communicate well. Only 17% have confidence that leadership will improve in the upcoming year. And after the 2020-21 Covid response, I doubt those statistics have changed much. Alain Hunkins, author of Cracking the Leadership Code, says “there is a path out of the muddle of mediocrity. Great leaders aren’t born—they’re made. If you are committed, you can learn and apply specific tools to improve how you lead.” Great leaders share these three fundamental qualities: connection, communication, and collaboration.
Connection The foundation of connection is empathy. Connection builds trust, insight, engagement, and results. So why don’t we see more of it? One reason is we simply don’t practice it. “It needs to be exercised regularly to get stronger. If you don’t use it, it atrophies.” Another reason is a rigid, right-wrong mindset. A right-wrong mindset can lead to controlling behavior. Needing to be right, disconnect you from others. “Clinging to a need to be right closes you off to the perspective and experience of others. You don’t listen—you fake listen.” A third reason is we fear empathy will open up an emotional can-of-worms. Not to mention the fear that expressing vulnerability will be taken advantage of. Fourth, we are too impatient to take the time to be empathetic. It’s true. Empathy takes time. “Leader with a bias for action may be operating with the unconscious belief that they don’t have time to offer empathy. But this belief has an unintended impact: Making those around them feel less valued and understood. When people feel devalued, their motivation plummets. These lead to declines in performance. Ultimately, results suffer.” There is also what is called the hot-cold empathy gap. That is, how our emotional state affects our ability to relate to someone else in an opposite emotional state. If I’m calm, it is difficult to relate to someone experiencing anger. And finally, the higher we go in an organization, the disconnected we become from those under us. Leading isn’t an abstract idea that exists between you and somebody else or a group of people. It’s a connection that’s built through a genuine relationship. Communication We would all agree that communication is critical to what we do, and we assume it is happening. We take it for granted. And we shouldn’t. There are three major obstacles to communication. The typical problem is that we are not on the same page. What I say is not what you hear. I know what I mean but do you. It’s called projection bias when we assume others know what we are thinking. Better to assume that what we mean is not what they understand and clarify. Those you are communicating with need context. You know why what you are saying is important and what needs to be done about it. When communicating, others need to know the background of your thinking. They need to know why you are saying what you are saying so they can act appropriately. Another common issue is overload. We are overwhelmed with information. “People have plenty of other messages competing for their precious brain cells. They’re not going to focus on you just because you want them to. People don’t want more information—they want insight.” Hunkins says to improve your communication you need to communicate with the end in mind, have a central message, create checks for understanding, own and fix communication breakdowns, make the implicit explicit, and master the medium—raise your communication game.” Collaboration To lead, you need the abilities and experience of everyone in the room. Collaboration takes your effectiveness to a whole new level. It is an increasingly important skill to have in our digital age. “Although you can’t motivate anyone else, you can design the conditions in which they motivate themselves. You can use your understanding of human needs and the employee experience to lead a team of joyful, engaged, and high-performing people.” Hunkins covers these topics well and also the need to simplify so that you don’t get in your team’s way. All three of these qualities are more challenging for the leader in this digital age. Organizations are increasingly made up of people who do not share common cultural backgrounds. These differences manifest themselves in the way people communicate and think. It becomes a challenge when building trust and collaboration. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:05 AM
06.21.21

What Your Organization Really Needs from You: Influence and Impact
LEADERS in today’s multinational, matrixed, diverse business world have impact through their ability to influence others. In many organizations, authority-based leadership is waning. Success is all about getting others to care about what you care about. The most effective leaders get their teams, their colleagues, and their suppliers to emphasize their priorities. People listen to what you have to say, and follow you, because they want to, not because they have to. When you have that kind of influence with others, the results begin to speak for themselves. In other words, you have impact on the organization. Why do some leaders “have a seat at the table,” and some feel they are struggling to bring others along? Why are some leaders able to influence in one role, but in another role, discover they aren’t having the influence they should? The solution is far from magical. For a large majority of leaders, the struggle to have influence and impact comes from things that you can manage and change. If you approach this situation with a growth mindset, you can build or rebuild that influence. In my new book, Influence and Impact: Discover and Excel at What Your Organization Needs From You The Most, written with George Bradt, we provide the tools every leader needs to grow and develop into the leader that others want to follow. Through my work with business leaders from CEOs to first-line managers, it has become clear that many people with strong technical prowess and powerful business acumen have unintentionally misunderstood an unwritten but essential aspect of their job. When organizations send clients to me for executive coaching, the work usually focuses on one of two things: How the leader thinks about their job, and how they do that job. Put simply, many leaders are not focused on two essential elements of their job. First, they are not completely focused on the priorities their organization needs from them. They may be doing the job mostly right, or they may be doing what their job description says. But many times, they are focused partly on what they know, what they wish, or what is comfortable, rather than what is needed. Tommy had risen to become the leader of a 1500-person business unit spanning four continents. He knew the economics of his business and was able convert his skills into practical technology and process solutions. But like many people, his strengths were also his weaknesses. Because Tommy understood the business in such depth, he often knew the answers well before his team did. As a result, he would identify the solution, inform others, and tell them to execute. Tommy felt overworked and underappreciated. His team felt undervalued, under-challenged, and demoralized. Through the coaching work we did, Tommy realized that he was avoiding the more complex and ambiguous aspects of his work where he had less confidence. As a result, Tommy was able to step back and let his team sort out operational problems without his involvement. Tommy’s boss saw that Tommy had freed up time and refocused his energies on what the manager needed from him, and told him, “I’ve been waiting for you to figure this out.” Second, leaders are doing the right things, but in a way that is not aligned with the style, attitudes and mores of their organization; in other words, the organizational culture. For example, they are decisive when they need to be collaborative. They are direct and blunt when they need to be tactful and patient. Or, they push for autonomy when their manager wants engagement. These are just a few examples. Fortunately, leaders can enhance their influence and impact by identifying and consistently focusing on the mission critical parts of their role and the essential aspects of the culture. The steps to building your influence are clear:
Every leader can identify the parts of their role that meet the needs of their manager, their colleagues, and their business. Every leader can understand the culture, and decide if it is a fit for them, or if they can change a few aspects of their style to adapt. All it takes is a willingness to confront the reality of the situation and grow as a leader. This is the key to professional success in organizations: Doing the job that is needed by the organization, in the way that is needed by the culture, consistently and reliably. Developing a deliberate focus, delivered in a manner that is aligned with the style and manner of your organization, invariably results in increased influence with others, a willingness to follow, and a larger impact on the organization and its mission.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:45 AM
03.05.21

Never Enough … Excellence, Agility, and Meaning
THE IDEA behind Never Enough isn’t perfection or even a state of dissatisfaction. It’s about realizing that the goal is not to get by but to “always look for more ways to make an impact.” Former Commanding Officer of Seal Team Two and White House Fellow serving with both George W. Bush and Barack Obama, Mike Hayes, says Never Enough is about aiming for excellence, agility, and meaning in everything we do. Adopting this mindset can “drive us all to lead more complete, more rewarding lives, each making the world a better place in our own unique way.” Never enough means realizing our full potential—intentionally. On an individual level, we must never look to be Never Excellent Enough and build our own capabilities in terms of knowledge and capacity, strength and control, and accountability and orientation. Never Excellent Enough Never excellent enough begins with knowing yourself and then having the will and the drive to do the work and stretch yourself. “The hungriest people will, in fact, do whatever it takes, and they’ll get better and better along the way.” It’s never easy. The discomfort lets you know you are on the right path. The way to get better over time is to know where we aren’t good enough, what aspects of our life are not satisfying enough, which goals we’re chasing aren’t the right ones. Our reactions are critical. Hayes says he’ll take control over raw intelligence. “The smartest SEAL isn’t the one with the greatest raw intelligence. It’s the one who has the best and quickest reaction to a problem. You want both—intelligence and control—but in the stressful moments, control matters, a lot.” In stressful circumstances, as leaders, we need “to be the person to pull others up, set the right tone, and keep everyone else on track.” Here’s the bottom line: We can’t—and shouldn’t—erase emotions from our lives. We can’t be good partners, friends, spouses, and parents without emotion, without feelings, without vulnerability and genuine honesty. But we also can’t be effective performers if we aren’t able to compartmentalize, to put those feelings aside when they’re not helpful to the situation at hand. Of course, the key to never enough excellence is humility. It means putting others first in all things. I needed to be humble enough to let others take the lead when their skills were the ones we most needed in the moment, and confident enough that I didn’t need to prove my worth and ultimately hurt the mission by trying to do what might be better handled by someone else. Hayes adds, “you’re not going to be the most productive performer unless you have the right attitude about the people around you.” And this goes when there is a need to discipline too. Discipline is not about you, “it’s about making people understand where they fell short, helping them to change their actions in the future, and altering their perspective.” And remember this: If someone is going to stay on the team, you make them better. If they need to leave, you let them leave with dignity and, in doing so, make them an ally in the future. Never Agile Enough Agility is about awareness and being flexible enough to do what needs to be done to get the desired outcome. That requires that you can be both a leader and a follower. Hayes calls it “dynamic subordination.” He says, “In an effective team, we must seamlessly move forward and back depending on the demands of the situation and the skills of the people around us. We don’t get locked into a particular job, a particular task, or a particular pattern: we maintain the agility to be whatever we need to be under the circumstances.” Dynamic subordination also has a flip side. When you are in a position to make the lives of the people around you better, step up. Always be ready to do what you can do. What plays into agility is knowing how to think. Have a process for decision-making that includes getting the broadest range of thought that you can. The concrete knowledge you need is the easy part—anyone can learn that. But the details don’t matter if you don’t have the right process. And if you do have the right process, you can go anywhere. It’s why strong leaders are able to jump from one industry to another, one organization to another. Some rules are made to be followed, and some are to be broken. Agility is knowing when to do which. Hayes asks everyone to think on two levels: run, and renovate. “You need to get the job done in the moment (‘run’) but you also need to figure out what might need to change to enable the greatest amount of long-term success (‘renovate’).” But run and renovate is about more than just making changes it should become part of everything you do. “When you push a teammate—when you challenge something they’ve done or try to initiate a hard conversation—you need to be thinking about how you’re trying to affect them in the moment (‘run’) and how you’re trying to shape their future (‘renovate’).” Never Meaningful Enough We all want to have meaning in what we do and impact the lives of those around us. It begins by having a belief system in place. Believe in something and start there. “The hard work is figuring out what the world needs and how it intersects with what feels most rewarding to you. Figure that out, and actually getting it done becomes the easy part.” Having an impact on others means getting to know others and having deep conversations. Hayes lives by three principles in this regard: “to be intrusive in people’s lives, to be a do-er rather than a be-er, and to push to have real impact on those around me.” That doesn’t mean being rude or overstepping other people’s boundaries, but “we have to be willing to intrude, to ask the hard questions and have the hard conversations—or we’re not really making a difference.” Being a do-er for others “means actually doing concrete things that make a difference in our friends’ lives, often at a cost to ourselves.” And impacting the lives of others gives meaning to our own lives as well. Never enough means it’s never over. I think we can simultaneously recognize how much we accomplish each day and also understand that our work is never done. There is always growth possible for each of us, ways we can push ourselves to be more excellent, more agile, and infuse our day-to-day with more meaning. There are always more people whose lives we can touch, more people we can lift up and inspire to get better and reach greater heights. Never Enough is an outstanding book. There is so much in the way of reliable, balanced advice. His wide-ranging experience—as a Navy SEAL, a White House Fellow, Chief of Staff and COO at Bridgewater Associates, and Head of Strategic Operations at Cognizant Technologies, among other roles—made his insights even richer. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:14 AM
07.24.20

Unleashing the Potential of Those You Lead
WHAT happens after you show up as a leader? Does the performance and potential of the people around you improve? In other words, it’s not about you. In Unleashed, Frances Frei and Anne Morriss want to change the conversation around leadership development from a focus on the leader to a focus on the people they are leading. And rightly so, because as they point out, the most important thing you can do as a leader is to build others up. To that end, they want to define this aspect of leadership as “empowering other people as a result of your presence—and making sure that this impact endures even in your absence.” Their point being that leadership really isn’t about how amazing you are, but how effective you are at unleashing other people. It is in that context hat they want us to look at leadership. I should note, however, that as a leader, self-improvement should be undertaken with a focus on the impact it has on those one is leading. The only way to improve the lives of those around us is to improve ourselves. It was Marie Curie that wrote, “You cannot hope to build a better world without improving the individuals. To that end, each of us must work for his own improvement, and at the same time share a general responsibility for all humanity, our particular duty being to aid those to whom we think we can be most useful.” Most leadership literature has this focus—at least implied. And it should go without saying that if one is thinking about how to improve the performance and potential of those they lead, it will improve your leadership. They go hand in hand. The impact of your self-improvement on others is the yardstick of its value. That said, there is an undue focus on the self in all of us. Although that affects everything we do, it’s not a leadership problem; it’s simply a human problem. But to be an effective leader, we must shift our focus off of ourselves. As the authors point out, “If you seek to lead, then your focus—be definition—shifts from elevating your self to protecting, developing, and enabling the people around you.” But often, we become focused on being seen as leaders than simply leading. Leadership makes us vulnerable as it exposes who we are. That’s the irony of many of the tactics we use to protect ourselves as leaders. They can backfire and undermine the perceptions we’re working so hard to cultivate. In order to look like leaders, we end up behaving like smaller, two-dimensional versions for ourselves. We obscure the parts of ourselves that real leadership demands, cutting off access to our full humanity. In the choice to insulate ourselves from the judgment of others, we disconnect from leadership’s core mandate to make those very same people better. Over and over again, you just can’t get away from the fact that effective leadership is built on humility. The authors are emphasizing what they call empowerment leadership. And this approach takes you outside yourself and creates a full-time job out of understanding and showing compassion and concern for those you lead. Only when you can imagine a better version of someone can you play a role in helping to unleash them. If you don’t have confidence in someone’s growth potential, then you can do many things with that person, but leading isn’t one of them. You can oversee, supervise, govern, persuade, and endure them. You can get through the day and instruct then to do things. This kind of approach is too often what we see being practiced and called “leadership.” Real leadership leads into the potential of others. To illustrate their point, they created the Rings of Empowerment Leadership. At the core is trust. “Trust creates the conditions for others to be guided by you.” They explain, once you build trust, you then “create a context where people around you can thrive.” And to create a context where teams thrive requires that you champion the differences of each member.
These first three competencies require that you be present for the action and limiting your influence. “The most successful leaders are influencing people far beyond their direct reach and are intensely aware that success depends on what happens in their absence. Which brings us to the outer rings of our model: strategy and culture.” From here, Frei and Morriss take us through each ring to develop the competencies and the mindset to become more empowering leaders. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:33 PM

10 Signs Your Leadership Might Be All About You
LEADERSHIP is never about me, but it is all too easy to make it about me. Frances Frei and Anne Morriss have written Unleashed to help us fix our perspective on unleashing the potential of those we lead. They have listed ten warning signs that you might be getting in your own way as a leader (or any other relationship for that matter):

Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:32 PM
06.12.20

You’re It: The Call for Meta-Leadership
A crisis demands a certain kind of leadership. But crisis leadership is not something you turn off and on. The ability to handle a crisis is something you develop long before a crisis hits, and people turn to you for guidance—before they declare, “You’re it!” You’re It: Crisis, Change, and How to Lead When It Matters Most by Leonard Marcus, Eric McNulty, Joseph M. Henderson, and Barry C. Dorn, details the mindset of successful crisis leadership. They call it Meta-Leadership. The following excerpt describes well exactly what the authors are advocating. Meta-leadership is a strategy and practice method designed to expand the impact of your leadership. It is both conceptually rigorous and intensely practical. It guides being, thinking, and doing. What they are describing requires quite a shift in thinking and behavior from much of the leadership we see today. It speaks to the question, why do you lead? It requires an outward mindset rather than the underlying motivation of leaders wishing to win points for themselves. Crisis leadership is complex. Some responses may be linear in nature—a checklist of actions—but the meta-view is most often complex. An adaptive approach that acknowledges the evolving nature of situations and the ambiguity of the unknowns is fundamental to meta-view, inclusive leadership. To illustrate this point, they present the Cone-in-the-Cube illustration.
Two groups of people are assigned the task of describing a shape inside an opaque cube. One group looks through peephole A on the side of the box. They see a triangle. The other looks through peephole B on the top of the box. They see a circle. The two groups fall into conflict about what is in the cube, and each substantiates the validity of its claims based on professed superior experience, values, intelligence, or power. It is the job of the meta-leader to integrate both viewpoints and to help others see the big picture as well. A crisis compounds the problem because when people are fearful or in a state of panic, they become very rigid in their thinking. Meta-leaders need to respond to the emotion of the problem as well as the technical issues. In a crisis, we are programmed to take a narrow view and become tightly focused. When a crisis hits, the first thing that happens is your higher-level thinking shuts down, and you descend into the basement. When this happens, “extraordinarily smart people can go to the basement, get stuck in the basement, and say or do the dumbest things, often to their later regret.” The trick is to learn what you can do to bring you up out of the basement and out of survival mode. It can be pausing, taking a deep breath, or something you do that prompts self-confidence. To overcome that overwhelming feeling, it is good to pull back and provide some structure to the crisis and to guide your thinking and your response. The authors have developed a tool called the POP-DOC Loop.
Start at the top on the left side of the figure-8 and move counterclockwise: Perceive what is happening. Orient yourself to detect patterns and understand what they mean. Distinguish between what you think and what you know. Test for bias-driven blind spots. And then, based on the patterns and the probability of their recurrence, predict what is likely to happen next. These are the learning steps. They integrate the dimensions of the person and the situation. The meta-leader’s role is to keep their eye on the big-picture, delegate, and allow others to do their job—to connect and coordinate all of those involved in the response. They practice the principle of “stay in your lane and help others succeed in theirs.” Through your meta-leadership, you are seeking a wider perception and a deeper understanding of people, their experiences, and what affects them. That understanding—through connectivity—allows you to find patterns of behavior, reaction, and response. The intersection between what occurs in your surroundings and its impact on people becomes clearer. You take and guide actions in this broad human panorama. You’re It is a playbook for crisis leadership to be sure, with many examples from various crisis situations. But more than that, it will develop you into a leader that can act when a crisis strikes. The principles found here are not only valuable in an organizational setting, but the mindset will help you personally to think through a crisis with clarity informed by a mind open to various perspectives on the situation. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:03 AM
04.24.20

Entrepreneurial Leadership
YOU don’t have to be an entrepreneur to be an entrepreneurial leader. Entrepreneurial leadership is a mindset. It is a mindset that is even more critical in today’s unstable world and is the sine qua non of crisis leadership. Joel Peterson has been around the block serving as a leader in various roles—CEO, CFO, founder, investor, entrepreneur—and is currently the chairman of JetBlue Airways and a professor at Stanford’s Graduate School of Business. Throughout it all, he says, he’s been lost more than once. “I’ve relied on more than one rescuer. And I’ve occasionally had to turn back, to recalibrate, to reboot. But over time, I’ve learned what to do—and how to think—when things don’t go as planned. I’ve figured out how to survive betrayal, miscalculation, and just plain bad luck. I’ve learned both how to live with disappointment and how to keep the occasional success from changing my values.” Through all of this, he’s “developed a framework—a set of principles, mindsets, and self-talk—that may help others on their quests.” He shares these in Entrepreneurial Leadership: The Art of Launching New Ventures, Inspiring Others, and Running Stuff. Five Types of Leadership To begin, he differentiates between five types of leadership: The Presider preside over the status quo and is a wise steward over the assets of the firm. The Manager excels at managing teams and delivering results without a limited focus on organizational strategy or trajectory. The Administrator manages process with predictability and efficiency. The Pure Entrepreneur starts things, innovates, and pilots with a mind to the future but often finds it difficult to scale or turn around a faltering organization. The Politician compromises, rationalizes, debates, and legislates and is skilled with the use of power. Peterson encourages the development of Entrepreneurial Leadership because these leaders are able to shift from one of the above styles to another as needed. In addition, they “demonstrate a particular mindset and approach to problem-solving. They are change agents. They are intentional, staying true to their vision and agenda rather than only reacting to day-to-day turbulence.” They are stewards and see their work as transformative. “Their work is messy, largely intangible, and never-ending. Each day brings new problems and new decisions that present ambiguity and shades of gray.” This type of forward-thinking, nimble leadership is needed now more than ever. Develop Your Leadership Around Four Activities He organizes his thoughts, approaches, and mindsets around four categories—four essential basecamps on the way to the peak of entrepreneurial leadership: 1. Build Trust
Entrepreneurial leaders build trust by knowing your core values—those things you spend your time, money, and mind share. And ask are any of these values getting in the way of your effectiveness. What guides your everyday actions? What is your personal operating system? “Next to knowing one’s core values, the most important attribute an entrepreneurial leader can possess is a predictable, reliable, and intentional personal operating system. If that operating system isn’t yet as reliable as the leader wants, refining it to that point should be a priority.” To create a mission, you have to describe three things that are unique about you: what you do, How you do it, and who you are. Set Memorable, Aligned, and Doable goals. In his entrepreneurial leadership classes, Peterson always asks his students: “What are you solving for? What is your objective?” Those who have clarity around winning tend to listen. They tend to compromise, to allow other parties to win, to sort out conflicts, and to arrive at solutions that allow everyone to move on. This means that entrepreneurial leaders are rarely perfectionists. Instead, they are practical problem solvers who keep their eyes on primary objectives. He most successful among them pursue strategies that are relentlessly aimed at achieving measurable results consistent with core values. Entrepreneurial leaders secure a team by hiring great people for values consistency and demonstrating effective attitudes—likability, gratitude, joyfulness, humility, humor—in their interactions. Delivering results is a matter of executing well on a number of challenges. Peterson covers ten of the most predictable: making decisions, selling, negotiating, raising capital, communicating, meetings, board relationships, overcoming adversity, surviving growth, and driving change.
A good entrepreneur will avoid the founder’s trap. In all likelihood, the company will grow beyond the capabilities of the founder and a founder should be prepared to turn it over to someone else at some point in time. Staying around past that point can ruin the company. Being an entrepreneurial leader can be exciting work, but becoming one “demands personal growth—no matter where you start—and along the way, you’ll likely discover more about the person you’d like to be and the meaningful work you want to do.” The world needs more entrepreneurial leaders to bring sustainable results. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:24 AM
04.14.20

The 3 Types of Humility That Impact Your Leadership
IN 2016, Harvard Business School Dean Nitin Nohria addressed the graduating class and spoke of three H’s: Hope, Humility, and Honor. These three qualities are reflected in leaders who make a difference. In speaking about hope, he turned to the example of explorer Ernest Shackleton, who, in a seemingly hopeless situation, “continued not only to remain optimistic himself, but he continually instilled hope in his crewmates. He refused to let them give in to the despair that logic would lead them to feel. He did not allow them to give up, either emotionally or physically.” He said we should think of honor as a verb. It’s an action. It’s about “making and keeping commitments.” What stood out for me was the way he broke down humility into three types: Intellectual, Moral, and Personal. It gives one a multi-faceted picture of humility and how we might cultivate this quality more fully in our lives.
How might we see our own lives differently from these three perspectives on humility?
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:11 PM
02.24.20

The Leader's Greatest Return
IF YOU want to make a difference in the world, go further, faster by developing other leaders. Your efforts are magnified exponentially by the investment you make in others. Of course, we talk about developing more leaders, but if we actually made it a priority, we would have more leaders. One issue leaders have always faced is the ability to identify potential leadership in the raw. It can be a bit counterintuitive. John Maxwell addresses these issues and more in The Leader’s Greatest Return. To help make this more practical and intentional, Maxwell has laid out a ten-step process for developing leaders. 1. Identifying Leaders: Find them so you can develop them. You need to know what you are looking for. What does a potential leader look like? Maxwell offers six As to guide us: Assessment of Needs (what do you need?), Assets on Hand (people within), Assets not on hand (people outside), Attitude, Ability, and Accomplishments. You’re looking for attitude before aptitude. Always begin with attitude. Good character is what holds together all the positive attitude traits I’ve mentioned—willingness to serve, selflessness, empathy, growth, and sacrifice. Character keeps everything secure. Without it, things can break down fast. Character is about managing your life well, so you can lead others well. 2. Attracting Leaders: Invite them to the leadership table. Leaders want to be around leaders. “Having a leadership table means creating a place in your organization or on your team where people have a place to learn, an opportunity to practice leadership with its successes and failures, and a chance to shine.” Leaders “see the future leader within the person, and help that leader emerge.” Inviting potential leaders to the table gives them a chance to practice leadership. As a learner there’s no substitute for participating and having access to people who know what they’re doing, can direct you, and give you feedback. That requires proximity. 3. Understanding Leaders: Connect with them before you lead them. Understand them. Learn their perspective. Before you lead and develop people, you need to connect with them. You need to find common ground with potential leaders, which is less about ability and more a function of attitude. They commit to you and follow when they feel understood. Maxwell lists ten actions to create that understanding: “Value them, let them know you need them, include them in your journey, adopt a teachable spirit, ask questions, listen well and often, seek to know their perspective, give credit to those who help you, express gratitude to those who help you, and replace me with we.” What Maxwell is talking about is humility. 4. Motivating Leaders: Encourage them to give their best. Don’t motivate. Inspire. I try to inspire people and help them find their own motivations. That means I must first find my own motivations and model the behavior I want to see in the people I lead. Good leaders inspire others only to the extent that they inspire themselves. 5. Equipping Leaders: Train them to be great at their job. Great leaders sponsor their potential leaders. “They position them and mentor them.” Sponsoring potential leaders is where you begin to see the return on your time and investment. Work yourself out of a job. Success doesn’t come from protecting what you have. It comes from equipping others to replace you so that you can move onto bigger and better things. When you become an equipping leader and teach potential leaders how to be great at their job, everybody rises. 6. Empowering Leaders: Release them to reach their potential. Give authority away. “Only secure leaders give power to others.” The main limitation most people have on their lives is their low expectations of themselves. Most people are unaware of the possibilities that lie within them. Good leaders introduce the people they lead to those wonderful possibilities. 7. Positioning Leaders: Team them up to multiply their impact. Bring your leaders together to develop a team of leaders. Maxwell explains the seven types of leaders to you want to invite to your leadership team. Teams of leaders are powerful. But they are difficult to create. Why? Leaders are hard to gather. And it can be a challenge to get them to work together. They all have their own ideas, and they would usually rather gather a team than be on one. 8. Mentoring Leaders: Coach them to the next level. Leaders have a responsibility to mentor others. For mentoring to work, it becomes a two-way street. As mentors, we should both teach and learn. The leader being mentored should move up to a higher level of leadership. The ultimate step in mentoring ends with the leader being mentored takin the baton from his mentor and surpassing him. 9. Reproducing Leaders: Show them how to develop leaders. “The only thing limiting the future of any organization is the number of good leaders it develops.” Maxwell says the kind of leaders you are trying to develop are what he calls 3-G leaders. “When I select leaders, I look for evidence of the three Gs. They have to be grounded, gifted, and growing. And as I develop them, I need to see them continue to develop in those areas to keep working with them.” Grounded as in possessing a foundation that makes them solid—humble, teachable, authentic, mature, and having integrity. Gifted in that they possess the strengths that can help them succeed in the service of others. And possessing a hunger and capacity to be developed—Growing. When you begin developing leaders, the most important thing you can do is let them know what you’re thinking and why. Bring them to the table and let them in on high-level meetings and discussions so that they can learn how you and other top leaders think. 10. Compounding Leaders: Receive the Highest return of developing leaders. Developing leaders benefits from what is called “accumulative advantage.” That is, a small initial advantage leads to a slightly bigger advantage that compounds over time to create a significant advantage. “That’s the return that comes from continually developing leaders. It compounds! And the longer you keep doing it, the greater your advantage becomes.” And you reap the compounding power of consistency. You can’t develop everyone. “Compounding results from developing the top 20 percent. If I have ten people on my team, I incest 80 percent of my time and effort into my top two—my top 20 percent. I add value to them, so they can multiply value to others.” Those two can then develop the top 20 percent of those they influence and so on. Developing leaders pays dividends to you, those you develop, and to everyone they influence. Developed leaders help you carry the load, leverage your resources, help you create momentum, expand your influence, ensure a future, develop others, and develop you. It’s dangerous to think you’ve arrived as a leader. As someone once quipped, today’s peacocks are tomorrow’s feather dusters. If you want to keep leading, you need to keep growing, and few things stretch a leader like leading growing leaders. The Leader’s Greatest Return is one of the most important books Maxwell has written. It brings together, in a meaningful whole, the culmination of over 50 years of experience leading and learning to lead. It provides a holistic view of leadership and applies the laws he has written about previously in The 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership and other classic leadership books to the most meaningful function of leadership—developing more leaders. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:30 PM
02.12.20

Why You Should Sponsor Others
MUCH HAS been written about mentoring. Mentoring is a gift you give to others. And while mentoring can be of tremendous value to the person being guided, it is one-way. Sponsoring is “all-in.” You have skin in the game. Sponsorship is a two-way, reciprocal investment where both the sponsor and the protégé are working for each other’s success. It goes without saying that having a sponsor is a huge career plus, but here’s the startling fact, being a sponsor is just as important as finding one. Sylvia Ann Hewlett reports in her book, The Sponsor Effect, “Senior-level managers are 53 percent more likely to have received a promotion in the last two years, if they have a protégé.” In addition, “Entry-level professionals who have a protégé are 167 percent more likely to have received a stretch assignment than those who don’t.” And for those who were actually doing sponsorship right, the results were even better. The point is, become a sponsor. It’s good for you too! The sponsor must devote serious attention to identifying top junior talent, developing their skills, scrutinizing their progress, and advocating on their behalf (or more practically stated, believing in them and using up precious political capital for them, advocating for them, and providing them with air cover to take the risks that success often demands). Protégés must deliver for their sponsor with stellar performance, rock-solid trustworthiness, and a differentiated skillset that adds value to the team and the organization, as well as to the individual sponsor. Take note: “The right protégé will complement your leadership skills and style, provide honest feedback, make you feel that you have extra hours in the day, and enable your influence to persist even after you’ve moved on to your next role or opportunity.” Seven Steps to Effective Sponsorship Hewlett offers a playbook to do this right. Taking a chapter for each, she explains how to get started, and answers questions like how do you contain risk? And What tools and tactics work best. After all, “If you’re going to sponsor someone—linking their career to yours—they’re going to be walking around with your brand on their forehead.” Step 1: Identify Potential Protégés Step 2: Include Diverse Perspectives Step 3: Inspire for Performance and Loyalty Step 4: Instruct to Fill skills Gaps Step 5: Inspect your Prospects Step 6: Instigate a Deal Step 7: Invest in Three Ways The following example Hewlett shares highlights the value of sponsorship to help leadership groups break out of their shared biases and points of view that so often hold them back. “In this business today, if you want to grow, you’ve got to be comfortable with being uncomfortable,” Lou Aversano, CEO of Ogilvy & Mather in New York (a division of WPP), told me. “You have to be willing to burn your lifeboats before someone burns them for you.” Yet industry veterans such as himself face a challenge that he calls “altitude.” Sponsorship requires an investment of time, but it has immediate value. You can begin to see the benefits very quickly. So, find some protégés today. The Sponsor Effect offers a formula to get it right. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:23 AM
02.10.20

Peak Leadership Fitness: Elevating Your Leadership Game
ELEVATING your leadership game is a mindset. Your mindset drives your behavior and your influence on those you lead. You are in control of your mindset. In Peak Leadership Fitness, author Timothy Tobin writes, “A leadership mindset is essentially the belief in yourself and your abilities as a leader. A negative leadership mindset is rooted in self-doubt, uncertainty, and lack of inquiry. A positive one, on the other hand, based on a realistic view of yourself, your potential, and how you view [the] potential of others.” This mindset can be developed with effort and curiosity. Tobin has found that these four principles will help you on that journey: Principle 1: You never know what you’re capable of until you take that first step. “Leadership is an extreme test of performance, stamina, and endurance. It requires sacrifice and training. It requires setting ambitious (stretch) goals for yourself. Progress—even when falling short of your goal—is a great way to calibrate your capabilities for your next effort.” Principle 2: You must put in the effort. Nothing happens by chance. “When you put in the effort, your current strengths and expertise become a platform or you to build upon. As you build, you raise the bar for your capabilities, establishing a new standard for your performance.” Principle 3: You learn more about yourself when times are tough. (In other words: Never give up.) “Adversity tends to be unpredictable, so you may not know when it will strike or what form it will take. The difference in whether you react or respond comes down to your preparation.” Principle 4: What you consume matters. “Leaders won’t perform at their best if they do not focus on their development to development activities that advance their skills.” Where to Begin? Any leadership development journey begins with a baseline established through self-awareness. Tobin believes that a 360-degree assessment—a process through which feedback is solicited from peers, subordinates, superiors, and yourself—is the best place to begin. If enough people are included in the assessment, it can give you a good idea of those areas you need to begin focusing on and track your progress. Self-awareness is crucial to leadership success. Begin by developing your leadership core, which encompasses four general areas: Technical Skills: Knowledge about your domain, your business (including financial), and your industry.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:03 AM
02.05.20

Five Foundational Truths of Youth Marketing (and Leadership)
WHO IS Gen Z? They are people born between 1996 and 2011. What is their frequency? Their generational voice is diverse, engaged, knowledgeable, pragmatic, collaborative. And while they share common values, they are very independent. In The Gen Z Frequency, authors Gregg Witt and Derek Baird tackle this demographic which is projected to be the largest consumer demographic in history. The HRC Retail Advisory forecasts this generation to drive 40% of all US consumer spending, and yet it is one of the most challenging generational cohorts for brands to reach. It is an important and comprehensive book for marketers, but there are some principles they share that have a much wider application, that I wanted to share. In the book, they list the five foundational truths of youth marketing (and leadership). Each truth is introduced by a well-chosen quote that is worth applying more broadly in a leadership context. They are: Truth 1: Identity Gone are the days when brand identity is built with a bullhorn. We all know that brand identity is now the sum of every consumer experience, but that doesn’t mean covering the spread of fragmented media with one brush stroke. In our opinion, context is just as important as content. It’s about brands boldly proclaiming a belief in why they exist in the first place, then proving it in ways that shape-shift within the medium and the context of media. In other words, prove that you are who you say you are in as many ways as you can. –Adam Wilson, 2018, Former director of brand marketing for Carhartt, North America Truth 2: Trust Trust? It’s everything. When it’s there, when it’s really there, that’s how a brand gets brought to life, protected and defended, grown and shared in the most authentic and powerful way possible. Trust takes belief, belief takes faith, and faith takes nurture and care. It takes more than a product, a promise, or a campaign. We work to earn trust in everything we say, everything we make and everything we do. Period. This is an important lesson I learned early on and continue to bring with me wherever I go. –Nicholas Tran, 2017, marketing executive and thought leader at global consumer electronics brand Truth 3: Relevance Staying relevant with Gen Z requires brands to stay on the pulse of everything happening in culture. And not just a gut check a few times a year…it requires a daily pulse of what this audience is talking about, feeling, and connecting with emotionally. From politics to pop culture, Gen Z admires brands who are willing to engage in timely conversations. –Michael Abata, 2018, cultural and consumer futurist Truth 4: Possibility Find a creator – a real creator, not a fake one – one that speaks to and inspires the audience you’re after. Partner with them for six months, a year or longer with a goal of becoming a true member of that creator’s community. Don’t tell them what to say – instead enable them – and through them, their community – to go places, do things, discover possibilities. Become part of that creator’s community, but let the creator chart the course, set the sails and choose the destination. You’re not buying media; you’re not running a campaign. You’re joining a community. Be respectful, but generous, but mostly keep your mouth shut. With the right match between creator, community and brands, the results will be amazing. –Jim Louderback, 2018, CEO Vidcon Truth 5: Experience A fundamental part… perhaps the fundamental part of humanity is to derive meaning from our existence, in the broader context of the universe. Gen Z is coming of age in a time period where we are constantly given digital reminders that we are not alone. An individual experience, recorded on a Snapchat or Instagram story, is almost immediately integrated into a broader ‘story’ pooled together by hashtag or geographic location. Technology has given us the tools to show us, in real-time, that we are one piece of a much larger puzzle. Brands need to become part of this larger puzzle and contribute to the overall experiences of this generation. –Sara Unger, 2018, Senior Vice President, Cultural Insights and Strategy, Civic Entertainment Group 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:52 AM
01.29.20

Responsive Leadership: Needed Now More Than Ever
THE leadership question is top of mind for many people here in the United States and throughout the world. The idea that leaders are trustworthy, honest, and can be relied on to operate in the best interest of the public, the employee, the student, the parishioner, or even the shareholder has been shattered. No matter what industry or organizational structure—business, politics, nonprofit, religious, entertainment or sports—examples abound where leaders have violated their trusted role and experienced a public downfall. As a result, confidence in our leaders and the institutions they lead has diminished, sometimes to the point of no return. In these fast-paced, ever-changing, turbulent, and most stressful times, a major challenge that all leaders face is how to reduce skepticism and build greater trust and confidence in their role, their decisions, and in the organization they lead. In a recent LeadershipNow blog, Mark Sanborn wrote about six warning signs of why leaders fail: a shift in focus; poor communication; risk aversion; ethics slip; poor self-management; and lost love. Responsive Leadership can be an antidote to failing leadership and the foundation for building and sustaining organizational trust and confidence. What is responsive leadership? Responsive leadership focuses on the people—the humanity—within the organization to achieve organizational success. Often leaders are described by action words such as “results-oriented, innovative, driven and visionary”. Sometimes leaders are described by what they believe leaders do and how they approach their role, such as the systematic leader (leaders who use and rely on a set of methods and management tools) or the servant leader (a leadership philosophy in which the main role of the leader is as servant). Responsive leaders may employ these and other techniques, skills and actions all in service to a deep understanding and appreciation that the people within the organization underpin the organization in both triumph and crisis. Over my many decades in leadership roles, reflecting on my own development as a leader, talking with colleagues, and reading and studying leadership, I have come to believe that there are four essential attributes that drive the responsive leader. My selection of these leadership attributes was affirmed during a conference of corporate directors when over dinner, a few of us had a discussion about the attributes of strong and effective leaders. I call these attributes “The Big Four.” The Big 4 Leadership Attributes Curiosity: The Desire to Continuously Learn Curiosity will play a critical role in steering an organizational transformation, creating a new product, innovation or better understanding the competition. With a curious mind, the leader will seek knowledge and understanding from a variety of sources including outside experts, subordinates, peers, experts, and trusted advisors. By leading with curiosity, the leader will instill in the organization culture of continuous learning, a respect for and value for deeper understanding. A culture of continuous learning will bolster organizational creativity and innovation. Empathy: The Ability to Feel and Appreciate Other Human Beings The ability to understand feelings of others will keep us in touch with our own feelings as the organization tackles problems and finds solutions. Empathy is considered foundational to workplace cooperation and productive collaboration. In many work environments people must work with other people in order to be successful. Empathy will keep leaders tuned into the impact that the dramatic changes are having on the people around and in the organization. Regardless of leadership style, many executives would agree that empathy is a basic and very important quality of a successful leader. The ability to demonstrate empathy during crisis and challenging times will also help build trust and confidence in the leader and the decisions they are making. Humility: A Sincere Regard for the Reality that We Cannot Go It Alone Never underestimate the power of humility. Humility reinforces our curiosity in others and the world around us. Humility opens the door for a leader to have the courage to surround herself with the very best, people who are highly competent, and perhaps even smarter than herself. With humility, we know that we can learn from others, fully aware that “I” do not have all the answers. Employees will often respond most effectively to a “humble” leader. Another key ingredient to building trust and confidence in the leader and the organization. Resilience: The Capacity to Recover, to Keep Going Forward in the Face of Adversity All leaders face adversity at some point in their careers. Some of the hardest challenges to resilient leadership is rebounding from a setback. An important and necessary key for the resilient leader is “not to take it personally”, sometimes very hard to do. Recovering quickly from what you perceive as a failure and perhaps what everyone around you perceives as a failure can accelerate your own personal recovery process and as important, it can provide the ability for accelerated organizational growth and continued development. I believe each of the Big Four attributes—curiosity, empathy, humility, and resilience—are integral to responsive leadership and responsive leaders are needed today more than ever. Do you incorporate the Big Four in your leadership? And is it effective?  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:37 AM
01.15.20

The Impact of Great and Terrible Leaders
MOST PEOPLE have been around a bad leader at some point. Someone who doesn’t communicate, sets impossible expectations, or is just difficult to be around. You’ve likely experienced the draining, exhausting feelings from having to work with or for that person. Hopefully, most people have also experienced a great leader. These are the people who inspire and motivate and encourage people to do their best work towards a common goal. If you’ve experienced a bad leader and a great leader, you know the difference between the two can be night and day. But how do we turn those feelings into real action to develop great, future-ready leaders? What Makes a Great Leader? As part of my new book, The Future Leader, I interviewed more than 140 CEOs around the world and asked them each to define leadership. Their definitions were all over the board and included things like leaders being able to drive business success and reach goals to human skills like connecting with people and being humble. One of the main themes was that people believe a successful leader is someone who makes money and grows a business. The financial results definitely contribute to being a successful leader, but there is so much more that goes into becoming a truly great leader. Consider these two definitions from CEOs I interviewed. Judy Marks is the CEO of Otis Elevator and leads a team of over 70,000 employees around the world. According to Judy, “I think it’s really the ability to drive results, and I’ll leave that word results fairly generic. My role in terms of leadership is to set the vision and to share it. To create an environment where people can resonate not only with the mission but deliver it. To eliminate obstacles so my team can succeed.” Hans Vestberg is the CEO of Verizon Communications, an American multinational telecommunications conglomerate with over 152,000 employees around the world. Hans believes leadership is: “Ensuring that people have everything they need to achieve the missions of an organization. That’s it. All else is footnotes.” Which one most resonates with you and why? First and foremost, great leaders care about their people. They are willing to go the extra mile to serve and get the job done. A great leader knows that a company isn’t really successful if its numbers improve but its people aren’t happy. Leaders help shape the world and have a profound impact on their employees’ lives. If you’ve had the chance to work for a great leader, you know those lasting feelings: a great leader inspires you to be better, mentors you along the way, and gives you the tools to succeed. Great leaders help the people around them improve, even to the point that their employees are better equipped than the leader themselves. When individuals are motivated and engaged, they naturally want to work harder and better, which brings financial success. Impact of Great Leaders Great leaders create engaged employees who want to come to work and give their best effort. A study by Zenger Folkman found that good leaders can double company profits, simply with their ability to motivate and engage employees. Organizations with the highest-quality leaders are 13 times more likely to outperform their competitors. Another study found that how managers lead accounts for a 28% variance in employee job satisfaction. Any company would love to have an increase in employee satisfaction, and it’s as simple as putting great leaders into management positions. Great leaders also breed other great leaders. If you work for someone you admire and who displays great leadership skills, you’re more likely to also develop those skills and abilities. A great leader is like a pebble dropped in a pond who creates ripples of other good leaders all around them for years to come. What Makes a Bad Leader? On the flip side, a bad leader doesn’t care about people or creating an environment where employees want to improve and do their best work. Bad leaders often make their employees feel like cogs in the machine who are just there to clock in, do their job, and then clock out. Bad leaders often only care about the numbers or advancing their own career instead of creating a team mentality and moving the company towards success. Impact of Bad Leaders Employees who work for bad leaders often feel like their jobs are unenjoyable and meaningless. Studies have shown that working for a toxic leader leads to lower job satisfaction, which shouldn’t come as a surprise. But that lack of satisfaction carries over into other areas of employees’ lives. A study from the University of Manchester found that employees working for bad leaders or managers were more likely to experience clinical depression and over time became overly critical of their co-workers, took credit for each other’s work, and showed aggressive behavior to other people in the company. Clearly, the attitude of a bad leader isn’t contained in a single person. A leader sets the tone for the organization, which means their bad example and energy can spread through the entire organization and poison even good employees. Bad leaders cause employees to become disengaged in their work and are one of the biggest reasons for employees leaving their jobs. In many cases, employees don’t quit companies—they quit managers and bosses who are difficult to work for. A Gallup survey of more than 1 million employees found a staggering 75% of people who had quit their jobs had done so because of their boss and not the actual position. Developing Great Leaders There’s a stark contrast between good leaders and bad leaders. It’s often easy to point out bad leaders in past organizations or looking in from the outside, but it’s more difficult to make a change when you’re in the midst of working for a bad leader. Companies shouldn’t be afraid to overhaul their internal teams and processes to get rid of bad leaders. It’s impossible to only hire superstar leaders; organizations also need to learn how to develop people internally to create great leaders. Good leaders have a strong impact on the culture and overall success of the company. Investing in future leaders can have a large return as they motivate employees and help grow the company. Leaders have the potential to make a huge impact in their organizations. Great leaders can inspire employees, attract talent, and increase revenue, while bad leaders can create a toxic environment and drive away employees and customers. Organizations need to prepare for the future by identifying and removing bad leaders and then replacing them with strong leaders and an internal leadership development program. What kind of a leader are you and what kinds of leaders does your organization want to create?  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:54 AM
12.16.19

The #1 Tactic That Will Help You Be More Productive as A Leader
FOR THE PAST DECADE or so I have spent a lot of time in organizations getting to know their leaders and how they work. That inside look has given me a firsthand account of what they are dealing with on a daily basis. Suffice it so say, this is not your father’s organization. For example, the amount of incoming communication is staggering. The average knowledge worker in the U.S. is interrupted every 11 minutes by some form of communication. Every 11 minutes! That kind of distraction takes an unseen toll on us as leaders. Add to that the mountains of data we are generating and the inability to keep up with it, let alone make real sense of it. Today’s leaders are being asked to both do more AND think more. Is that even possible? I’m a fan of multi-tasking but this seems unreasonable. Expecting leaders to succeed in the context of a constant, act-more, think-more, produce-more world is self-defeating, at best. At worst, it could be disastrous for our projects, for our teams, and for our health. So, how do we keep pace and, at the same time, get better as leaders. Evolved leaders have figured out that they need to hit the pause button. Instead of making action the default for every challenge, these leaders are pairing that alternative with an opposite response. It’s not about replacing action, which we know is a necessary leadership ingredient. We still need to reach our goals, meet deadlines, and produce results. This is different. They think of it as developing a companion habit that celebrates THINKING rather than DOING. It involves a strategic pause. A “mental time-in”. Space for their brains to percolate and process the mounds of the information they’ve been packing in. If you want more time for big-picture-thinking and the “mental space” to envision vastly different solutions, follow these steps: 1. Make an Unbreakable Appointment with Yourself Set time aside every day (or at least every week) to step away from the chaos and let yourself reflect and plan. To connect the dots between information in different ways and to look at challenges from a fresh angle. It can help you gain remarkable clarity and give you the mental space to finally execute on ideas you’ve been sidelining. Yes, I know that will feel awkward at first. Your calendar is probably jam-packed with meetings and commitments, so it might seem unnecessarily selfish to mark off some “me time.” Don’t let that stop you. Consider this an unbreakable appointment with yourself. 2. Make everything you do earn its rightful place on your calendar Why? Leaders often feel trapped by an endless treadmill of meetings and tedious paperwork and that level of chaos has likely become their new normal. Even strangely comfortable. In fact, NOT doing all of those things would somehow feel wrong. If you want to free up time to let all that you have consumed percolate, you need to take a fresh look at everything you do. Ask yourself: • Does this meeting or task move me or my team forward?
Taking a fresh look at everything inevitably uncovers opportunities to free up time for big-picture thinking. 3. Make a “Stop Doing” List Ironically, some leaders approach downsizing their to-do lists by…creating another list: a “Stop Doing List.” This is actually an excellent mental exercise and an important step in making room for a “mental time-in”. Your “Stop Doing List” might include things such as: I will stop saying “yes” to every request without first considering its worth. Through the process of letting go, you can find time you never knew you had. 4. Encourage your team to pause. As a leader, you have the power and influence to help your team members develop new habits that can make them more productive. Make sure they also have time in their schedules to stop and think. That’s tricky when deadlines are tight, but the long-term benefits will be worth it. Give them the calendar space that encourages them to give it a try. As hard as it is for us doers to believe, all the evidence says that maximum effectiveness and innovation start with…STOPPING. Yes, it’s tough to do. I admit it. We’ve been taught to move forward, to finish, to be relentless. We have even been handsomely rewarded for it. But if you want your organization and your team to grow, take a strategic pause. Give yourself time and space. You, your team, and all your stakeholders will be glad you did.  Her insights come from her real-world experience and a surprising phenomenon she noticed in her own rise up the corporate ladder: The most successful people aren’t necessarily the ones with the highest IQs or best job skills. Career advancement is actually more closely linked with how people apply their knowledge and talents—their capacity to collaborate, communicate, and influence others. Sara is the author of Leadership Unchained: Defy Conventional Wisdom for Breakthrough Performance and You—According to Them. She is a sought-after leadership speaker and educator, a leadership instructor for LinkedIn Learning and is an adjunct Executive Coach with the Center for Creative Leadership.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:03 AM
12.09.19

Asking Smart Questions Changes Everything
WE LIVE IN A TIME when accountability is often sidelined. When it is, there can be disastrous consequences in government, in politics, in the media, and in business. The antidote, I’ve found during my two decades as an accountability speaker and business consultant, is a thoughtful and persistent effort to infuse accountability into every objective, every task, and in every colleague-to-colleague and company-to-customer interaction. For the world-class companies that do this well, accountability isn’t an esoteric mandate handed down from senior leadership. Instead, it is a systemic root-to-tip effort that makes accountability an organic state of being that is cultivated on a daily basis by everyone within the organization. And believe it or not, it doesn’t take a Herculean effort. Accountability is easily nurtured by curiosity. Simple Questions are the Seeds of Accountability As a writer and accountability speaker, I stress the importance of my Seven Pillars of Accountability™: character, unity, learning, tracking, urgency, reputation, evolving. Every member of an organization can build and strengthen accountability by asking fundamental questions related to these pillars. Ask your peers and colleagues. Ask your immediate supervisor and members of the senior leadership team. Their answers, along with your own, will create a blueprint for better performance. Here are some starter questions to help you begin cultivating the mindset that builds accountability. You don’t have to be a management expert, accountability speaker or business guru to be a catalyst for excellence. The important thing is to begin the discovery process that fosters it. Character
Unity
Learning
Tracking
Urgency
Evolving
Asking Isn’t Easy
While good leaders may solve problems, great leaders ask questions. In fact, great leaders create an environment where questions, especially tough questions, are welcomed, asked, and answered before decisions are made and after results are assessed. Are you ready to start asking smart questions in your organization? That’s A Great Question With years of first-hand experience, and in working closely with a variety of organizations, both leading and emerging, I’ve collected a list of over 500 provocative questions that explore 18 compelling topics centered around leadership and business. These questions, and other insights, are compiled in my book, That’s A Great Question: Are You Asking The Right Questions In Business? In Life? If you’re ready to take that next step towards becoming a great leader, this book will guide you in asking smart questions. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:20 AM
12.06.19

3 Things You Need to Control to Succeed as a Leader
SUCCESSFUL LEADERS know that we can control only 3 things in our life: our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. If we can take charge over those, we can lead our organizations, and our lives, to our own vision of success. That vision may differ for successful leaders: some want to grow their business into a huge company, while some want to stay small and keep a family atmosphere in their company. Regardless of how you view success, to achieve it you need to invest into understanding how your mind works. Then, you need to direct your thinking and feeling patterns, and the behaviors that result, to evaluating reality clearly, making the wisest decisions, and accomplishing your goals. So how do our minds work? Intuitively, our mind feels like a cohesive whole. We perceive ourselves as intentional and rational thinkers. Yet cognitive science research shows that in reality, the intentional part of our mind is like a little rider on top of a huge elephant of emotions and intuitions. Roughly speaking, we have two thinking systems. Daniel Kahneman, who won the Nobel Prize for his research on behavioral economics, calls them System 1 and 2. I think autopilot system and intentional system describe these systems more clearly. The autopilot system corresponds to our emotions and intuitions. Its cognitive processes take place mainly in the amygdala and other parts of the brain that developed early in our evolution. This system guides our daily habits, helps us make snap decisions, and reacts instantly to dangerous life-and-death situations, like saber-toothed tigers, through the freeze, fight, or flight stress response. While helping our survival in the past, the fight-or-flight response is not a great fit for modern life. We have many small stresses in our work that are not life-threatening, but the autopilot system treats them as saber-toothed tigers. That produces an unnecessarily stressful everyday life experience that undermines our mental and physical well-being. Moreover, while the snap judgments resulting from intuitions and emotions usually feel true because they are fast and powerful, they often lead us wrong in systemic and predictable ways. For example, we make bad hires if we rely on our autopilot system. The autopilot system leads to us making too-optimistic plans and ignore weaknesses and threats in our businesses and our careers. It leads us into errors in negotiating with others, in mergers and acquisitions, and in assessing company performance. True leaders learn to avoid simply trusting their gut to address autopilot system errors. By contrast, the intentional system reflects our rational thinking, and centers around the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain that evolved more recently. According to recent research, it developed as humans started to live within larger social groups. This thinking system helps us handle more complex mental activities. These include managing individual and group relationships, logical reasoning, probabilistic thinking, and learning new information and patterns of thinking and behavior. Notice how these activities are exactly the kinds of things necessary for leaders to succeed. While the automatic system requires no conscious effort to function, the intentional system takes deliberate effort to turn on and is mentally tiring. Fortunately, with enough motivation and appropriate training, the intentional system can turn on in situations where the autopilot system is prone to make errors, especially costly ones. The autopilot system is like an elephant. It’s by far the more powerful and predominant of the two systems. Our emotions can often overwhelm our rational thinking. Moreover, our intuitions and habits determine the large majority of our life, which we spend in autopilot mode. And that’s not a bad thing at all – it would be mentally exhausting to think intentionally about our every action and decision. The intentional system is like the elephant rider. It can guide the elephant deliberately to go in a direction that matches our actual goals. It can help you address the systematic and predictable errors that we make due to how our brain is wired, what scholars term cognitive biases. Over 100 cognitive biases exist, and more are found all the time by scholars in behavioral economics and cognitive neuroscience. We make these mistakes not only in work, but also in other life areas, for example in our shopping choices, as revealed by a series of studies done by a shopping comparison website. Fortunately, recent research in these fields shows how you can use pragmatic strategies to notice and address these dangerous judgment errors. The elephant part of the brain – which is most prone to cognitive biases – is huge and unwieldy, slow to turn and change, and stampedes at threats. But we can train the elephant. Your rider can be an elephant whisperer. Over time, you can use the intentional system to change your automatic thinking, feeling, and behavior patterns, and reach true success!  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:02 AM
11.20.19

General Jim Mattis on Learning to Lead
IT’S NOT SURPRISING that we learn a lot about character from the military. Good character is mission-critical. Under extreme circumstances, if you don’t have good character, the result is extremely bad consequences. In war, character is not a platitude. Good character development is evident in Call Sign Chaos. Written by Jim Mattis and made better with the help of Bing West, the book details the lessons Mattis learned from more than 40 years in the Marine Corps. He organizes the book in terms of the changing nature of his leadership responsibilities as he moved up the ranks. First, he learned face-to-face or direct leadership. At a time when, “alongside those I led, I had a personal, often intense bond with troops I frequently knew better than my own brothers.” Next, he discusses executive leadership, where commanding a force of 7,000 to 42,000 troops, it was impossible to know them all individually, so communications and leadership styles must adapt. Finally, he covers the challenges and techniques relevant to strategic leadership from a senior military officer’s perspective. (His call sign, CHAOS, was given to him by his operations officer, John Toolan.” It stands for, “Does the Colonel Have Another Outstanding Solution?” “There’s always a Toolan, “he writes, “waiting out there to keep your ego in check, providing you keep the risk-takers and mavericks at your side.”) As is commonly done, a book is a good place to settle scores and vent your opinions. Although Mattis resigned halfway through his appointment as Secretary of Defense at the end of 2018, he writes, “I’m old-fashioned: I don’t write about sitting presidents.” “Old-fashioned” is often another way of saying character. Importantly, he talks about the challenge of communicating the commander’s intent. When commanding a large number of troops or a large organization, a leader must be able to communicate their intent in such a way as to allow people to act. It requires discipline and trust. Developing a culture of operating from commander’s intent demanded a higher level of unit discipline and self-discipline than issuing voluminous, detailed instructions. It highlights the need for clear and consistently enforced values to guide teams and organizations. Commander’s intent provides a framework that everyone can operate from. Mattis also mentions the need to get inside the enemy’s OODA loop—to adapt faster than they could. The OODA loop is a concept developed by Colonel John Boyd and stands for observe–orient–decide–act. In uncertain and changing environments, one can gain the advantage if they can ensure that their OODA loops are functioning, as Mattis puts it, “at the speed of relevance. It is possible then, to get inside the enemy’s OODA loop. This is made possible, in part, by having the commander’s intent clearly communicated and understood. The OODA loop helps us to shift our perspective from what we want things to be to what they are in reality. A common organizational problem. Our campaign’s success was based on not giving the enemy time to react. To win a dogfight, Boyd wrote, you have to observe what is going on, orient yourself, decide what to do, and act before your opponent has completed his version of that same process, repeating and repeating this loop faster than your foe. Call Sign Chaos has actionable ideas throughout for any team. What follows are quotes taken from the book that will give you a flavor for what is addressed here: The Marine philosophy is to recruit for attitude and train for skills. Marines believe that attitude is a weapon system. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:51 AM
11.04.19

Sailing True North and the Voyage of Character
THERE IS NO SUBSTITUTE for character. Better systems, better laws can’t make up for it. Without good character, leaders can go south fast. The problem is that there is very little attention paid to how to develop good character. We learn best by example, but it is wise to look into the lives of others and understand the outcomes of their lives as a result of their character or lack of it. Four-star U.S. Navy Admiral and former Supreme Allied Commander of NATO James Stavridis gives us a comprehensive look at ten admirals in Sailing True North. He looks at their differing character traits and personalities and the effect it had not only on their careers but on those they lead. He begins 25oo years ago with the Greek Themistocles and moves forward to the lives of 14th-century Chinese admiral Zheng He, Sir Francis Drake, Horatio Nelson, Alfred Thayer Mahan, John Fisher, Chester Nimitz, Hyman Rickover, Bud Zumwalt Jr., and finally, Grace Hopper. While each of their voyages on the open sea was demanding, it was “vastly easier than the inner voyage we all must sail every day of our lives. That voyage of character is the most important journey each of us ever makes.” Stavridis writes this out of a growing sense that “in this postmodern era that we are witnessing the slow death of character, driven by a global culture that has turned increasingly away from classic values—honesty, commitment, resilience, accountability, moderation—to a world that moves at breakneck speed and refuses to slow down and consider what is right and just.” Sadly, he notes too that “we have lost the ability to hone our character in private, and our lives are on display seemingly from the moment we are born. We overshare publicly and under-reflect privately on what our individual voyages mean.” It is good for us to slow down and look at these lives and use what we learn to adjust the course of our lives to be the best we can be. There is much we can learn from others. Biographies provide us with feedback on our own lives in a most palatable way if we take the time to apply what we learn. None of these admirals was perfect, but we can learn from them all. “The nature of any human is not what they do when the choices are easy, and the metaphorical sun is shining, but rather what they do when the options are morally ambiguous, and the seas are rough.” Some of the navigational advice we can learn from the lives of these admirals is: A leader should avoid getting into a position where the only way to persuade an audience is by an almost magical feat of rhetoric. Stavridis shares ten character traits that he has learned from the admirals he showcases and from his own experience as an admiral. At the top of his list is creativity—“a willingness to embrace the new, despite the difficulties and challenges of doing so.” You must find a way to bring along the nonbelievers. Second is resilience. Learn from your experiences and set new goals and keep moving. Third, he lists humility. Arrogance is toxic to a leader. “It is a lot easier to be resilient when you are humble to begin with.” The fourth quality is the need to find balance in our lives. Most of the admirals he lists in the book failed this test. After all, ambition often drives the lack of balance in our lives. Fifth is honesty—“being truthful no matter the cost.” Make truth a habit. Sixth is empathy. “Most of us are terribly self-centered.” See outside yourself. “A virtuous person begins every encounter with the world not from their own perspective alone, but rather by trying to understand the situation, mindset, and challenges that others are facing.” Seventh is believing a sense of justice matters. Self-control is at work here. Eighth is decisiveness. Ninth is determination. Never give up, as Churchill said, “except in convictions of honor and good sense.” The final character trait he lists is perspective. We can’t take ourselves too seriously. “We need to understand that in the end we are but sailing in a tiny ship on the boundless sea.” A good sense of humor goes a long way toward maintaining a proper perspective. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:01 AM
09.09.19

Learning to Lead with Ron Williams
WHO IS looking out for you? “No boss or mentor drove my success—although they did open doors for me. My success came about through a combination of hard work, continual learning, fortunate career choices, and a bit of luck—by being in the right place at the right time,” writes Ron Williams. Williams is best known for his tenure as CEO and Chairman of Aetna, where he transformed a $292 million operating loss into $2 billion in annual earnings. In Learning to Lead, Williams shows how anyone can grow and succeed as leaders. He grew up in a working-class family in one of the poorest neighborhoods of Chicago in the 1960s. The book is exceptional. He weaves the experiences of his career with the lessons we can all learn from them. Well told and insightful. He begins by asserting that the single most important asset you have is you. As a result, you need to focus on getting better. “Two things are essential: a deep personal commitment to excellence in everything you do and a commitment to continual improvement.” He encourages us to strive to become 15% better each year in concrete and actionable ways. To do that you need to really think about what you are going to do differently. If you want to be extraordinary, you need to stretch yourself above the average person. Exceed your job description. Do it for you and build a reputation. “By sticking to tasks listed in your job description, you are refusing to demonstrate your ability to perform at a higher level. Why should anyone think of you as a potential leader when you’ve provided them with no evidence to suggest it?” For him, his underprivileged background represented an opportunity. “The world and its people were a puzzle for me to solve.” He reframed his world. It is our mindset that often makes it impossible to escape the box we find ourselves in. “Reframing is about creating a new mental landscape with a larger scope of freedom, a greater degree of flexibility, and a set of alternative ways of approaching any problem—which can often lead to new and unexpected solutions.” You know you need to reframe when what you hear around you is, “Everybody knows” and “It’s obvious that.” “It’s a sign that you and your colleagues may be trapped in a box of your own making—one in desperate need of reframing.” On the topic of mentors, Williams believes that they are helpful, but you shouldn’t spend your time looking for one. “Mentors come along without planning. Mentorship must arise naturally out of the situation rather than being forced.” However, and his is key, “that doesn’t mean you can’t make a conscious effort to learn from the people around you. As you work on learning to lead yourself, you should also seek out others whose examples, experiences, and insights can be of value to you.” When people do (or seem to) get in your way, rather than finding blame, assume positive intent. You can choose how you respond to negative events. We don’t need to take it personally. “If there’s something that will make you feel really good to say—something you are itching to say—don’t say it. Blowing up in the face of provocation is a way of losing power, not of claiming it.” Assuming positive intent has been one of William’s secret weapons throughout his career. It is an “empowering strategy that disarms defensiveness and turns potential enemies into allies.” When leading others and you are faced with opposition to a project or deadline, Williams says that the leader’s job is to ask a lot of pointed questions. “When people protested that a particular deadline I suggested was ‘impossible,’ I would ask, ‘Can you help me understand how you determined that?’ or ‘What are the factors that led you to conclude it’s impossible?’ I avoided starting my questions with the word why, having long ago discovered that ‘why’ questions tend to make people feel defensive—and respond accordingly. By contrast, the more oblique wordings I used directed attention away from the blame game and exactly where I wanted it—toward uncovering the root causes behind their objections.” A leader also needs to ask questions that lead people to think about the problems they face in a new way; to overcome their mental barriers—“those unquestioned assumptions, unexplored options, or unchallenged rules of thumb that keep people stuck at a low level of achievement.” These mental barriers cause us to reinforce them with information that supports them and ignore the evidence that should alert and enlighten us. We hurt ourselves and our organizations when we act on our untruths. Williams includes a chapter on managing up and down and presents his Two-Up/Two-Down System. “Paying close attention to the ideas, information, and concerns of the people around you—especially those operating from a different perspective or from a different location in the organizational hierarchy—is key to leadership success. Learning to correctly grasp what I call strategic intent of those in important positions above you and below you in the organizational hierarchy is a vital leadership practice, one that you should try to make into a daily habit.” Williams provides lessons in communication, creating a positive culture, defining reality, and many more. Putting in practice what he presents here does not require extraordinary gifts. “Your own abilities can suffice to make you an effective leader—provided you focus on the daily challenges around you and then work doggedly, thoughtfully, and positively with the people around you to overcome them.” There is a lot of emotional intelligence contained in this book. Reading it is a good way to develop your own EQ and check your self-awareness. Use Learning to Lead to prepare yourself answer the call to lead when it comes. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:10 PM
08.28.19

The Best Mentor You Can Find is Up to You!
“The greatest good you can do for another is not just to share your riches but to reveal to him his own.” WHEN I WAS a young Army lieutenant, I met with my Assignment (Personnel) Officer, Major Tom Montgomery in Washington D.C. on my way to Germany in the summer of 1977. I never expected that he would become my first true mentor. There was no contractual agreement or even a discussion about such a relationship, and through all these years, I’ve never mentioned the word “mentor” to him. But, throughout our relationship, our conversations have given me volumes of knowledge about leadership and a host of other topics. I saw in him a leadership style similar to my own, just more seasoned. I wanted to learn as much as I could from him and use similar techniques as my own leadership responsibilities grew. He helped me get certain jobs and I worked directly for him once. We remain great friends to this day. Receiving mentorship is a vital element in learning about leadership… and being a mentor is a responsibility of all great leaders. I believe there are four types of mentors: assigned, self-appointed, sought-after, and what I call “virtual.” I have experienced all four. The first three are rather self-evident in terms of what they mean. What I’ve found the most valuable, however, is this last one, virtual. What do I mean? Virtual mentorship is something you do on your own. You simply pay attention to all of the people around you and learn from them. This can apply to both your professional and personal life. Pay attention to what others do or say that is particularly smart or good, then adopt it as your own habit. Notice also when a leader does something incredibly dumb or harmful to others, then put that in your leadership reservoir as well, so that you will never do the same. We’ve all seen good and bad behavior and said to ourselves: “If I ever get into that position, I hope I behave—or do not behave—like that.” Think of your life as a journey carrying a backpack, and observed behaviors are rocks you find along the path. Pick up both the good and bad—the good for future use and the bad to remind you not to repeat what those rocks represent. I’ve got plenty of rocks in my backpack—of both kinds—that I’ve picked up along my life’s journey. All great leaders learn something from those they encounter along their journey. It’s also a good practice to acknowledge those who provided meaningful lessons. I regularly cite those who taught me something that I now use myself. I also store away lessons that I want to avoid from leaders who I don’t want to emulate, though I generally refrain from naming them. Perhaps one of the greatest periods during which I learned from others was my time in the Pentagon in the late 1990s. My 23 years of service to that point had been exclusively within Army ranks, with no duty served in another military branch. But in 1996, when I became a new brigadier general, I was assigned to the Joint Staff in the Pentagon. I served during this time with a number of great military leaders who influenced me. Lieutenant General Pete Pace (later Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff) was the J3 of the Joint Staff. I had to brief him each morning. My immediate supervisor was first Major General John Van Alstyne, then later Rear Admiral Tim Keating (who eventually became the Pacific Command Commander and Northern Command Commander as a 4-star admiral). Brigadier General Jim Conway (later Commandant of the Marine Corps) was a fellow 1-star and Colonel David Petraeus was the Executive Officer for the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, General Hugh Shelton. Lieutenant Colonel Terry “Guts” Robling served there as well and would later become my boss as a three-star general when he commanded Marine Corps Forces Pacific and I was his civilian Executive Director. That was a particularly interesting relationship, as he was a lieutenant colonel when I was a brigadier general in 1996. While he didn’t report to me, we knew each other and occasionally worked together. Seventeen years later, I reported to him. I remember our first discussion in his office in 2013, where I made clear that while we had a different relationship in the Pentagon, I was perfectly fine working for him. I remember him saying he was, as well. He was very comfortable in his own skin. We got along great in the two years of his command tenure and remain good friends to this day. Good leaders don’t patent their behaviors; they willingly pass them on. I have borrowed many leadership techniques—perhaps most of them—from others who freely gave them up, and from some who didn’t even know I took them. Let your greatest legacy be that you pass on the best-of-breed leadership traits you’ve learned from others. I freely pass on mine. Many are in my new book, Leadership: The Art of Inspiring People to Be Their Best.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:13 PM
08.14.19

It’s the Manager: Moving from Boss to Coach
NOT SURPRISINGLY, a Gallup World Poll found that the great global dream is to have a good job with mission, purpose, and at a living wage. But the vast majority—85%—hate their jobs. If you couple that fact with George Gallup’s “single most profound, distinct and clarifying finding ever” that 70% of the variance in team engagement is determined solely by the manager, then the issue becomes the manager. That being the case, the single key to maximizing human potential and organizational growth is to improve the quality of the manager. The most important person in your organization to bring teams together and lead them to great decisions is the manager. Jim Clifton and Jim Harter of Gallup explain how to build a strengths-based culture that attracts the best employees and maximizes their potential in It’s the Manager. They cover five major topic areas—Strategy, Culture, Employment Brand, Boss to Coach, and Future of Work—an offer 52 discoveries from Gallup’s largest study of the future of work. The most important sections for me are Employment Brand and Boss to Coach. The practice of management has been stuck in time for more than 30 years, despite the world and workplace going through extraordinary historical change. “The problem is, while the science of management has advanced significantly in the past three decades, the practice of management hasn’t.” In the new working environment, one of the biggest challenges is for managers to go from boss to coach. The old boss-to-employee, command-and-control leadership environment has “worked” when it comes to building process-efficiency systems, engineering large buildings, and creating infrastructure. But the top-down leadership techniques of the past have not adapted to a workplace that now demands coaching and collaboration to thrive. However, I would argue that top-down and coaching and collaboration are not necessarily mutually exclusive. That said, coaching requires three things: establish expectations, continually coach, and create accountability. Their research has found that “employees whose manager involved them in setting goals were nearly four times more likely to be engaged than other employees” and those who receive “daily feedback from their manager are three timed more likely to be engaged than those who receive feedback once a year or less.” Gallup analytics finds that most current team leaders do not have the natural tendencies for managing people. We often promote people for the wrong reasons like success in a prior non-management role and tenure. Organizations still think largely in terms of promoting up the corporate ladder when other options exist like changing teams, projects, or even managers. Unfortunately, many organizations still offer only one way “up”: Become a manager, even if your strengths aren’t in management. Some people who aren’t really cut out to be managers may do an OK job, but they never feel quite right managing. And this affects their wellbeing—and the wellbeing of those they manage. Gallup research fronds that great managers have these five traits: Motivation (inspiring teams to get exceptional work done), Workstyle (setting goals and arranging resources for the team to excel), Initiation (influencing others to act; pushing through adversity and resistance), Collaboration (building committed teams with deep roots), and Thought Process (taking an analytical approach to strategy and decision-making). There is a code to take the CliftonStrengths assessment and an appendix section that provides guidance for leading with each of the 34 strengths. (As a side note, I found this statistic enlightening: “Your employees are grumbling, as 50% of them are making less than they were 35 years ago. In real terms—overall—your employees have not received a raise in more than 35 years. Their expenses of housing, healthcare, and education are exploding while paycheck sizes are frozen or declining.”) 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:18 AM
07.05.19

Grace: A Leader's Guide to a Better Us
GRACE, a concept present in all of the world’s major religions, has a divine meaning. Grace, in a secular sense—that is on a human level—is about perspective. A perspective larger than ourselves. A perspective that reaches to a purpose beyond who we are alone. In short, our connectedness. Grace is a critical part of who great leaders should be. To that end, John Baldoni has tackled for us in Grace: A Leader’s Guide to a Better Us, an attribute that is in short supply today. Grace is something all leaders should model for the benefit of those around them so that it spreads to society in general. Grace is foundational to service. Baldoni writes: Love, sacrifice, truth, and courage are virtues made actionable by grace. We may be disposed to do what is right; grace gives us the impetus to act upon doing it. Grace then becomes the inspiration for treating individuals with generosity, respect, and compassion. It manifests itself as action in the name of others, and it energizes us to act upon our beliefs. To help us better understand grace and to help us intentionally apply it in our leadership, Baldoni explores grace from five perspectives with this acronym: G is for Generosity: the will to do something for others.
Generosity Gracious people give of themselves. Gracious people leverage who they are and what they have for the benefit of others. Baldoni shares a great quote from British Prime Minister Benjamin Disraeli, “The greatest good you can do for another is not just to share your riches but to reveal to him his own.” Gracious leaders share time, knowledge, and power. They cultivate a selfless approach to life. Generosity emanates from an abundance mindset. A selfless person, even in the midst of personal adversity, can find something to share with others. That attitude is contagious. Respect Self-awareness opens the door to respect for others. A fully self-aware person knows her faults as well as her strengths. Such awareness compels the self to acknowledge the dignity of others.” Humility plays a big part here. Respect and self-respect fuel each other. They grow together. Action Grace is intentional. A reactive mind rarely manifests grace. While grace that has been shown to us comes freely, it requires effort for us to generate it ourselves. Grace means rising above a perceived slight. Grace is often manifested in clarity of purpose and civility. Civility is a decision we make. “No matter what leaders may feel inside, they think before they speak. They focus not on themselves, but on the needs of others—on healing.” Instilling civility in the workplace is the job of leaders. Compassion Gracious people have the capacity to forgive and show mercy. “Grace enables us to take the higher road, to think more clearly.” It meets rage with love and civility. Gratitude enables compassion—both gratitude expressed and felt. “Gratitude is that capacity to care. We need to reframe our lives with a constant awareness of just how important feeling gratitude within ourselves is because it actually helps our overall well-being.” Energy Grace requires energy. “It renews itself through practice as well as by taking in life, doing one’s best, enjoying the highlights, mourning the losses, and do so in the full spirit of life. In forgiveness, mercy, joy, and humor.” Grace draws energy from a positive outlook and an abundance mindset. When we demonstrate grace in our leadership, it spills into other areas of our life as well because it is an approach to life. Our example encourages others to begin to think that way as well. Grace—in all of the dimensions Baldoni explores in this book—is a value that has fallen on hard times. It is time to revive it in our personal lives, in the workplace, social media, and in public discourse. Grace celebrates grace as well as advocates for it. Baldoni shares many examples of people from all walks of life who demonstrate grace in their lives. They are an inspiration to us all. Grace reduces the space between us. Our environment often pushes us into negativity; into the differences between us. Grace intentionally overlooks the negative and leverages the positive. It finds the connection and promotes it. Baldoni breaks the often intangible idea of grace into down-to-earth actionable behaviors that we can all intentionally implement into our lives. You will find a self-assessment tool of 20 questions to help you take an honest look at how much you have allowed grace to fill your thoughts and behaviors. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:08 PM
06.19.19

Scaling Leadership the McKinsey Way
BEFORE YOU BEGIN your next leadership development program, read this. It is not uncommon to hear leaders complain that leadership development programs are not delivering the effective leaders necessary to execute their strategies and purpose. While there is no end of leadership advice, it doesn’t always translate into leaders that can deliver the results the organization needs. In Leadership at Scale, McKinsey partners Claudio Feser, Michael Rennie, and Nicolai Chen Nielson share the McKinsey method for developing more and better leaders across an organization. “Scale implies touching a critical mass of leaders and employees to reach a tipping point—after which point the change become self-sustaining and the organization fundamentally changes how it leads.” To begin, to improve leadership effectiveness in an organization as a whole, it is imperative that leaders “think at an organizational, system-wide level, and the approach one takes to do this differs markedly from that of increasing the effectiveness of individual leaders.” The McKinsey approach is founded on four beliefs that constitute effective leadership: 1. Leaders align, execute and renew. “Leaders make decisions about people and direction (alignment); they see that their intent is carried out (execution); and they think about the next evolution of activity (renewal).” Renewal refers to the constantly changing environment. “Organizational contexts have and will always be changing, and a key element of leadership is thus to display resilience and agility in order to continue to thrive.” 2. All leadership takes place within a context. “We strongly believe that there is no such thing as standard leadership behavior that works irrespective of contextual factors, such as corporate strategy or the level of hierarchy of a given position.” 3. Skills built through real-life experience enable effective leadership behaviors. “Great leaders’ skills are forged on-the-job, and the experience and skills that leaders have accumulated help them display more effective leadership behaviors.” 4. Leaders must develop the right mindsets based on introspection and self-awareness. “We focus on mindsets because mindsets ultimately drive behaviors. Making one’s mindset the subject of conscious scrutiny is an indispensable prerequisite of leadership effectiveness.” That leads us to the Leadership at Scale Diamond. Leadership at Scale Diamond Underpinning the McKinsey approach are four core principles they call the Leadership at Scale Diamond. These principles must exist to increase leadership effectiveness across an organization.
Core Principle 1: Focus on the critical shifts that drive disproportionate value. Link leadership development to the organizational context and strategy and focus on the three to five shifts (behaviors, skill, and mindsets) that will have the biggest impact on performance. Surprisingly, leadership development is often not aligned with the organization’s purpose and strategy. In their research, executives have told them that “their organizations have not translated their strategy to their needs.” Instead, they have used “generic and broad competency models.” The result is not surprising. Their research identified three categories of leadership behaviors: Baseline Behaviors: Effectiveness at facilitating group collaboration, Demonstrating concern for people, Championing desired change, and Offering Critical perspectives. These behaviors apply in any context, but they by themselves do not differentiate between mediocre and top performance.
McKinsey also concluded that only a few behaviors drive organizational performance and that varies by context. So, in addition to context-specific behaviors is the ability of a sufficient number of leaders in an organization to be able to rapidly adjust to different situations and the accompanying behaviors. Core Principle 2: Engage a critical mass of pivotal influencers across the organization to reach a tipping point. Organizations must ensure sufficient breadth, depth, and pace in order to change leadership behaviors across the organization, and to give all employees an understanding of what great leadership looks like. Pivotal influencers are those 5 to 15% that others look to for cues as to what success looks like in the organization. Work first with these people with the understanding that developing a repertoire of leadership capabilities takes time. And of course, the training should reflect that truth. Core Principle 3: Architect programs that maximize behavioral change based on neuroscience. Design interventions with an explicit focus on helping individuals become “better at their daily jobs” using the latest principles linked to neuroscience, to maximize the value and organizational impact of what is taught and learned. Rather than just the teach and classroom approach, leaders need to practice the new behaviors. McKinsey designs programs around seven adult learning principles:
Core Principle 4: Integrate and measure the program in the broader organization Organizations must ensure that the broader ecosystem directly supports and reinforces the shift in behaviors, skills, and mindsets that the leadership development program promotes. You can’t run a leadership development initiative in isolation and expect positive results. The culture of the organization must support it or enable the new behaviors that the organization needs both formally and informally. The authors note that the actual capability building journey is only 25% of what is required. “People’s behaviors are heavily influenced by their broader context, and in order to sustainable shift their behaviors, you need to shift the context.” In part two of the book, they share this approach in practice. It is quite comprehensive, and the case studies are instructive. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:39 AM
04.22.19

Becoming a 100X Leader
A 100X LEADER is a 100% healthy leader who multiplies that mindset to those they lead. A leader that climbs their own Mount Everest every day and acts as a Sherpa to others at the same time. A 100X leader has become a leader worth following and builds leaders worth following. Jeremie Kubicek and Steve Cockram wrote The 100X Leader to help you become a 100X Leader in all spheres of influence in your life—leading yourself, a company, a team, or a family—and to become a Sherpa for others. Your climb to becoming a 100X leader begins with self-awareness and courage. The courage “to invest in yourself and what is most important in your life, the courage to do difficult things that are contrary to your natural tendencies, the courage to hold up a mirror and take a hard look at what others see and wish you would do something about, the courage to make the subtle changes you view as insignificant but are likely the most important to others, the courage to stay at it when the positive results see slow to come.” You don’t become a 100X leader by accident. It’s hard and requires a deliberate process. Kubieck and Cockram guide you through that process. Leading yourself or others is a balance between the right amount of support and challenge. “Support means to provide the appropriate help others need to do their jobs well.” To equip them. Challenge “means to motivate people by holding them accountable to what they could do if they had the resources.” It is important to remember that we must begin with support before we challenge. Support builds trust. “The art of leadership is the appropriate calibration of support and challenge at a specific moment, in a specific context for a specific reason.” The authors present the Support-Challenge Matrix shown below. You want to operate in the top right quadrant—liberate—as much as you can. Each quadrant represents a different leadership style and the culture it creates.
Dominator
Protector
Abdicator
Liberator
Being a Liberator means knowing how other people experience you and then helping others to do the same. It’s being intentional about what you are doing. Having the humility to “commit to a process of uncovering our weaknesses. Our natural tendencies don’t really change, but with intentionality, humility, and effort we can begin to have a choice between the default patterns of how we normally respond to a situation and what we actively choose to do or say instead.” We liberate ourselves from leading on autopilot. Once we liberate ourselves, we can then help others see the mountain ahead of them and equip them to get to the next level. Kubieck and Cockram provide a comprehensive look at how to become a 100X Leader by showing us the mountain and then illuminating the way and providing the tools and equipment necessary to complete the climb. Climbing Mount Everest is dangerous and demanding, but without a Sherpa, it is virtually impossible. The 100X Leader is our Sherpa and teaches us how to become a Sherpa for others. And as with the Sherpa, success is measured by not how many times they reach the top of Everest but by how many they have helped reach the summit. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:38 AM
03.11.19

You Might Be a Bad Leader If…
NONE OF US would readily admit to being a bad leader. We see ourselves as pretty good or at least well-intentioned. But people don’t experience our intentions; they experience what we actually do. When we struggle to get along with others or simply get things done, we would be wise to look at our assumptions and behaviors. Even just focusing on improving in one area can do wonders for your leadership and have a huge impact on those who follow you. No matter how good we are as leaders, we all do a little harm along the way. So it’s good to look at the ways bad leadership shows up so we can minimize the bad and amplify good leadership. You might be a bad leader if you are motivated by power and status. This motivation invariably leads to corruption and unethical behavior. It’s most often why otherwise effective leaders go bad. It opens the door for every other kind of mindset we associate with bad leaders. Our leadership must be about something bigger than us. Power is something to be shared. You might be a bad leader if you are easily overwhelmed. It is the nature of leadership to function in uncertainty. What makes it possible is a clarity of purpose about why we are doing what we are doing. Leaders must continuously communicate that purpose to lead others an often volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous world. You might be a bad leader if you are too rigid. This is a failure to stay relevant. Staying the course is admirable, but a leader must know the times they are in. They must be effective in their current reality. Barbara Tuchman noted that a bad leader is not “deflected by the facts.” You might be a bad leader if you lack self-control. Leaders are not a superset of human beings. Leaders have impulses, desires, and needs, just like everyone else, but when we fail to control our impulses, we most often get in our own way and derail our leadership. We lose credibility as followers expect—and rightly so—leaders to put the needs of the group above their own. Of course, there are impulses that are merely a distraction for others, and then there are impulses that destroy us and hurt those around us. We must exhibit self-control for the sake of ourselves and others. Leaders who lack self-control take themselves down. You might be a bad leader if you think the ends justify the means. By crossing one too many lines, we put ourselves on the road to unethical and even evil behavior. This failure of leadership is based in self-interest. It’s self-serving. Leaders are rightfully judged by their results but not at any cost. This toxic mindset is most often gradual, and when tolerated in an organization it begins to infect all decisions and diminishes everyone involved. You might be a bad leader if you lead by fear. This kind of leader exerts a high degree of control. It also leads to incompetency as the organization can never rise above the leader themselves. In the end, the whole organization is incompetent. Good leaders must know what they don’t know. As Dirty Harry said, “A man’s got to know his limitations.” You might be a bad leader if you have a lack of respect for others—for just being people. A lack of respect manifests itself in being unkind, dismissive of the opinions and needs of others, controlling others, or showing partiality because of status or importance. We respect others when we are curious about them and listen to them. You might be a bad leader if you fail to see beyond ourselves. As leaders, we are responsible not only to the people we lead but to all of those affected by our leadership. It is a failure to do the right thing—to not do right when it is in our power to do right. You might be a bad leader if you lack the competency for our job. This doesn’t mean stupid. It’s about skills. Do we have to skills to move forward in the areas we have been tasked to lead? You might be a bad leader if you lack emotional intelligence. Leaders must be aware and sensitive to others and importantly, how their leadership is experienced by others. This implies the need for honest and candid feedback and daily reflection. Our ego creates blind spots, so we must always keep our ego in check. This is where humility comes in. A good leader leads themselves first. We must be able to recognize the signs of bad leadership so we can deal with it before it undermines us. These mindsets come up time and time again because they are common to humankind. We can’t change that. None of us are immune. Sticking our heads in the sand won’t help. Only by recognizing them when we see them in our own leadership we can effectively deal with them.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:32 PM
03.08.19

Lessons in Leadership to Last a Lifetime
AFTER 18 YEARS on the MIT faculty, I thought I knew a thing or two about leadership. After all, I was tenured and had supervised dozens of students seeking undergraduate and postgraduate degrees. But in 1999, at the height of the Internet boom, I took a two-year leave of absence to serve as director of system architecture at Akamai Technologies, an MIT start-up located here in Cambridge. That position humbled me and taught me lessons about leadership that I still use today, some 20 years later. Back then, the vast majority of Akamai’s 100 engineering staff had been recruited directly from MIT and other top universities. Like me, most had only worked in academia up to that point, and we assumed our corporate roles and responsibilities with anticipation and a healthy dose of swagger. What could possibly stop this juggernaut of collective brilliance? Well, one collective deficit could, and did: The lack of effective leadership. You see, despite their immense talent, our teams were completely dysfunctional. Within weeks, people started to feel disgruntled, and then even worse—angry, jealous, vindictive. Morale sunk, and our productivity did, too. Fortunately, Akamai’s VP of Human Resources, Steve Heinrich, recognized what was happening and brought in Chuck McVinney, a management consultant with expertise in teamwork and leadership training. Chuck began teaching the engineering leaders about topics we had never been exposed to before: situational leadership, dealing with diversity and conflict, providing effective feedback, fostering creativity, and how to build a motivated team that leverages individual talents. Remarkably, after only two off-site workshops, our teams started to function better. We were able to focus and work collaboratively toward our goals. The workshop content wasn’t complicated, but if you’re currently running a research lab, odds are, you’ve never seen it. That’s because academia and other research organizations rarely offer leadership and management training—and as a result, far too many engineers and scientists waste their time and resources dealing with unproductive interpersonal issues and unnecessary conflict. To help right that wrong, here are five the most important lessons I learned while at Akamai, all of which I continue to use in my lab today: Research is a human endeavor
Know thyself
Mental diversity strengthens teams
Communication is key—and it involves effort
To keep leading, keep learning
It’s been about 20 years since I returned to MIT from Akamai, and businesses now routinely spend billions of dollars per year teaching employees “soft” leadership skills like the ones I just listed. If universities and other research organizations would invest even a fraction of that, their labs would be a more enjoyable place to work and their teams would be more creative and productive. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:04 AM
03.04.19

11 Shifts Every Leader Needs to Make
TO GET FROM where we are to where we want to be requires a shift in our thinking. When our thinking shifts in an area, our perspective changes, and new opportunities become visible. We serve people differently. In Leadershift, John Maxwell states, “every advance you make as a leader will require a Leadershift that changes the way you think, act, and lead.” Shifts in thinking require that you see a bigger picture, rethink your perspective, and understand your context. Your leadership potential depends on these shifts. It’s is unlikely that you would make all of these shifts at once. Some will happen gradually. Some will happen almost overnight. Some will come naturally to you and others will seem counterintuitive. We’re all different but we all need to make these shifts. Essentially they all boil down to making the shift from me to we. Maxwell suggests eleven leadershifts that have helped him grow as a leader. Here are a few ideas from each of the leadershifts he describes: Leadershift #1 Soloist to Conductor – The Focus Shift You can’t do it alone. Leadership is not a solo practice. Of course, working with others has its challenges. A big part of this shift is changing your focus from receiving to giving. Adding value every day without keeping score. “As leaders, we must stop wishing and start working. Instead of looking for the ‘secret sauce’ of success, we must start sowing seeds of success.” Leadershift #2 Goals to Growth – The Personal Development Shift Rather than focusing on goals, focus on growth. “Goals helped me do better, but growth helped me become better.” Begin on the inside. “Growth on the inside fuels growth on the outside.” You can’t do everything, so focus on four areas: attitude, developing strong relationships, your leadership, and equipping others to carry on without you. To become more growth-oriented, you need to embrace change, be teachable (humble), learn from failure, connect with other growth-minded people, believe in yourself, and understand that real wisdom is acquired and applied over time. Leadershift #3 Perks to Price – The Cost Shift Great leadership isn’t about control, the income or the corner office. It’s about sacrifice. Great leadership costs us something. American missionary Adoniram Judson is rumored to have said, “There is no success without sacrifice. If you succeed without sacrifice, it is because someone has suffered before you. If you sacrifice without success, it is because someone will succeed after you.” Great leaders go first. “What sets great leaders apart from all other leaders is this: they act before others, and they do more than others. Great leaders face their uncertainty and doubt, and they move through it to pave the way for others.” Leadershift #4 Pleasing People to Challenging People – The Relational Shift You can please some of the people some of the time, but you can’t please all of the people all of the time. But if you want the best out of people, you have to challenge them. “You have to put doing what’s right for your people and organization ahead of what feels right for you.” This means keeping your eye on the big picture. Sometimes you have to have tough conversations, but you must balance care with candor. Leadershift #5 Maintaining to Creating – The Abundance Shift Maintaining isn’t always easy, but it is the easiest mindset to slip into. It’s not about change for change sake, but it’s about “can we do better?” Create a creative environment where people gather ideas and value multiple perspectives. “Being inflexible and sticking to my plan put a lid on me and my organization.” Larry Stockstill said, “I live on the other side of ‘yes.’ That’s where I find abundance and opportunity. It’s where I become a better and bigger self. The opportunity of a lifetime must be seized within the lifetime of the opportunity. So I try to say ‘yes’ whenever I can.” Leadershift #6 Ladder Climbing to Ladder Building – The Reproduction Shift This shift is about equipping others. We being with ladder climbing (How high can I go?), then we shift to ladder holding (How high will others go with a little help?), then ladder extending (How high will others go with a lot of help?) to finally, ladder building (Can I help them build their own ladder?). “If you want learners to follow directions, you only need to provide the what. If you want them to lead others and give directions, they must also have the why.” Leadershift #7 Directing to Connecting – The Communication Shift You must learn to connect with people to be the best leader you can be. To move from directing people—talking, ready answers, your way—to connecting—listening, asking, empowering. Be a person people can trust. Lift others up. “When you interact with others as a leader, what is your mindset? Is your intention to correct them or connect with them?” Leadershift #8 Team Uniformity to Team Diversity – The Improvement Shift If everyone around you thinks like you, you need to expand your network. A diverse team will fill in gaps in knowledge, perspective, and experience. “Malcolm Forbes said diversity is the art of thinking independently together.” Leadershift #9 Positional Authority to Moral Authority – The Influence Shift Moral authority is not about position it’s about who you are. People follow moral authority before they follow positional authority. Maxwell lists four areas a leader needs to develop to have moral authority: competence, courage, consistency, and character. “Every leader who possesses moral authority has had to stand alone at some point in time. Such moments make leaders.” Leadershift #10 Trained Leaders to Transformational Leaders – The Impact Shift Maxwell believes that if you only make one shift in your leadership, this is the one because it “will bring the greatest change to your life and the lives of those around you.” Transformational leaders inspire others to become more. But that’s because they have worked to become more themselves. “If you want to see positive changes in your world, the first person you must change is you. As leaders, you and I have to be changed to bring change. We teach what we know, but we reproduce who we are.” Leadershift #11 Career to Calling – The Passion Shift This is the shift from just doing a job to do what you are gifted to do. Aristotle wrote, “Where our talents and the needs of the world cross, there lies our vocation.” Your calling is not about you. “A calling moves us from the center of everything in our world to becoming the channel through which good things come to others.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:30 AM
02.06.19

Scaling Leadership
THE INEVITABLE CONSEQUENCE of leading in an increasingly complex world is that we will have developmental gaps in our leadership. As our context change, we have to grow with it. In the words of Robert Anderson and William Adams, authors of Scaling Leadership, “We are running an Internal Operating System that is not complex enough for the complexity we face. This is our Development Gap.” We are often pushed to our limits. The solution is to scale our leadership. Leadership must learn to scale itself, but not any kind of leadership will do. We need much more of the kind of leadership that is capable of scaling innovation, adaptability, sustainability, agility, and engagement as its growth strategy. Scaling leadership is about becoming the kind of leader that scales the conscious leadership capable of creating what matters most of all the stakeholders it serves. So just what is this “conscious leadership?” To answer this question, they asked 50,000 leaders and employees worldwide, “What kind of leadership, if it existed, would enable the organization to thrive in its current marketplace and into the future?” The answer is displayed in the Optimal Leadership Circle Profile below. The top half of the circle are the 18 Creative Competencies that lead to leadership effectiveness. The bottom half is comprised of 11 Reactive Tendencies. These are our go-to strengths and behaviors we rely on when we feel under pressure. The reactive tendencies often get the job done but at a cost—disenchanted and disengaged employees and stakeholders that feel bullied or let down.
In order to scale your leadership, the right conditions must exist. First and foremost, we have to consciously move our leadership from reactive to creative. Also a Generative Tension or Strategic Intent must exist as leaders take responsibility for and establish a development agenda for themselves and their organization. Finally, as represented by the top half of the inner circle, four more conditions must exist: Relating or Deep Relationship, Self-Awareness, and Authenticity or Radically Human, Systems Awareness or Big Picture, and Achieving or Purposeful Achievement. How do you show up as a leader? Creative? Reactive? In their study, High-Creative leaders consistently demonstrated the following 10 strengths. Interestingly, the first four represent the areas with the highest leadership gaps—areas where leaders need the most work.
It’s not surprising that these were the most strongly endorsed strengths. People perform better when respected and your leadership is perceived as better when you are respectful. As Bill Adams father told him growing up, “How you get results is as important as the results themselves.” It’s easy to forget in a world where the end seems to justify the means. In the authors consulting work they have found that when leaders derail it’s because while they are very talented, they are highly reactive. They underuse their High-Creative strengths. Often what got them where they are, is no longer working in their new leadership context. Their research indicates areas that all leaders need to consider and develop where necessary. But of course, simply following a list is a bit simplistic. Or to say because I am relational, I’m a better leader. Because I’ve got good people skills, I’m naturally effective. We all come to leadership with strengths and weakness. Learning to honestly face where you need work and where you need to temper your strengths, is the sign of a great leader. Scaling leadership is a good place to begin the journey. In conclusion, the authors state that there’s more. Creative Leadership alone isn’t going to get the job done. “No matter how you cut it, we are up against a level of escalating complexity and disruptive change that requires, and will continue to require, an unprecedented level of innovation, adaptability, scalability, sustainability, resilience, collective intelligence, engagement, empowerment, agility, systemic thinking, and global cooperation.” What we need they term Integral Leadership “supported by a Self-Transforming Internal Operating System in some depth.” That’s to say we are no longer leading for ourselves but for a purpose larger than ourselves that comes through in everything we do. It means we go deeper to develop our character—who we are. We no longer sponsor change in the organization, we radically, humanly, and in deep relationship lead change from the perspective that the system is mirroring the function and dysfunction in us, individually and collectively. We project our shadow less and less, and therefore, we can engage conflict without reactively making the other into an enemy or adversary. We experience others as much like us, a work in progress, and we engage in dialogue from a place of listening, learning, compassion, and strength. Humility. Empathy. Faith. Grace. We are more alike than different. Integral leadership sees through our differences “to a deeper unity that we all share—that we all are. We are all each other.” You can learn more about the Leadership Circle Profile and take your free self-assessment on the Leadership Circle website. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:16 AM
01.16.19

Conquering the 5 Misconceptions that Hold Leaders Back
THERE ARE THINGS we believe that when we really think about them, we might find that they are not helpful. We might think of them as blind spots that adversely affect our leadership effectiveness. In What Are Your Blind Spots? Jim Haudan and Rich Berens hope to help you uncover five common leadership blind spots by exposing the underlying assumptions behind the consequences we see played out over and over again in all types of organizations. This is how they lay it out: Leadership Blind Spot #1: Purpose The Misconception: Purpose matters, but it doesn’t drive our numbers. An organization primarily focused on the hitting the numbers is a push mentality. To focus on the purpose is a pull strategy. A firmly ingrained purpose has the power to pull the numbers we are seeking. At the same time, it is nimble and responsive to changing circumstances as it is attached to a point of view and not a procedure. They note: Organizations with a strong purpose at their core are more likely to be able to change when they truly need to. They will view their current operating model and customer offerings as merely a means to achieve their larger purpose and should, therefore, be able to change direction more easily when market forces require a more radical shift. Leadership Blind Spot #2: Story The Misconception: We have a compelling story to tell that people care about. If you have a clear purpose, there is usually a good story behind it. Stephen Denning wrote in Telling Tales, “Analysis might excite the mind, but it hardly offers a route to the heart. And that is where we must go if we are to motivate people not only to take action but to do so with energy and enthusiasm.” The truth is that to reach the heart, you have to create a sense of adventure and a sense of belonging, while also outlining a meaningful journey where people can see how their contributions make a difference. Leadership Blind Spot #3: Engagement The Misconception: Rational and logical presentations engage the hearts and minds of people. We can’t present our way into the hearts and minds of people. The authors suggest that we connect with others with relationships that inspire hope. We contribute disengagement and stifle inspiration. Through authentic conversations, we can co-create with our employees. “We simply suggest,” they write, “that leaders repeat their own personal thinking journey with their people.” Invite people to co-think with you. Inviting your people to help you solve the problems of your business begins with leaders believing in the immense creation capability of their people. Shifting your thinking from “I am the creator, and my people are the implementers” to “I know this business well, but so do my people, and I can learn from them if I really listen” will transform your organization. Leadership Blind Spot #4: Trust The Misconception: People will not do the right thing unless you tell them what to do and hold them accountable to do it. With the first three blind spots exposed and conquered, trust becomes much easier. People know what to do and why they are doing it. Rigid controls are counterproductive, and standards become easier to maintain. They become agents of the vision. To this point: People must believe it’s their store, their hotel, their office, their factory, or their hospital. They must feel that they’re more than a cog in a wheel with overseers watching and waiting to catch them in a screw-up. They note, “It’s the job of the leader to invite that uniqueness to be a part of the work experience every day.” That only happens when we stop controlling our people and trust them and their judgment. Leadership Blind Spot #5: Truth The Misconception: My people feel safe telling me what they really think and feel. I think it is safe to say the people don’t always feel comfortable speaking truth to others especially superiors. For any leader, it’s safer to assume that they don’t and make a conscious effort to create a culture where people will feel safe to come to you with the truth even if it’s just the truth as they see it. Humor helps to break the ice. Truth is a critical blind spot that can create an environment of poor decision making mixed with a significant lack of trust and disengagement in your organization. What Are Your Blind Spots? is a short but well thought out book. Inside you will find an assessment to help you see where you stand on each of these issues as well as exercises and tools to help you conquer each of them. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:56 PM
12.21.18

5 Distinguishing Traits of High-Performing Leaders
WHO WE ARE speaks louder than what we say. Respect for others is the cornerstone of high-performing leaders. Respect is demonstrated daily through skills that we can all learn and make a part of who we are. Through his experience as an executive coach, Fred Halstead has defined in Leadership Skills that Inspire Incredible Results, seven skills that when practiced yield meaningful results. You may not be an expert at all but you can get better at every one of them. Demonstrating respect is more about asking the right questions than being ready with answers. Halstead admits though that “asking questions—in particular, questions than can inspire clearer thinking, solutions, and action plans—is challenging, especially when we are used to just telling others what we know should be done.” But to succeed we must have teams that are self-reliant, who understand their purpose and can execute on that purpose. Asking questions and guiding requires real focus. It’s about our team’s success. “Those who truly want others to excel are the ones who also achieve the greatest personal success.” To demonstrate respect and quip others we need to practice these skills with others: 1. Become a Fully Connected Listener Listening shows respect and appreciation. Listening must come first. It requires patience. As Fran Lebowitz observed, “The opposite of talking is waiting.” Our natural desire to talk, judging others, our biases ego, and our business, all inhibit our inclination to listen. “The less we worry about appearing smart, the smarter we will appear to be by just listening and asking smart questions.” Listening is easier when we are curious. It’s easier too when you know and believe in your purpose for listening. More than just gathering information, “when you listen to someone, you learn how that person thinks, which provides insight into how you can use them most effectively on a project, team, or in the organization.” Listen for intent and observe body language. Much of what you need to know is communicated in this way. Respect others by taking a breath. “When we’re great listeners, we give others the gift of silence. We’re not in a hurry, so silence—time to think—gives the speaker the opportunity to formulate and express her best thinking.” 2. Ask Powerful Questions When you ask questions, you become more engaging and it creates bonds with others. It means they will want to listen to you. The right questions are important. “The right question is often a crystallizer. It helps put a bow of clarity around one’s thoughts.” It can help them to articulate their own thoughts and expand their thinking. Clarity questions are “What concerns you most about this?” “If there is one thing you could do to begin to resolve this issue, what is it?” “What are your instincts telling you?” Timing matters when you are listening. Ask when you need clarity. Great questions open the door to additional thought. “Is this the solution?” opens the door to additional thought but closes the door on the conversation. A better question would be “If there is one thing that would make this solution better, what is it?” Halstead helpfully provides examples of powerful questions to achieve specific goals. The response, “I have not thought about that” is one of the best you can receive from your questions. You’re giving the other person the opportunity to think about new solutions in a positive way. You also show respect for the person being asked the question. 3. Develop Other’s Best Thinking Great listening and questions lead others from “I don’t get it” to “I got it.” You bring out the best in others. “By helping others grow, you give them the opportunity to take ownership of their actions and the results.” That’s leading. Be forward-thinking—solution-oriented. “When leaders focus on what can be done, people are inspired to achieve more, especially when they think of and articulate what it is that they are going to do.” One of the best ways to inspire your team to follow you because of you rather than in spite of you is to acknowledge the things they do well. More than a compliment, by acknowledging someone you are “calling attention to a specific behavior or talent, and it comes without any type of extra modifiers.” 4. Wise and Thoughtful Delegation Delegating demonstrates that you believe in others and they often respond by “expanding their ability to do more and perform at a higher level.” As a leader, the more you put everyone in the sweet spots of their talents, including you, the greater the likelihood of achieving short- and long-term exceptional performance. Delegating wisely both develops and uses those talents Thinking we are can do it better, impatience, a lack of trust, a lack of clarity about the job to be done, all inhibit our desire to delegate tasks. And that’s on us. 5. Create Consistent Accountability A culture of accountability means that people will do—actually accomplish—what they say they will do when they say they will get it done. Accountability builds trust. What often holds us back from creating a culture of accountability says Halstead, is that we what to be seen as nice. But when seen properly, accountability is nice. Accountability builds others up. Like delegating, we think we could do better and so we don’t hold people accountable. But when we do, we might learn from how they achieve the desired result. And frankly, we lack faith in others. We don’t really believe they have what it takes to get the job done properly. If this is the case, Halstead recommends that we walk them through the process so they can see what it will take to get the job done. Also, remind them of the talents they have that will be useful in accomplishing the task. These five skills, when practiced consistently will help to inspire incredible results. The thread running through them all is “as you respect others and put the interests of others in a paramount position, our personal success thrives, maybe in ways that you could not imagine.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:25 PM
11.26.18

Leading Matters: John L. Hennessy on the Leadership Journey
A Leading Matters is about the journey. The stories he tells here are revolve around the ten elements that shaped his journey and how he relied on these traits in pivotal moments. The elements are relevant to any leader at any level. As he observes, the higher up you go the crises just get bigger and come faster.
Here are some of his thoughts on each element extracted from his stories: Humility A true sense of one’s own skills and character—arises not from ego, but from humility. Arrogance sees only strengths, ignores our weaknesses, and overlooks the strengths of others, therefore leaving us vulnerable to catastrophic mistakes. Leading with humility means letting others announce your accomplishments because you don’t need to, it means realizing and openly admitting that your understanding might not be right, it means taking the opportunity to learn from mistakes, and it means stepping up to the moments that challenge and grow you. Authenticity and Trust Authenticity is essential to building trust. Consider the wisdom popularly attributed to Socrates: “The way to a good reputation is to endeavor to be what you desire to appear.” It’s a start down the path to a deeper practice of authenticity—you must identify those good and true characteristics you admire, and then you must work to embody them. So this is part of the practice: identify the virtue you admire, strive to embody them, and be humble about the journey—you probably aren’t there yet. In fact, just when you think you’ve arrived, life has a way of returning you back to the beginning. Leadership as Service The larger one’s leadership role becomes, the bigger the role of service in that leadership. If you take a leadership role as a step toward a personal goal of gathering ever-greater titles, awards, and salaries, you will never see true success in that role. Recognize the service of others. As a leader it is easy to get wrapped up in big projects and ambitious initiatives, and, in the process, to forget the smaller, but no less important, individual acts of service taking place all around you. Much of that service supports and enables the widely celebrated success of others. Empathy Empathy should always be a factor in making decisions and setting goals. Empathy represents a crucial check on action—placing a deep understanding of and concern for the human condition next to data can lead to decisions that support the wellbeing of all. Empathy usually implies compassion and perhaps charity, but we are looking for more than that: we are looking for the kind of empathy that changes people as a result of their interactions with each other, the kind of empathy that arises when one sees the world anew through someone else’s eyes. Courage Humility, authenticity, empathy, service-mindedness—these characteristics shape a leader’s vision and chart a course toward right action. Courage, on the other hand, compels a leader to take that right action. While many people can discern what is right and true, acting on that discernment is more difficult. Even if risk-taking is against your nature, for the good of your organization, you must find the courage to practice it. Collaboration and Teamwork Most significant endeavors will be accomplished by a team. Certain ground rules circumvented interteam rivalries. First of all, I reminded everyone of our shared goal: we wanted to achieve something great. Further, to support innovative, cross-disciplinary thinking, I set a second ground rule: at the start, we don’t criticize ideas. To this, I added a third ground rule: tough questions aren’t only allowed, they are necessary. This led to my final ground rule: team members must be treated with the utmost respect. Innovation I can’t tell you how many times I’ve had this conversation with students: the student opens with, “I want to create a start-up.” I ask them to tell me about their technology, and they answer, “Well, I don’t have it yet, but I want to do a start-up.” I remind these students that great start-ups begin with great technology discoveries. Innovation presents great opportunities for smart entrepreneurs, not the other way around. Intellectual Curiosity Beyond personal enjoyment, though, this lifelong curiosity has served me well in my career. It has enabled me to engage in meaningful dialog about the world and its future. Literature, biographies, and histories—they’re like laboratories in which we can examine and learn critical lessons without having to live the difficulties ourselves. In challenging moments, great leaders show their true character. …Their stories taught me if you can’t take the blame for failure, you shouldn't take the job. Storytelling If you really want to inspire a team to action, best to engage them with a story. Once they become receptive—once they can imagine themselves as part of your vision—you can back your story up with facts and figures. When you turn that dream into a vivid story, you make it so attractive and so real that people will want to share it with you by joining your team. When it came time to respond to change, these companies moved quickly and efficiently, because every employee already understood the company identity and therefore knew how to respond without direct coaching. In every profession and career, as we climb to higher leadership positions, the role of facts and data decreases. Legacy Instead of worrying about my legacy too much or too early, I’m choosing now—as I always have—to follow the path of making meaningful contributions. Legacy means the institution serves people more effectively now than it did when you arrived. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:08 PM
11.12.18

Six Essential Practices to Grow Your Leadership
T It is in this spirit that the authors state, “the best way for any aspiring leader to succeed and to navigate turbulent times is to tune out the noise and refocus on these fundamentals” of leadership. They define leadership as “Achieving significant positive impact—by building an organization of people working together toward a common goal.” The Harvard Business Review Leader’s Handbook is designed to help you grow your leadership. It is organized around six practices. While not meant to be all-encompassing, these are areas that “differentiate those who have the strongest impact.” Naturally, an understanding of human nature—the so-called soft skills—makes these six practices exploitable. The six practices are practical and provide a useful guide taking responsibility to lead and improve your effectiveness. Building a Unifying Vision Organizational success requires a bold and compelling vision that brings people together and inspires them to achieve extraordinary results. The vision needs to be exciting, clear, and simple—and stakeholders should be involved in its creation. Developing a Strategy Implementing a strong, measurable strategy is the key to realizing a vision. A great strategy is composed of key actionable choices about what to do, and what not to do to create distinctive value. Strategies are iteratively developed in the context of the company’s audience, challenges, and opportunities. Getting Great People on Board Smart and dedicated people help bring strategies to life. Executing strategies skillfully begins with recruiting, developing, and retaining high-performing talent. People need feedback to grow and incentives to feel recognized. Focusing on Results The experience of achieving short-term results motivates teams to strive for even more. Setting high expectations and sharpening accountability is necessary for high performance. Sold metrics and reviews can help this process become an organized one. Innovating for the Future Balancing current performance while investing for tomorrow is a key for enduring success. By keeping an eye on the demands of the future, leaders can continually drive innovations that will reshape the company to keep up with a changing world. Leading Yourself In order for leaders to lead others, they need to know and grow themselves. Feeling healthy, energized, and balanced also helps leaders do their best work. Leaders need to raise their own bar—in turn they’ll raise it for their organization. Grasp the Leadership Opportunity Already In Your Reach The authors make a good point. You shouldn't wait to be anointed a leader. Step up and take the responsibility now. Seizing the leadership opportunity and making the leadership difference in fact requires courage and also an ability to look beyond the every day and near-term tasks of basic management.… To be a leader, you need to anticipate like a great chess player who looks ten moves ahead and also quickly adjusts to the opponent’s play. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:02 PM
09.25.18

What Happens Now? A Look at 7 Reasons Leaders Stall
T As you take on more responsibility, the demands on you as a leader change. If disrupting yourself isn’t part of who you are, you will get left behind. If you are just doubling down on what you’ve always done, you will miss the opportunities. When conditions change, you have to change too. That’s why John Hillen and Mark Nevins wrote What Happens Now? to help you remain a leader. “If we are to generalize, we can say that you advance as a leader, the technical and tactical skill you need—distribution expertise, for example—pale in comparison to the strategic and interpersonal.” Complexity Skills and Sophistication Skills They divide leadership capabilities into two groups: complexity skills and sophistication skills. Complexity skills are often what got you in the door. Complexity skills are those abilities that help you to deal with complexity “in a traditional-management-centered way, such as knowing how to design and implement processes and systems, and having the required technical and functional knowledge.” Sophistication skills are behavior and mindset related. They are about changing how you do what you do. “How you pull back and understand the bigger realities of the job. How you approach doing the job having done so. How you think and behave so your people eagerly receive your leadership. Getting the how right is the challenge when it comes to sophistication.” Too often, we don’t look at ourselves when we run into problems. We look around and ask what’s wrong with them. Warren Bennis and James O’Toole wrote, “Most of us wear the concrete shoes of our earlier successes.” We tend to focus on and fall back on Complexity skills rather than grow and develop our Sophistication skills. Complex challenges are easier to wrap your mind around. You can measure them. Sophistication challenges are not as clear. They can be more painful as they get into more personal aspects of who you are as a person. But distinguishing between the two challenges is critical. Our leadership stalls when we try to use tools for solving complexity issues when we “need to develop the capabilities to lead in a more sophisticated way.” Complexity challenges, which often come with growth in scale, can make your job bigger in ways you can’t anticipate. Sophistication challenges, which usually come with change in kind, make the job broader in ways you don’t anticipate. If you’re like most leaders, you’ll display more comfort with complexity and decidedly less comfort with sophistication.  As you rise as a leader, sophistication skills take on greater importance. What are the new capabilities on which your leadership success will depend? More importantly, which skills that you value today should you deemphasize—or resist exercising at all? No matter how good your complexity skills are if you fail to access your sophistication skills by regularly challenging yourself as to what and how you do what you do, you risk stalling as a leader. The authors identify seven inflection points that can trigger a stall in your leadership. Purpose Stall
Teamwork Stall
Stakeholder Stall
Leading Change Stall
Authority Stall
Focus Stall
Leadership Development Stall
What Happens Now? is a great look at some of the most critical issues in leadership. The authors walk you through each of these stalls to help you overcome or avoid them. Of course, self-awareness is key here—understanding the impact you have on others. Elevate your view and understand where you are and determine where you need to be. They call for a three-part approach: become more aware of what’s changing in your environment, know where you are, and then act deliberately to develop capabilities that will change your behaviors and thinking. Every stall is an opportunity for growth. When you deal with each stall head-on, “you position yourself to evade the pain and consequences of being caught in future stalls. When you ask yourself, ‘What happens now?’ you’ll be ready to answer: ‘I will look inside, see myself as others see me and as they want and need me to be, and act to remake myself.’ You won’t blame your troubles on your organization or people, or ask, ‘How do I change the institution to overcome these challenges?’ You’ll see yourself as part of the slowdown. And then you’ll be ready to become you own ‘Best Leader Ever.’” This is not a process of abandoning the complexity skills that got you where you are, but instead adding to and developing “your leadership repertoire with a new set of executive capabilities, mindsets, and behaviors” to help you to overcome the new challenges of sophistication that will come your way. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:00 AM
09.07.18

Didn't See It Coming
T Carey Nieuwhof is the author of Didn’t See It Coming. He wrote this book because too often we don’t. And even though these seven challenges never really go away, we can create some life habits that keep them at bay. Nieuwhof writes from a been-there-done-that Christian perspective about the issues as they manifest themselves in our lives and follows up each one with a chapter on how to combat it. It’s not really just for leaders. These issues affect everyone and some you'll find hit close to home. The seven challenges are: Cynicism
Compromise
Disconnection
For me, the sense that a conversation is going nowhere always carries with it an underpinning of judgment and even arrogance on my part. I just assume I’m better, smarter, or wiser or that I have greater emotional intelligence than others. Which, of course, should drive me right back to my knees in confession. After all, we’re encouraged to think of others as better than ourselves. That’s a cornerstone habit of the humble. Irrelevance
Pride
Burnout
Emptiness
Didn’t See It Coming is full of understanding and insight. The practical advice found here will benefit anyone on their leadership journey.   
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:01 AM
04.03.18

Servant Leadership in Action
T Ken Blanchard begins by telling us that some people think you can’t lead and serve at the same time. But that is because they don’t understand that there are two parts to servant leadership: a visionary/direction, or strategic role—the leadership aspect of servant leadership and an implementation, or operational role—the servant aspect of servant leadership. “The leadership aspect of servant leadership is the responsibility of the traditional hierarchy. The servant aspect of servant leadership is all about turning the hierarchy upside down and helping everyone throughout the organization develop great relationships, get great results, and, eventually, delight their customers.” Raj Sisodia is a leader in the Conscious Capitalism movement and relates servant leadership to the acronym, SELFLESS: Strength, Enthusiasm, Love, Flexibility, Long-Term Orientation, Emotional Intelligence, Systems intelligence, and Spiritual Intelligence. He explains, “The servant leader is a whole person, not a fragmented being. SELFLESS reflects a harmonious blend of mature masculine and mature feminine qualities.” Steven R. Covey says that trust is essential. “Both servant leadership and trust-based leadership stand in opposition to traditional positional leadership, which is steeped in the language of control: ‘You have to do what I say because I’m the boss.’ On the other hand, servant leaders and trust-based leaders alike draw from a deeper well of meaning. They serve first and they extend trust first. Leadership is the by-product and positional authority is, at best, an afterthought.” Mark Floyd admits, “Servant leaders are not always perfect, but they stay true to their leadership style. They stay humble by turning the organizational chart upside down and serving others. They communicate to their teams the goals and values that form their culture so that everyone stays in focus. They are aware of their own strengths and weaknesses—through feedback and by following the greatest servant leader of all time [—Jesus]. And they continually strive to do the right thing.” Simon Sinek adds, “The daily practice of servant leadership is less grand than people tend to think. It is not based on a series of transactions, but on the promise of being there when someone needs you most. … A leader who offers money or the potential for future riches is not earning loyalty. They are setting up a transactional relationship that is likely to promote self-interest. … A few scattered, well-intentioned actions by a leader can’t hurt, but they won’t breed loyalty. They won’t be enough to earn trust. Just like any relationship in which trust is the basis, it is the combination of a lot of little things that makes all the difference.” To avoid the triggers that would pull you off course, Marshall Goldsmith recommends that the next time you run into a conflict, ask yourself this question: “Am I willing, at this time, to make the investment required to make a positive difference on this topic?” Erwin McManus illustrates that servant leadership is not a technique but a way of being. After his wife watched him perform a reluctant act of service for a homeless man in a downpour, she said, “That was the greatest sermon you have ever preached.” Those words changed his life. He writes, “Frankly, I had always hoped my greatest message would be to an audience of thousands, not to an audience of one. Now I know better. Our message is always given to an audience of one—the person we are serving. In serving others, our message is our lives. We must live our message for our message to have life. To me, that’s what servant leadership is all about.” To McManus' point, Jon Gordon adds in his essay, “My company’s mission is to inspire and empower as many people as possible, one person at a time. One person at a time means we will never be too busy to help one person in need.” In other essays by Brené Brown, Cheryl Bachelder, Henry Cloud, Jon Gordon, James Kouzes, Patrick Lencioni, Dave Ramsey, Art Barter, Larry Spears, and many others, you will find many more helpful ideas and thoughts that will help you shape and refine your leadership approach.   
Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:08 PM
03.21.18

The 3 Mental Qualities of Great Leaders
L In The Mind of the Leader, authors Rasmus Hougaard and Jaqueline Carter of the Potential Project, report that there are three mental qualities that stand out as being foundational for leaders today: Mindfulness, Selflessness, and Compassion. They call it MSC Leadership. All three work together and enrich the others. 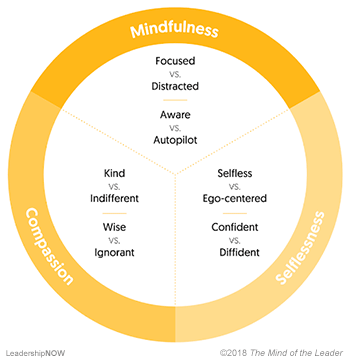 Mindfulness Mindfulness is about managing your attention and in turn managing your thoughts. Mindfulness enables us to respond to our circumstances instead of reacting. The two key qualities of mindfulness are focus and awareness. These two qualities “help us to be mentally agile and effective.” “As your mindfulness increases, your perception of ‘self’ starts to change. More specifically, a stronger sense of selfless confidence arises, helping you develop the second quality of MSC Leadership: selflessness. Selflessness They describe selflessness as “the wisdom of getting out of your own way, the way of your people, and the way of your organization to unleash the natural flow of energy that people bring to work. Selflessness combines strong self-confidence with a humble intention to be of service.” It is interesting the way they put that. Selflessness is often thought of as weak by the uninitiated. It is important that selflessness is combined with self-confidence. You become an enabler. “You are not worried about being taken advantage of, because you have the confidence to speak up for yourself if needed. At the same time, you’re not driven by your own interests. You have a strong focus on the well-being of your people and your organization.” This is a tough one for many leaders. According to a study completed at the University of California, Berkley, “when many leaders start to feel powerful, their more benevolent qualities start to decline. Leaders are three times more likely than lower-level employees to interrupt coworkers, multitask during meetings, raise their voices, and say insulting things.” Also, they are more likely to be rude, selfish, and unethical. We have seen many leaders that think they are above the mores of everyone else. It’s not easy to keep yourself in perspective. Mindfulness plays a big part in that. As we become more selfless, “we naturally begin attending more to other people: we show more interest in them and offer more care. In this way, compassion arises as a natural outgrowth of selflessness.” Compassion Compassion is benevolent leadership. “It’s the ability to understand others’ perspectives and use that as a catalyst for supportive action.” Compasion combines with wisdom. Wisdom gives compassion a compass so that choices can be made that are thoughtful and holistic. A compassionate organizational culture “supports positive intentions toward others, and at the same time instills the wisdom and professionalism in everyone to make tough choices. This includes sometimes doing things that are difficult bit will benefit the culture and the organization in the long term.” MSC Leadership begins with you—inwardly—and then flows outward to your people and then your organizational culture as a whole. “It requires that we take an unflinching look at ourselves, at how we interact with our people, and at how our organizations operate.” The Mind of the Leader looks at this whole process and provides practical methods to apply each of these three qualities of mind to your leadership. This book provides a well-articulated and comprehensive look at these essential qualities of leadership. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:10 PM
02.19.18

The Little Kindnesses Matter
P He was considering the appointment of a minister to a foreign country. There were two candidates. The President outlined their qualifications, which seemed almost identical. Both were able, experienced, honest, and competent. Each was equally entitled to preference from a political standpoint. Then he told this little story, an incident apparently so unimportant that, except for its consequences, it never would have been told, an incident so trivial that the ordinary man would have forgotten it. But McKinley was not an ordinary man.Dawes relates this lesson: We never know what determines one's career in life. Indeed, it may be these little-forgotten deeds, accumulated, are the more important factors; for it is they which must, in many cases, provide us with the opportunity to do the greater deeds, and we unconscious of it. Why comes this reward in life? Why that disappointment or failure? We cannot know with certainty. This we can know, however, and this story illustrates it: There is no act of kindliness, however small, which may not help us in life; and there is no act of unkindness, however trivial, which may not hurt us. More than that: The habitual doing of kindness always adds to our happiness, for kindness done is duty performed. Unkindness always breeds an unhappy spirit, for unkindness is duty neglected.Malcolm Forbes once said, “You can easily judge the character of a man by how he treats those who can do nothing for him.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:01 PM
02.15.18

3 Strategies to Prepare Your Millennials for Their Leadership Roles
M Consider these three action steps as you prioritize Millennial leadership development. 1. Boost Accountability by Strengthening Character A lack of determination and resilience, low accountability and, a know-it-all attitude were some of the character concerns raised by 270 business owners and CEO’s who participated in our Millennial Survey. Our sales force development work also indicates that 60% of sales professionals often play the blame-game. They adamantly inform management that the reason they aren’t hitting their numbers is due to the economy, the competition, the weaknesses of their company, or a combination of all of these. This externalized perspective is futile. It robs the complainer of their growth potential. How can we be proactive in developing strong character in our up-and-coming leaders? Take action:
2. Build Confidence by Leveraging Strengths Some Millennials believe they possess an unlimited well of knowledge just because they are able to find the answer to just about any question on Google or YouTube. This phenomenon is validated by research. Yale doctoral candidate, Matt Fisher, and his colleagues Mariel Goddu and Frank Keil, conducted fascinating research on this topic. They asked people a series of questions that appeared to be general knowledge but were actually difficult to answer. Some of the participants had access to the internet and others not. They published their findings in an article, “The Internet Makes You Think You’re Smarter Than You Are.” [Interview] They came to the conclusion that head knowledge lacks the deep roots of real-life experience that provides the confidence to stand in any storm and press through any obstacle. Take action:
3. Maximize Collaboration by Aligning Core Purpose I was inspired when I first learned about the process, Life’s Core Purpose, developed by Jeff Pelletier. It is a powerful mentoring tool to help your Millennial leader get a deeper understanding of where they can create win-win synergy. Their best synergy is when their vision and values align with the company’s vision and values. Life’s Core Purpose process invites leaders to serve at the intersection of their core competence and core passion by asking: “Is there something I am personally great at all the time at a core level? And, is there something I care deeply about all the time at a core level?” The goal is to apply what we do well to what we care about deeply so that performance can accelerate! Take action:
Will you be left high and dry when your Baby Boomers retire? If you are concerned about filling the voids left by your experienced Baby Boomers, it’s not too late. Step up and take action to implement real-world, rubber-meets-the-road leadership development strategies. Prioritize time to transfer skills, knowledge, and experience to boost accountability, build confidence, and maximize collaboration in your up-and-coming leader so that your business will thrive even after your last Baby Boomer has retired.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:18 PM
01.10.18

How to Avoid the 5 Career Derailers
W In The Right—and Wrong—Stuff, Carter Cast shares with us the turning point in his career at PepsiCo. Blissfully unaware of how negative perceptions were shaped, he was stunned when called into his boss’s office, and told he was “unpromotable” because he was obstinate,” “resistant,” and “insubordinate.” More often than not, people get fired, demoted, or plateau not because they lack the “right stuff,” but because they let the “wrong stuff” act out. Cast’s research led him to five defining archetypes. These archetypes are present across all organizations, genders, and levels of seniority. Captain Fantastic
As you progress [in your career], your relationship with others is more important than your knowledge of and relationship with data. This need kicks in as you move into middle and upper management. It’s a mindset change. You have to suppress your ego, let go of having the answer and embrace the relational world. It becomes less about having competencies and more about engendering trust. The Solo Flier
For many talented people “skilled in and rewarded for ‘doing,’ the shift to manager and leader is a hard one. We’re required to operate differently, getting work done through others, moving from athlete to coach. We need to move from ‘me’ to ‘we.’” Version 1.0
Version 1.0’s resist learning new experiences. They lack curiosity preferring the status quo. Agility in your personal learning is the “subtle skill of picking up on cues and changing one’s behavior quickly.” Cast recommends that Version 1.0’s become more approachable. “Some people’s fear of change can be masked as assured arrogance or by being a contrarian. They protect themselves by being rigid and aloof and acting with complete assurance. Then, when challenged with a contrary point of view, they become combative and aggressive, like Captain Fantastic.” The One-Trick Pony
This archetype is not strategic. That is, they lack a holistic understanding of the organization. “People with a strong strategic orientation approach problems from an ‘outside-in’ perspective.” The Whirling Dervish
Whirling Dirvish’s need to be in tune with the steps in “the work flow process—their proper sequence, how long each will take to complete, and whom to include along the way.” This includes being able to plan and prioritize tasks before a project is started. Say no when you have to and delegate task to keep things moving. Having the Right Stuff To avoid derailing, you must learn to lead yourself first. We all come close to derailing from time to time, but having the right stuff means that you have the “ability to bounce back, to learn from your mistakes, make adjustments, take corrective actions, and get back on track.” Cast finds that people with the right stuff act on their own initiative, they have emotional intelligence, and have tremendous perseverance and drive for results. And of the three, taking the initiative is the most important. “High performers with the right stuff accelerate their personal and professional development be having a ‘learning orientation’—a curiosity to constantly learn and improve. Avoiding derailing requires that you continuously reflect on your performance. Know where you want to go and understand where you are. Then take steps to bridge the gaps. Cast provides abundant examples of the archetypes and corrective measures for each. We are all a work-in-progress. Carter Cast provides an assessment on his website to find out where your career is vulnerable. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:17 PM
11.03.17

Leadership Forged In Crisis
L It is a misconception of leadership that if you engage in the best practices of a great leader, you will become that leader. Applying the idea that if I do this or if I have this quality I will become a great leader like my chosen mentor, can derail your leadership development. That said, there are principles you can discover that if adhered to will propel you in the right direction. Harvard professor Nancy Koehn illuminates some of these principles for us in Forged in Crisis as seen through the lives of five exemplary leaders: polar explorer Ernest Shackleton, President Abraham Lincoln, legendary abolitionist Frederick Douglass, Nazi-resisting clergyman Dietrich Bonhoeffer, and environmental crusader Rachel Carson. These principles set the stage for leadership effectiveness, but the decision to step into leadership is yours alone. Koehn borrows from David Foster Wallace and defines an effective leader as one “who can help us overcome the limitations of our own individual laziness and selfishness and weakness and fear and get us to do better, harder things than we can get ourselves to do on our own.” Coach Tom Landry said it this way: “Leadership is getting someone to do what they don't want to do, to achieve what they want to achieve.” Henry Kissinger said, “The task of the leader is to get his people from where they are to where they have not been." It is intentional influence. But the ability to do that doesn’t come to us naturally. We have to work at it. But that’s good news. We can all get there. Leaders are not born, they are forged. Each of the leaders Koehn has chosen faced an uncertain outcome in the midst of a crisis. Shackleton was marooned on an Antarctic ice floe trying to bring his men home alive; Lincoln was on the verge of seeing the Union collapse even as he tried to save it; escaped slave Douglass faced possible capture while wanting to free black Americans held in slavery; Bonhoeffer was agonizing over how to counter absolute evil with faith while imprisoned by the Gestapo; Carson raced against the cancer ravaging her to finish her book Silent Spring, in a bid to save the planet. The crisis that can break one person can give birth to leadership in another. It’s a conscious choice to lead. Koehn brings out key lessons common to these people as they struggled with their thoughts in what were do or die situations. Here are some of the lessons that we should all take to heart: They Were Made, Not Born These leaders “were made into effective leaders as they walked their respective paths, tried to understand what was happening around them, and encountered failure and disappointment.” They Were Ambitious but… “The drive to make their respective marks was important in shaping them. It took each of them some of the way. But then, interestingly, ambition ceased to motivate and influence them as it once had. As they discovered a larger purpose and embraced it, each found his or her impetus, strength, and validation in the mission itself.” And importantly, Koehn adds, that “their leadership was partly shaped by a willingness to subordinate personal drive in a broader end, one inexorably linked with service to others.” They Did the Inner Work of Leadership They all worked on themselves, looking for opportunities to grow. “They did not do this as a single endeavor, but rather as a lifelong project in which they each kept working on themselves, learning specific lessons, developing more resilience, and using these resources to lead more effectively.” (“Lincoln would have been flummoxed by talk of authentic leadership when he told a few constituents in 1862 that he did not have the luxury of publically expressing his disappointment about Union army defeats.”) They Understood the Importance of Solitude These leaders learned to detach themselves from the situation in order to see things from different perspectives. They “learned how to step back from a specific instant, assess the larger landscape, take the measure of their own emotions, and only then make a decision about what, if anything, they wanted to do.” Reflection and solitude helped them stay focused on the big picture. They Learned to Manage Their Emotions In dark moments, what Bonhoeffer called a “boundary situation,” they determined to manage their emotions. It was not willful blindness or forced optimism. They knew what they were up against. “Because they did, they used their emotional awareness and discipline to concentrate directly, almost exclusively, on how to move forward, how to take the next step, however small.” These people realized that “the emotional penetrability they experienced and that caused them so much suffering was also a door into new insights about themselves and new ways of being in the world.” They Learned to Respond Rather Than to React “At times, doing nothing at all was the best action each of these leaders could take. Time and time again as president, [Lincoln] refused to be goaded by the force of his own emotions or of those around him into taking precipitate action that might compromise his larger mission. Even when he was at his most frustrated, he managed somehow to acknowledge his feelings without acting on them in a way that was destructive to larger matters.” They Were Resilient Though these leaders didn’t always see a way through in the heat of the moment, “they vowed to find a way through the obstacles they confronted. They came out the other side of calamity without falling through the floorboards of doubt, without giving up on their mission and themselves.” All five leaders were well chosen because of their humanity. They were not born leaders. They became leaders through successes, but mostly through failures and mistakes. Leaders can come from anywhere. As we look around the world today, if we are looking for larger-than-life heroes, we misunderstand what leadership is. Although these leaders appear to be larger than life to us now, as you read their stories you see that they are you and me. They are ordinary people in turbulent and trying circumstances. They were often overwhelmed and depressed, but they kept moving on. What distinguishes these people from many of the leaders we see today is their approach to the experiences of their lives. Throughout their lives, they purposefully extracted the lessons they needed to grow. It was thoughtful and intentional. If you go through life any other way, you are just collecting experiences to no end. Experiences alone ensure nothing. We must reflect on them to gain insights and learn from them. All of the lessons these leaders learned are relevant to any leader in any situation. There are no hacks to effective leadership, and you won’t find them here. You will find well-told accounts of these leader’s lives that will inspire and inform your own leadership. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:06 AM
07.14.17

5 Leadership Lessons I Learned by Walking the Camino de Santiago
T 1. Welcome Help When you walk for a month, you inevitably get lost. In one little village, three older gentlemen sitting in a shady spot outside the little café jumped and pointed me in the right direction when I took a wrong turn. I realized that they were sitting there specifically to help direct lost hikers. It was their pastime. That experience taught me that welcoming help from others was not just about the specific piece of help I received when I asked. It also made the person helping me feel good and be invested in my success. Ever since the Camino, I have vowed to be more welcoming of help from others, at work and beyond. 2. Learn from the Past When I decided to walk the Camino, I eagerly jumped into the planning. I plotted out a 29 day itinerary that optimized my distances per day and found a bed I could reserve each night. That exercise took days, tapped my analytical skills, and resulted in a large spreadsheet that I was proud to show off. That is until I realized that I had recreated the same itinerary that several guidebooks had already figured out. People have been walking the Camino for over 1000 years. Instead of taking a step back to see what I could have learned from others who went before me, I plunged right into the task. Since the Camino, I am more thoughtful when I start a new project to look for lessons from the past. 3. Think About the Future Any trail that has remained popular for over 1000 years can teach us how to build longevity in our organization. One thing behind the Camino’s longevity is the ethos of the hikers who walk it to leave it better than they found it. Hikers generally don’t litter on the trail and pitch in where they can to keep the churches, hostels and facilities along the trail in good shape for hikers to follow. That same ethos is important for leaders. Leaders need to think about their successors as they make decisions in their jobs. Their goal should be to leave their role and team in a better position than they inherited it. 4. Don’t Judge Others People from many different backgrounds from all over the world hike the Camino. Everyone dresses in much the same way while walking, giving few clues from their outward appearance about their background. Hikers learn to reserve judgment about others. Instead of silently critiquing others, hikers support each other as they go through the same difficult challenge of walking across a country. They may not know how or why another person got on the trail, but they know the shared challenges they are facing and simply focus on those. 5. Stretch Yourself Walking across a country sounded like a crazy thing to do before I did it. By doing it, I gained self-confidence to do other bold things. Walking the Camino emboldened me to check off a goal that I had long thought was beyond my abilities – writing a book. While I was walking the Camino, I thought a lot about my career and the leadership lessons I had learned. I decided to write a book about those insights. That book, Lead Inside the Box: How Smart Leaders Guide their Teams to Exceptional Results (Career Press), was named a Top 20 Leadership Book of 2016. This week, my third book, The Camino Way: Lessons in Leadership from a Walk Across Spain (AMACOM) comes out. I recommend hiking the Camino to anyone who can. The combination of the physical challenge, the alone time for introspection, and the opportunity to meet people from around the world is a wonderful means of self-improvement. If you can’t walk the Camino, search for other experiences that provide those three elements.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:53 AM
06.20.17

Humility is the New Smart: Are You Ready?
S Are you ready? The Smart Machine Age (SMA) will revolutionize how most of us live and work. In Humility is the New Smart, the authors state that “smart technologies will become ubiquitous, invading and changing many aspects of our professional and personal lives and in many ways challenging our fundamental beliefs about success, opportunity, and the American Dream.” This means that the “number and types of available jobs and required skills will turn our lives and our children’s lives upside down.” New skills will be needed. Uniquely human skills. Those skills, while uniquely human, are not what we are typically trained to do and require a deal of messy personal development. We will need to become better thinkers, listeners, relators, and collaborators while working to overcome our culture of obsessive individualism in order to thrive in the SMA. Humility is the mindset that will make all of this possible. Most of today’s adults have had no formal training in how to think, how to listen, how to learn and experiment through inquiry, how to emotionally engage, how to manage emotions, how to collaborate, or how to embrace mistakes as learning opportunities. In short, say the authors, we need to acquire and continually develop four fundamental NewSmart behaviors: Quieting Ego Quieting Ego has always been the challenge for us humans. As they observe, “Even if we don’t consider ourselves part of the ‘big me’ cultural phenomenon, for many of us to feel good about ourselves we have to constantly be ‘right,’ self-enhance, self-promote, and conceal our weaknesses, all of which drive ego defensiveness and failure intolerance that impedes higher-level thinking and relating.” This tendency negatively affects our behavior, thinking, and ability to relate to and engage with others. Managing Self—Thinking and Emotions We need to get above ourselves to see ourselves impartially. We all struggle “to self-regulate our basic humanity—our biases, fears, insecurities, and natural fight-flee-or-freeze response to stress and anxiety.” We need to be willing to treat all of our “beliefs (not values) as hypotheses subject to stress tests and modification by better data.” Negative emotions cause narrow-mindedness. Positive emotions, on the other hand, have been scientifically linked to “broader attention, open-mindedness, deeper focus, and more flexible thinking, all of which underlie creativity and innovative thinking.” Reflective Listening Because we are limited by our own thinking, we need to listen to others to “open our minds and, push past our biases and mental models, and mitigate self-absorption in order to collaborate and build better relationships.” The problem is “we’re just too wired to confirm what we already believe, and we feel too comfortable having a cohesive simple story of how our world works.” Listening to others helps to quiet our ego. Otherness To create these new behaviors and mindsets, it should become obvious that we need to enlist the help of others. “We can’t think, innovate, or relate at our best alone.” As Barbara Fredrickson observed, “nobody reaches his or her full potential in isolation.” Jane Dutton out it this way: “It seems to be another fact that no man can come to know himself except as the outcome of disclosing himself to another.” The NewSmart Organization Optimal human performance in the SMA will require an emphasis on the emotional aspects of critical thinking, creativity, innovation and engaging with others. “The work environment must be designed to reduce fears, insecurities, and other negative emotions.” To do this it means “providing people a feeling of being respected, held in positive regard, and listened to. It means creating opportunities for people to connect and build trust. “It means allocating time and designing work environments that bring people together to relate about nonwork matters.” Finally, it means getting to know employees and helping them to get the “right training or opportunities to develop and provide feedback.” The NewSmart organization needs to be a safe place to learn. “Feeling safe means that you feel that your boss your employer, and your colleagues will do you no harm as you try to learn.”  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:28 PM
06.09.17

9 Things Positive Leaders Do
J Positive leadership is grounded in reality. We must confront the negativity we come across, but we shouldn’t dwell on it. We deal with it and move on. It is because we will have to overcome negativity, adversity, and problems that we should be positive. “Positive leadership is not about fake positivity. It is the real stuff that makes great leaders great.” Positive leaders focus on solutions. Gordon cites psychologist Barbara Fredrickson’s research that finds that “people who experience more positive emotions than negative ones are more likely to see the bigger picture, build relationships, and thrive in their work and career, whereas people who experience mostly negative emotions are more likely to have a narrower perspective and tend to focus more on problems.” Positivity doesn’t guarantee you will succeed, but it makes it much more likely. A positive mindset reveals possibilities and gives you the courage to take the actions required to move past negative situations. Gordon explains nine things positive leaders do. Nine actions that will enhance your leadership capabilities and positively impact all of your relationship—your family, your friends and your team. 1. Positive Leaders Drive Positive Cultures Culture is everything. A positive leader lives the culture because it is an extension of who they are. “They understand that every day there are forces seeking to sabotage their culture and success, and so they work relentlessly to keep it strong.” “When you create a culture worth fighting for and invest in your people to the degree that they want to fight for your culture and for each other, your organization will have grit and strength to overcome the challenges you face and become an unstoppable and positive force.” 2. Positive Leaders Create and Share a Positive Vision Former President and Chief Executive Officer of the Ford Motor Company Alan Mulally, said, “Positive leadership—conveying the idea that there is always a way forward—is so important because that is what you are here for—to figure out how to move the organization forward.” Positive leaders see and create a brighter and better future. They see “what’s possible and then take the next steps to rally and unite people to create it. Every invention, project, creation, and transformation starts with an idea, an imagination, and a vision of what’s possible.” A positive leader needs a telescope and a microscope. The telescope helps to keep your eyes on the big picture. The microscope helps the leader to focus in on what needs to be accomplished in the short term to realize the vision in the telescope. “If you only have a telescope, then you’ll be thinking about your vision all the time and dreaming about the future but not taking the necessary steps to realize it. If you only have a microscope, then you’ll be working hard every day but set-backs and challenges will likely frustrate and discourage you because you’ll lose sight of the big picture.” 3. Positive Leaders Lead with Optimism, Positivity, and Belief “Ultimately, being a positive leader is all about leading with faith in a world filled with cynicism, negativity, and fear.” We all face this battle between faith and fear. A leader’s job is to fill your people with faith. How we respond to our world depends on the stories we tell ourselves. When you face adversity you can tell a positive story and then work to create a positive outcome. It’s always your state of mind and your thinking that produces how you feel and respond. When you see that the world has no power over you, you will lead more powerfully in the world.” 4. Positive Leaders Confront, Transform, and Remove Negativity “Positive leadership is not just about feeding the positive, but also about weeding out the negative.” You must address negativity. Develop a culture where negativity is not acceptable. People will either change or leave. A positive leader is more positive than the negativity they face. Every negative situation is an opportunity the strengthen your positivity. Don’t allow complaining unless one or two possible solutions are brought forward also. “Complaining causes you and your team to focus on everything but being your best.” 5. Positive Leaders Create United and Connected Teams “Positive leaders unite instead of divide. They are able to create unity, which is the difference between a great team and an average team.” It starts at the top. “As a positive leader, you must be a unifier and connector who fosters relationships between others.” “You can be the smartest person in the room but if you fail to connect with others you will fail as a leader.” Also, “You may not have the most talented people on your team, but if you are a connected team, you will outperform many talented teams who lack a close bond.” 6. Positive Leaders Build Great Relationships and Teams People first follow who you are. “Leadership begins with love.” Love your people. Build relationships first. Too many leaders share rules before they have first built a relationship. I’ve had many leaders tell me,” writes Gordon, “that when they focus less on rules and invest more in their relationships they experience a dramatic increase in performance, morale, and engagement.” Positive leaders are also positive communicators. They smile. They spread positive gossip. They listen and welcome ideas. They rely on positive non-verbal communication. They encourage. 7. Positive Leaders Pursue Excellence Not satisfied with the status quo, positive leaders pursue excellence. “How can I get better to make the world better?” Positive leaders are humble and never stop learning. Pablo Casals, one of the greatest cellists of all time, was asked why he continued to practice the cello at the age of 95. He said, “Because I think I’m making progress.” Positive leaders ask daily: “What do I need to know that I don’t know?” and “What do I need to unlearn to learn?” 8. Positive Leaders Lead with Purpose Purpose fuels positivity. “Hard work doesn’t make us tired. A lack of purpose is what makes us tired. We don’t get burned out because of what we do. We get burned out because we forget why we do it.” Have purpose-driven goals. “The truth is that numbers and goals don’t drive people. People with a purpose drive the numbers and achieve goals.” 9. Positive Leaders Have Grit “When we look at successful companies and organizations, we see their current success and prominence but what we don’t see is the leadership and grit that powered them through all the failure and moments of doubt, heartache, fear, and pain.” Positive leaders embrace failure and trust the process. “Leadership is knowing the critics will criticize you while still saying what needs to be said and doing what needs to be done.” Positive leadership is a choice. Through great stories, Gordon encourages you to make a positive difference as a leader. 

Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:58 AM
06.05.17

How to Avoid Your Leadership Gap
T In The Leadership Gap, Lolly Daskal addresses this gap—what it is, why it happens, and what we can do about it. The gap is always there but at some point, it comes the surface to sabotage us. What if we don’t know what we think we know? The problem is that one day, suddenly, what once worked so well to propel their rise stops working. And the very same traits that had worked for them actually start working against them. It is at this point that we need to begin asking ourselves some questions. “What is the gap between who I am and who I want to be, and do I know what it is I still need to learn?” In short, “Who am I being?” We need to rethink how our behaviors are perceived by those around us. And when there is that gap between how we want to be perceived and how we are actually being perceived, we need to take action. “Learning to recognize your leadership gap is the factor that determines your greatness as a leader.” Sometimes we overuse a strength and sometimes we drift into the shadow side of our strengths. Either way, an understanding of what drives can give us the insight we need to avoid our leadership gaps. Daskal invites us to look at who we are being and the instincts that drive our behaviors. The “shadow” you. She has developed seven leadership archetypes to help us gain some clarity as to what drives our beliefs and therefore our behaviors. We aren’t necessarily one type as we tend to shift from one to another depending on the circumstances but “we tend to lean repeatedly toward the same archetype persona.” The Seven Archetypes
Daskal reminds us that understanding our weaknesses is our greatest strength. From these seven archetypes, we can see how each has powerful abilities and hidden impediments. By knowing the gaps we can get into we can better use our strengths to achieve our own leadership greatness. Daskal explains each of these archetypes in detail and importantly how we avoid these gaps. She describes what the positive looks like and what the negative looks like with examples for each. The Leadership Gap provides the antidote for leading on autopilot. Daskal provides insight into our behaviors and beliefs that can if not managed properly can derail even the most talented and successful leaders. Confronting and avoiding our leadership gaps is the key to attaining long-term leadership success. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:03 PM
05.19.17

9 Key Principles for Business & Life from Sam Zell
B He doesn’t claim to be self-made. He credits his parents with handing down to him values that have served him well in life. He is the son of Jewish immigrants who fled Poland in 1939 to avoid the Holocaust. “My parents were very disciplined and very focused on work and achievement, and they led by example.” His parents “never dumbed down the conversation for the kids.” Lessons were taught through examples and stories. His parents provided Zell with a different perspective than his friends. They were given a bigger-picture orientation. As a result, he was “more comfortable standing apart” than he was trying to fit in. It was to be a defining characteristic of his life. “Conventional wisdom,” Zell writes, “is nothing more to me but a reference point.” But he notes, you can’t create your own playbook “unless you understand the rules of the game and play well within the lines. As long as you know where everyone else is, you can play the game.” Below are nine of Zell’s key philosophies for how he approaches business and life: 1. Be Ready to Pivot
2. Keep it Simple
3. Keep Your Eyes (and Mind) Wide Open
4. Be the Lead Dog
5. Do the Right Thing
6. Shem Tov – A Good Reputation
7. Prize Loyalty
8. Obey the Eleventh Commandment
9. Go All In
Zell advocates an owner/entrepreneurial mindset in business and life. “An owner is consumed with making the most out of what he already has. He’s all in. An entrepreneur is always looking for a new opportunity. He’s always reaching.” As he tells his grandkids, “Your responsibility is to maximize the skills you were given. But whatever you decide to do, invest everything you have in it—excel. What I’ve done is not the example I wanted to set; it’s the way I’ve done it that I hope you emulate, through focus, effort, and commitment.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:29 PM
05.11.17

Be a Spark!
T Sparks initiate action and create the conditions for success for themselves and others. Knowing the pathway to leadership development is a personal development job. In SPARK: How to Lead Yourself and Others to Greater Success, they offer seven essential behaviors that every leader needs to develop. None of us are born leaders. These behaviors are not innate and take time to develop. Character: By gaining awareness of what you truly value, you can think and act in ways that allow you to direct your life and have influence over others. Leading with your own values is the gateway to leading others. Credibility: Credibility is the foundation of your leadership style. It forms the basis of trust. If people can’t trust you, you can’t lead them. Accountability: Sparks resist the powerful, human instinct to place blame. They seek to identify how their own actions, or inactions, have contributed to the situations in which they find themselves in. Act with Intent: By having a clear vision and making choices consistent with it, take actions that lead themselves — and others — towards it. Sparks differentiate themselves by having the discipline and the fortitude to execute, even when they aren’t sure what to do next. Be of Service: Sparks are always aware of others’ needs and take action to meet them. This outward focus strengthens relationships and creates camaraderie and connection. When people feel cared for because you’re serving them, they begin to feel safe and experience your commitment to them. They focus less on themselves and more on the team. Confidence: Your confidence level will determine the level of results you experience. Sparks don’t leave their confidence to chance. They consciously manage their internal thought process to achieve a level of steadiness as their sense of confidence rises. We can control our confidence. Consistency: Sparks set a high standard for consistency in their everyday work. To achieve it, they first need to understand the value of readiness, know what perseverance really means, and have the courage to “own” their time. Consistency is about being a “sometimes person” or an “always person.” A chapter is devoted to each of these seven behaviors and conclude with practical suggestions on how to develop these qualities not only within yourself, but how to inspires others to begin their own Spark journey. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:26 PM
03.20.17

Leaders Made Here
T This occurs for a number of reasons: They don’t see the immediate need, they don’t understand how or are too busy to do it, they don’t walk the talk, and their own insecurities. Leadership cultures are built from the top down. Miller describes a leadership culture is one where “leaders are routinely and systematically developed, and you have a surplus of leaders ready for the next opportunity or challenge.” Leaders Made Here is the story of a typical organization that found themselves short when they needed more leaders to fill some gaps and what they did to create a leadership culture. Frankly, a leadership culture does more than to have leaders in waiting. It provides for the growth and development of all people throughout the organization. It makes whatever you’re doing work better. To create a leadership culture, Miller boils it down to five ongoing commitments: 1. Define it.
There’s certainly real power in a common definition of leadership; there’s even more power in a common leadership skill set. 2. Teach it.
3. Practice it.
We discovered that for most people—leaders included—the natural tendency is to avoid risk. So, when a new project would come along, the leader responsible would assign a seasoned leader regardless of opportunity. It did not matter what was needed; our existing leaders rarely gave an emerging or inexperienced leader a shot. This did nothing to help young leaders grow and develop in a real-world setting. 4. Measure it.
A scorecard should answer at least four questions: What is most important now? Is our performance improving or declining? What impact are our interventions having? And are we winning? 5. Model it.
Leaders Made Here is not a bold initiative that comes and goes. It must become what the organization is. It has to become part of the organizational DNA. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:44 PM
03.13.17

Create the Target Before You Shoot the Arrow
I Having just returned from our annual meeting with over 5,000 chicken people present, I am thankful we took the time to draw the target before we shot the arrow. We will see what the attendees have to say, but preliminary reports are positive. I think the event hit the mark. Here’s the leadership lesson that comes to mind as I reflect on the event. One of the reasons it was a success—not the only reason, but one of them—is that we decided what we were trying to accomplish before we created the event. We drew the target BEFORE we shot the arrow. I’m wondering how often, as a leader, we fail to clearly define the target. I think about all the times my leadership efforts have fallen short . . . how many of those failures can be attributed, directly or indirectly, to an unclear target or goal? There are many things leaders CANNOT do for their people. However, clarity regarding intent should never be in short supply. People must always know what they are trying to accomplish. The power of clarity transcends targets, goals, and objectives – it includes vision, values, and strategic intent, as well as other tactical issues. But what we are trying to accomplish cannot get lost in the process. When you identify the target with crystal clarity, I think you may be amazed at how often your team will hit the mark.  His latest book, Leaders Made Here, describes how to nurture leaders throughout the organization, from the front lines to the executive ranks and outlines a clear and replicable approach to creating the leadership bench every organization needs. 
 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:22 AM
11.24.16

Gratitude is Good for You Too
WE KNOW GRATITUDE makes relationships thrive and makes trust possible. Gratitude encourages, clarifies, motivates, includes, and unifies. When we show gratitude, people feel valued, they know what’s important, they want to do more, and they feel part of something bigger than themselves. But gratitude is good for you too. Gratitude puts you in the right mindset to lead. Gratitude and humility are interconnected. They reinforce each other. Gratitude says, “I didn’t do this alone.” French philosopher Andre Comte-Sponville wrote, The narcissistic leader or “the egoist is ungrateful because he doesn’t like to acknowledge his debt to others and gratitude is this acknowledgement.” A lack of gratitude is at the core of narcissism. We alone are not responsible for who we are and what we do and that is the essence of leadership. We are never truly self-sufficient. In a practical way, gratitude provides guardrails in our life. Gratitude helps us to protect from ourselves. It is amazing how much gratitude plays into avoiding poor behavior and wrong thinking. Gratitude sets a boundary on our thoughts by making us mindful of others. It helps us to avoid going where we should not go because we are more self-aware. Gratitude requires that we slow down and reflect. Gratitude is the basis of emotional intelligence. It puts other people first. It says you know and you care. While empathy has been found to be essential to leadership, empathy is not empathy if it is silent. It must be expressed. Gratefulness helps to curb unproductive emotions such as frustration, resentment, and revenge. Studies have shown that it is an antidote to depression. It has the power to heal and move us forward. It improves relationships and is a remedy to envy and greed. Instead of trying to strive with others we are thankful for what they do. It eliminates a leader’s tendency towards entitlement. Grateful people find more meaning in life and feel more connected to others. In these changing and uncertain times, gratitude is a leaders ally. Gratitude looks at the long term and doesn’t focus on the present situation. Life is a continuum. Gratitude allows a leader to appreciate where they are and the resources they have at their disposal to face what life throws at them. A habit of gratitude gives us perspective. It doesn’t blind us to the negative but it facilitates a solution. Gratitude can’t just be something we do is has to be who we are as a leader. More than a behavior it must come from the heart. It must be the mindset we lead from, manage from, and make decisions from. Gratefulness is grounded in reality because ultimately we must realize that everything good in our life is a gift. Leadership begins and ends with gratefulness.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:34 AM
03.10.15

Being a Responsible Leader
THERE has always been a call for responsible leaders, but perhaps we just hear the call more clearly today. In The Responsible Leader, author Tim Richardson begins with a well-written overview of how we got where we are in our leadership understanding and the forces that are shaping our leadership context today. It points to the need for more responsible leadership.What is at the core of being a responsible leader? What are the mindsets the shape the behavior of a responsible leader? Richardson identifies four characteristics: Internal Assuredness and Attractiveness These leaders are confident but humble and their being—who they are—is attractive to others in the sense that they have a natural presence that engages with others and appeals to others at a deeper emotional level. “This is built on a real understanding and acceptance of one’s uniqueness—personality, motivations, strengths and weaknesses—and a confidence that means ‘I do not need to pretend to be someone I am not.’” This is also demonstrated in consistent behavior. “A clear and established values and belief system also helps to smooth out irrational swings of behavior.” “Modern leaders need to be wiser than simply being caught up in the moment.” Adaptability and Learning Orientation We must be comfortable with not knowing and living with paradoxes. This means we must have a willingness to listen and learn—even from the mostly unlikely sources. Once we “know” something we tend to want to hear only from people like us—people who filter the world through the same eyes we do. And when we do, we miss a lot. “We become judgmental and evaluative rather than inquisitive.” We also need to be confident and humble. When an inner confidence “is not balance with sober self-assessment or mature emotional intelligence, it becomes skewed and egocentric.” This is more than intellectual learning, this is behavioral learning. We need to be able to connect what we (and others) are experiencing and connect it to what we know. When it doesn’t connect we need to dig deeper and learn from it. Unfortunately, “individuals may deny that the situation is any different and fail to notice that their normal patterns are proving unhelpful. They may succumb to a personal blindspot and fail to learn.” Thinking and Operating Relationally This is a major shift for most leaders. We tend to grow up thinking of leaders as independent of instead of interdependent with other people. More autocratic than co-creators. Responsible leaders view themselves in relation to others. “Those whose perspective of success relies on others’ success are becoming a stronger force than perhaps many realize.” Purpose and Focus Responsible leaders have a guiding purpose that enables them to focus their energy and activity. “Leaders with a strong driving purpose—that answers the ‘why am I doing this?’ question—need commensurate levels of focus to ensure that their dreams and visions do not remain out of reach. The question is: “Where do I need to focus my attention and my energy and therefore what are distractions to be avoided?” Responsible leadership requires an “other” focus, humility and awareness. “To be a responsible leader is to step forward into the space and the moment with an ‘I can and I will’ mindset to impact situations and systems for the greater good.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:16 PM
02.03.15

4 Keys to Finding Hidden Leaders in Your OrganizationJim Kouzes writes in the foreword of The Hidden Leader that “Our images of who’s a leader and who’s not are all mixed up in our preconceived notions about what leadership is and isn’t.” Well put. That is the issue.He goes on to say that “hidden leaders are those people in your organization who share the belief that what they do matters.” And they are all around us. The authors Scott Edinger and Laurie Sain have developed some key indicators for finding the hidden leaders in your organization or team. These people can be “defined, identified, nurtured, and encouraged to help an organization develop a competitive edge.” Some will accept a position and others will prefer to stay off the organizational chart, but all can drive excellence throughout the organization. Hidden leaders display four key identifiers: they demonstrate integrity, lead through relationships, focus on results, and remain customer-focused no matter what role they have in the organization. Let’s look at them one by one: Demonstrate Integrity. Edinger and Sain believe that this is the “absolute bottom-line requirement of hidden leadership.” It means a consistent display in thoughts and actions of a strong ethical code of conduct that is “focused on the welfare of everyone.” Their consistent adherence to their beliefs makes them predictable and therefore dependable. They have the courage to do the right thing even when it is difficult. Lead Through Relationships. Leading through relationships is the basis of leadership. They get along with others and value others. They “lead and inspire because of who they are and how they interact with others.” They don’t depend on their position or lack of it to influence the actions of others. Focus on Results. The hidden leader “maintains a wide perspective and acts with independent initiative.” They use the end to define the means, which can mean working outside of strict processes to achieve the end result. “They aim for the end they are supposed to produce” so “they feel responsible and accountable, not just for the demands of their jobs but also for successful outcomes for stakeholders involved.” Remains Customer Purposed. This is different than customer service; it is an “awareness of how an action in a specific job affects the customer.” It is a big-picture focus and having a deep understanding of the value promise of an organization. For some hidden leaders one characteristic may dominate and others may need to be fully developed, but a hidden leader who lacks integrity, isn’t a hidden leader. Any leader needs support from other leaders in the organization and a good leader will make a priority out of developing others. Hidden leaders are easier to spot in flatter organizations and those that provide a greater number of areas to contribute. Listening to people at all levels is a big part of that. By recognizing hidden leaders we help to create a culture that develops more leaders. The hidden leaders are there. It is a leader’s responsibility to discover and develop them. The Hidden Leader contains worksheets and access to online resources to evaluate hidden leaders in your organization or team. Of Related Interest: 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:08 PM
12.08.14

Things You Can Do to Build Their Future
THIS last summer, my son Mark attended a youth leadership conference for the first time. I attended the opening session with him in a room of about 300 kids that all seemed to know each other. Mark is a very personable and approachable young man but as a parent I naturally thought, “How is he going to get up and running in a group this size? He doesn’t know anyone.” But the opening session wasn’t over for 30-seconds when a young man walked up and said, “I’m Hunter. Would you like to hang out with us?” And they were off and never looked back. As I walked away, I thought that this is the kind of leadership that makes a difference in people’s lives. It’s leading from where you are, without title and without fanfare. Just doing the right thing. It’s the little things like this that we teach our kids that enrich their lives and those of others. Leadership begins in the home. It’s where we have the greatest impact on the future. Here’s a few things we can do: We can help them to look further out. Help them see the long-term effects of the decisions they make today. Define a future and help them to line up the decisions needed to get there. It will help them to gain a perspective on life. We can take the time to talk about their experiences. Help them to see them in the most constructive way possible. While some rules are important, principles will last them a lifetime. Rules are easy to churn out. Principles take time to teach and integrate into a person’s life. We can teach them that connection with others matters and that’s not done behind a screen. People are experienced when you can look into their eyes. Life is experienced when you can see what is going on around you—both the sights and sounds. One of the greatest gifts you can give someone is your full attention. We can give them responsibility. Help them to value contribution over consumption. If not, we can be guilty of what President George W. Bush called “the soft bigotry of low expectations.” He added, “No child in America should be segregated by low expectations.” Help them raise the bar in their life and thereby help others to discover the possibilities in theirs. And the most important thing we can do is to set an example of the kind of people we want them to become. Remember we are training future leaders not just raising kids. It’s an investment.
We can’t give to others without being affected positively ourselves. And this is the secret of giving: When we make the world better for others, you make the world better for yourself.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:27 PM
11.19.14

The Ten Golden Rules of Leadership
MICHAEL SOUPIOS and Panos Mourdoukoutas have reviewed the writings of the Classical philosophers and selected ten ideas that will positively impact our leadership effectiveness in The Ten Golden Rules of Leadership. Not surprisingly, the philosophies of classic figures remain relevant in today's workplace. Early on, the authors suggest that the raw material of leadership is not latent in just about everyone and rightly discredit the idea that it “just takes a nudge to trigger its unfolding.” Further, they say that the “special qualities of genuine leadership are remarkably complex and rare.” It is true that good leaders are not as common as they need to be and that we do confuse administration with actual leadership as they suggest, but the potential is there in each one of us. The problem is that it remains latent in many of us. We choose not to do the work necessary and instead assume reading “Leadership Lessons I Learned from My Cat” is enough to unlock our potential. The authors do expose the real culprit at the end of the book: “Achieving the rank of genuine leader is a daunting task that most will find prohibitively challenging.” In short, “leadership requires a special form of courage: the courage to fashion a code of conduct governed by principled conviction.” Genuine leadership is not complex, but it is difficult because it requires that we do the inner work on a continual basis. And that is a lot to commit to. It’s lifelong. And what we want to do is to check it off and mark it as good enough. Sustainable leadership requires a radical life-long commitment to rule one of leadership: Know Thyself. Rule 1: “Know Thyself.” –Thales
Rule 2: “Office Shows the Person.” –Pittacus
Rule 3: “Nurture Community at the Workplace.” –Plato
Rule 4: “Do Not Waste Energy on Things You Cannot Change.” –Aristophanes
Rule 5: “Always Embrace the Truth.” –Antisthenes
Rule 6: “Let Competition Reveal Talent.” –Hesiod
Rule 7: “Live Life by a Higher Code.” –Aristotle
Rule 8: “Always Evaluate Information with a Critical Eye.” –The Skeptics
Rule 9: “Never Underestimate the Power of Personal Integrity.” –Sophocles
Rule 10: “Character Is Destiny.” –Heraclitus

Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:24 PM
09.04.14

Why Reframing is Important to Great Leadership
LEADERS need to be able to look at the situations they face from different perspectives. The need to be able to reframe a situation in order to understand what it really going on and deal with it effectively. A leader’s “ability to reframe sets them free” and helps them to “avoid getting trapped in cognitive ruts,” write Lee Bolman and Terrence Deal, authors of How Great Leaders Think. “Leaders can expand how they think by using different mental models to determine what’s going on and what to do in complex situations.”Bolman and Deal are the authors of Reframing Organizations. They have taken the model they introduced there and applied it specifically to leadership. The model has four frames, scripts, or perspectives. Each has its advantages and shortcomings and we tend to lean towards one more than the others. This idea, of course, is to develop the ability to use the appropriate frame or script to generate a unique approach to handling challenging circumstances instead of relying upon our tried and true default approaches. Our single approach will only be “right” a small percentage of the time. Too often leaders will approach everything they deal with the last approach and insist they are right as they head right over the cliff. They insist that the world is as they see it. To grow is to recognize your blind spots. The four frames are: Structural — Leader’s role as architect. An emphasis on finding the right design for the task at hand. Structural leaders help groups get clear about why they’re there, who is in charge, who is supposed to do what, and how team members can work with on another to achieve the group’s purpose. Human Resources — Leader’s role as coach. The central theme is improving the fit between the individual and the organization and begins with caring—or in a word, love. Leaders who commit themselves to key practices of effective people leadership—developing a philosophy for managing people, hiring the right people, keeping employee investing in their future, empowering them, and promoting diversity—have repeatedly built businesses that thrive on the strength of employee talent, energy, and creativity. Political — Leader’s role as peacemaker. Organizations and societies are networks as well as hierarchies, and the power of relationships is a crucial complement to the power of position. Misreading the political map and overlooking the power of potential players can lead to catastrophe. That’s why it’s critical to treat the map as a work in progress—a guide to be tested as you move along. Symbolic — Leader’s role as storyteller. The central theme is the way humans discover and create meaning in an ambiguous and chaotic world. Symbolic leadership begins with the leader’s deeply rooted faith and passion. Symbolic leaders infuse magic into organizations through their artistic focus on history, shared values, heroes, ritual, ceremony, and stories, and serve as icons who embody a group’s values and spirit. The authors write: “Consciously or not, we all read situations to figure out what scene we’re in and what role we’ve been assigned so that we can respond in character. But it’s important to ask ourselves whether the drama is the one we want and recognize that we have latitude as to which character to play and how to interpret the script.” The authors provide practical lessons from examining these frames through the leadership of Jeff Bezos, Howard Schultz, Tony Hsieh, Ursala Burns, Steve Jobs, and others. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:51 PM
07.28.14

8 Shifts Young Leaders Need to Make
I WAS STANDING in a hotel lobby waiting on my buddy to get some coffee before we were headed out for a day at a conference we were working. I was standing against the wall with my computer bag on my back. We were running a little late, so on the spur of the moment, I decided I'd go get the rental car and bring it to the lobby's front door. As I stepped away from the wall, I had no idea the pandemonium that would ensue. Apparently my bag had gotten caught on the fire alarm in the hotel lobby. In an odd case of events, when I stepped away from the wall, the fire alarm went off and people began to scatter. The hotel lobby that was rather full of folks eating breakfast and enjoying their morning coffee suddenly began to empty as people began to look around and evacuate the lobby. You see, that's what happens when alarms go off, people move. For the next generation, an alarm of sorts is going off. An alarm that, if ignored or simply silenced, will continue to get louder and louder. An alarm that, if left unanswered, could mean serious trouble for the next generation and our world as we know it. Poverty rates have never been higher, unemployment rates are astronomically high, and people are hurting all over our world. Children are being abandoned by parents that have other priorities and people are willing to kill over hearsay and gossip. Our culture is in need of young leaders that are willing to not just silence the alarm with quick fixes but sustain lasting change in the world we live in. We need young leaders that can rally people around them and begin bringing people together for lasting change. How can we answer the alarm? By making some shifts in our lives and in our leadership in order to help lead lasting change in our society. Here are 8 shifts that we need to make as young people in order to set ourselves up to lead well now and in the future. From Entitlement to Honor From Unreliable to Consistent From Dissension to Cooperation From Conformity to Integrity From Pride to Humility From Passive to Passionate From Selfishness to Love From Premature to Patient We can make the shifts as a generation. We can answer the alarm and change the world for our kids and their kids. The question is, "Are you willing?"  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:58 AM
05.14.14

Finishing Well
SPORTSWOMAN, polar explorer and author of On the Edge, Alison Levine, recently told Forbes about finishing well: Most of the deaths on Everest occur on the descent—after a climber reaches the top. The reason so many accidents happen on the descent is because people use everything they have—all of their energy reserves—to get to the top, and then they have nothing left in them to get themselves back down the mountain. Every year there are mountaineers who collapse just below the summit; many of them die there. Getting to the top is optional. Getting down is mandatory. You have to know yourself well enough to judge when it is time to turn around and head back down. And you need to make that call when you still have enough energy left to descend. The hard part is that quite often that turn around point is before you reach the summit. The number one goal of any expedition: come back alive. Number two is come back with all of your fingers and toes. Tagging the top of a mountain should never be the goal. The goal isn’t getting to the top. The goal is getting back down—finishing well. Many leaders struggle with finishing well. Ironically, success plants the seeds for derailment. Success encourages complacency and arrogance both of which erode character and obstruct growth. Finishing well requires a lifelong commitment to self-awareness and growth. And that means feedback. Any leader that struggles with openness to feedback is flirting with disaster. Finishing well is not an event. It is a process. It doesn’t just happen. It is a discipline—a road that the self-aware leader embarks on. Leaders who finish well develop these characteristics as part of their leadership style:
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:58 PM
12.12.13

Could the Leadership Contract Help You Be a Better Leader?
IT IS no longer surprising to hear of another leader letting us down. They’re disconnected, they behave badly (if not disgracefully), and they are entrenched in wrong thinking. And we have begun to expect not much else. It numbs us generally, but it also lowers the expectations we have of ourselves. We become bystanders. In The Leadership Contract, author Vince Molinaro thinks that this is due to four primary reasons. First, we have relied on the heroic model of leadership—the idea that the leader at the top of the organization has all the answers and can single-handedly lead the way. “It is risky to put your faith in just one individual. And when you focus on only one leader at the top, you actually take your attention away from other leaders in an organization.”Second, we have glorified charismatic leaders. We turn them into celebrities. They become the face of the organization. We give them too much money and power. Charisma isn’t bad. “All leaders need a certain amount of it, but charisma can have a bad side too.” When leaders think that they can act any way they want without any accountability, we glorify jerks. Third, we have promoted technical superstars into leadership roles. “The thinking was that if you were strong technically, you would obviously be strong in a management or leadership role.” The problem is that they are entirely different activities and expectations began to move you further away from what made you a strong performer. “To cope, you then relegated the people issues to second place and focused on the more stimulating technical parts of your job. Then you became a leader in title but not in action.” Finally, Molinaro says that we have a quick-fix view to developing leaders. “We have been too simplistic about what it really takes to develop leaders.” Leadership is hard work. “We need to come to terms with the real, hard work required to be consistently great at the practice of leadership and to drive the sustainable performance of our organizations.” Molinaro believes the way out is the leadership contract and its four terms: 1. Leadership is a Decision—Make It
2. Leadership is an Obligation—Step Up
3. Leadership is Hard Work—Get Tough
4. Leadership is Community—Connect
Is it time for you to sign the leadership contract? 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:20 PM
11.28.13

Adversaries into Allies
Adversaries into Allies is Leadership 101. Every leader that aspires to be a good leader should read Bob Burg’s book on influence. “Unless you are able to influence the way others think and act, your chances for success in any aspect of your life are limited.” Leadership is intentional influence. Burg calls it Ultimate Influence or “the ability to get the results you want from others while making them feel genuinely good about themselves, about the process, and about you.” He adds, “Consciously shifting your focus away from yourself is about the very best way you can ever influence another.” This is a guidebook to emotional intelligence and should be read from cover to cover. It’s the little things we forget. But here’s a caution: You can’t fake this stuff … for long. These ideas need to be practiced until they become part of who you are. If they are just tools to get what you want, people will know it and it won’t work for you. Influence becomes manipulation when it is about you. “Manipulation aims at control, not cooperation. A manipulator will play on your negative emotions in order to elicit your compliance.” As leaders, we need to keep our motives in check. Burg presents what leadership looks like when it isn’t about you; when the focus is others. While the title states that this book is about turning adversaries into allies, Burg points out that the job of leaders is to “make sure that a potentially difficult person doesn’t become an adversary in the first place.” Our ego often creates these situations. Ultimate Influence is based on five key principles that occur on an ongoing basis: 1. Control your own emotions. When we have our emotions under control we are able to “act out of thought, out of consciousness, and help create a situation in which everyone involved can come away as winners.” Your default setting to pressure situations is directly proportional to your ability to problem solve, to live in the solution, and to lead. 2. Understand the clash of belief systems. Learn to get out of your own head and into the head of the person you’re trying to influence. Not only is it our responsibility to be certain our message is understood by the recipient, it’s just as important to be sure we understand their message, as well. 3. Acknowledge their ego. When dealing with others, remember that “their ego is highly sensitive, and if you want someone to agree with your wishes, you must handle it with extreme caution and care.” Be a judge, not a lawyer. Whereas a lawyer is paid to win the case for his or her client by any legal and ethical means possible, a judge is not. A judge needs to understand both sides of the issue and be as impartial as possible. Human that we are, being impartial is difficult when the ego wants to win at all costs—even if you’re wrong. But the best way to overcome this unproductive desire is to practice being a judge. 4. Set the proper frame. The frame—the context—determines the direction of every interpersonal transaction. If you set the frame you are in control. Expecting someone to be helpful doesn’t change them, it changes you. And that is what changes them. 5. Communicate with tact and empathy. “Tact is the ability to say something in a way that makes the other person feel less threatened or defensive and more open to you and your ideas.” It’s key to becoming an Ultimate Influencer. Empathy—the ability to identify with another’s feelings—and tact go hand-in-hand. “You will naturally display tact when you are truly empathetic to another’s situation. And speaking tactfully will communicate your empathy to that person.” [Give people an out.] You have honored this person by removing pressure and giving him or her the option to escape through the back door. You are not giving them the out so they will take it. Your goal is to make them feel comfortable enough not to feel the need to take it.Burg ends with character. “Even more important that what you say and what you do is who you are.” Your character is what ultimately determines your long-term influence. Be who you say you are. Say little and do much. Develop a reputation as a person who, rather than talking a good game, actually plays a good game. One who, instead of talking about being honest, is honest. Instead of talking about thinking of others, thinks of others. These ideas aren’t rocket science, but they do take work and thought. The problem is we get lazy and resort to command-and-control in a desire to push our own agenda and ideas. Real leadership—ultimate influence—is not easy but it is rewarding. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:25 PM
10.28.13

5 Leadership Lessons: The Heart of Leadership “Leaders are different,” begins Mark Miller’s The Heart of Leadership. “They see the world differently and they cultivate different character traits.” It’s a business fable that explains that “you can have impeccable character—be honest, loyal, dependable, and so on—and still not demonstrate leadership character.” Leadership character sits on top of these traits and are foundational. Leaders who don’t possess these traits and others like them, are disqualified before they start. Skills are important, but “if you don’t demonstrate leadership character, your skills and your results will be discounted, if not dismissed. The Heart of Leadership is a well told story and is built around five lessons: The key issue though is discussed at the end of the story. If these qualities don’t become part of who you are, your leadership will never really change. Our leadership reflects who we are inside. You can fake it for a while, but eventually it will come out. “If you do all those activities and your heart doesn’t change, you won’t be the kind of leader you want to be. Leadership is not about what you do nearly as much as it’s about who you are becoming—the heart of leadership is a matter of the heart.”

Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:01 AM
10.09.13

The Good Struggle NOT surprisingly, Joseph Badaracco has written an essential read for leaders of all kinds. The Good Struggle addresses the question of how to lead successfully and responsibly in our uncertain, high pressure, turbulent world.
NOT surprisingly, Joseph Badaracco has written an essential read for leaders of all kinds. The Good Struggle addresses the question of how to lead successfully and responsibly in our uncertain, high pressure, turbulent world.
Badaracco says that the inescapable pressures of leadership are intensified today because of the market-driven world in which we live. “Almost everything—how we manage our organizations and our lives, how we make decisions at work and at home, and even how we think about ourselves—is deeply shaped by markets and market-based thinking.” This creates greater uncertainty, obscures right choices, and puts pressure on us to abandon principles that we used to rely on. Responsible leaders find themselves engaged in the good struggle: “a long effort, demanding perseverance and courage, to make good on serious but profoundly fallible commitments in an uncertain and often unforgiving world.” He adds, “Struggle has always been central to accomplishing anything worthwhile, and this is especially true today.” He offers five enduring—inescapable—questions. Responsible leadership consists of thoughtful and lived answers to them. Am I Really Grappling with the Fundamentals? “The first responsibility of leaders is intellectual. It is the struggle to develop—to the extent possible—a deep, careful, analytical, data-driven understanding of the driving forces in the markets and society around them and to keep this understanding loose, flexible, and revisable.” Grasping the fundamentals can “reduce the chance of being blindsided, by encouraging the mental habit of looking for emerging patterns and odd developments with larger implications. It also promotes modesty, a healthy, low-level paranoia, and vigilance rather than hubris.” He notes that everything now is modular—constantly being recombined. “Recombination also makes it much harder for leaders to inculcate values when people in their organizations know they and their leaders are basically modules in a plug-and-play world and could be moving on soon. The natural instinct is to take care of yourself, here and now.” What Am I Really Accountable For? “Without clarity about accountability, leaders and their organization can drift or zigzag aimlessly.” Of course, many leaders do not want to be accountable to anyone or anything. “Accountability originates in an obligation to make good on the spirit of some jointly designed, provisional, and evolving objectives.” Here’s the question for any leader: “What pressures, scrutiny, and risks do we want to create or invite in order to build a strong, resilient, responsible organization?” How Do I Make Critical Decisions? We need a broader view of critical decisions. Instead of viewing them as deep, abiding pledges that we must make good on, we need to see them more as evolving commitments. That is, “a pledge, by a leader and an organization, to move in a particular direction, but to do so in a flexible, open-ended way.” Decision making has to be as fluid as the markets around them. “Execution as learning.” “Instead of periodic big decisions, responsible leaders make or orchestrate an unending series of smaller ones—all aimed at some larger, broad, flexible objective.” Do We Have the Right Core Values? Values are important because “they may be the only force that can counter the power of markets and market-based thinking….Today’s ever-present markets have their own implicit values, and they can easily overwhelm whatever values leaders want to instill in their organizations.” To lead responsibly, leaders must commit to “clarity, meaningful projects, and bright ethical lines. In different ways, each of these helps leaders and organizations respond to the risks and opportunities created by pervasive market forces.” Why Have I Chosen This Life? People seek positions of leadership not despite the struggles involved, but because of them. “Responsible leadership is a challenge that—despite its inevitable risks, frustrations, and failures—demands and merits the best efforts of talented men and women, tests their competence and their characters fully, gives purpose and intensity to their lives and helps them lead the kind of lives they really value.” The purpose of our struggle matters. Badaracco writes, “If the purpose of life is ease and comfort, no sensible person would take on the demands of leadership.” Perhaps in developing leaders at all levels we need to change that very prevalent mindset. Without it we can’t discover what we are and the person we are meant to be. Badaracco doesn’t offer hard answers because they are evolving answers and should be individual answers created from introspection and reflection. But the insights and provocative concepts are enough to get you thinking in new ways. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:24 AM
08.28.13

7 Metaphors for Leadership TransformationPeter Fuda introduces in Leadership Transformed, seven interdependent metaphors to explain and accelerate leadership transformation in leaders at any level.The seven metaphors help you to get a grasp on the concepts and issues involved in leadership development. Leadership development doesn’t happen in parts. These interdependent metaphors emphasize the holistic nature of leadership development. They are: 1. FIRE: The motivational forces that initiate and sustain transformation efforts; including a burning platform and burning ambition, as well as personal and organizational reasons for change. Fire is at the center of the seven metaphors because if the why isn’t there, the other factors are just going through the motion. Fuda emphasizes burning ambition—fire from within—as the only motivation that sustains. You may change out of fear—burning platform—and it may provide the initial spark, but it burns briefly. 2. SNOWBALL: A virtuous snowball of accountability that propels the change effort forward; starting with the leader, and building momentum as others are "swept up" in the journey. Building momentum is contingent upon getting a critical mass of leaders on the journey—perhaps even replacing those who are not committed to growth. Uncommitted leaders only cause drag on the snowball by not living the agreed standards of behavior. 3. MASTER CHEF: Artful application of the "leadership science" (frameworks, tools and strategies), which enable a leader to advance from amateur cook to "master" chef. Pioneering French chef Marcel Boulestin once said “cooking is not chemistry, it’s an art. It requires instinct and taste rather than exact measurements”. Similarly, transformation is accelerated when leaders work fluidly within a recipe (change frameworks), and artfully deploy their utensils (tools) and cooking methods (strategies). Leaders should become less rigid and more intuitive over time. This requires that a leader develop critical thinking skills and a deep understanding of where they are going and what leadership is. Otherwise they become tied to formulas and rote practices. 4. COACH: A team of consultant(s), colleagues and supporters that collectively coach a leader toward their aspirations. It’s not about coaching. It’s about being coached from a variety of sources—consultants, colleagues, and family members. We can learn from anyone. Coaching is most powerful when all groups identify mutually beneficial outcomes from the leader’s transformation, and create a trusting environment for that coaching to take place. Hunter S. Thompson said, “He who is taught only by himself has a fool for a master.” 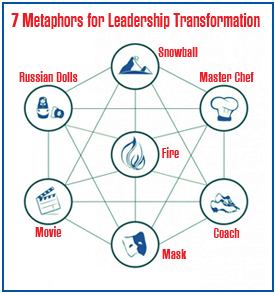 5. MASK: This metaphor has two aspects: the concealment of perceived imperfections, and the adoption of an identity that is misaligned with a leader’s authentic self, values or aspirations. 5. MASK: This metaphor has two aspects: the concealment of perceived imperfections, and the adoption of an identity that is misaligned with a leader’s authentic self, values or aspirations.
The mask is a heavy burden to carry. It creates inner conflict with a leader’s deeply held values and aspirations, and can negatively impact on important relationships. When leaders drop their mask in favor of being their "authentic self," the power this unleashes is atomic in scale; they get more done, build more trust, have far more enriching interactions and feel more fulfilled. 6. MOVIE: Processes for increasing self-awareness and reflection, which allow a leader to "edit" their performance, and direct a "movie" in line with their leadership vision. Often leaders find themselves acting in a repetitive movie—their own version of Groundhog Day, doing the same thing day after day with the same result. By stepping out of the movie and viewing the footage objectively in the editing suite, leaders can hone their reflective capacity, and eventually, learn how to slow down their movie. From this place of stillness, leaders can begin to direct their own movie and choose a better response—in real time. A good metaphor for understanding purposeful leadership. 7. RUSSIAN DOLLS: A complimentary set of journeys that interact with a leader’s personal journey of transformation. A leader’s personal journey never exists in isolation; it is surrounded by multiple other journeys occurring concurrently. When the journeys are aligned, something magical can happen. Conversely, whenever one doll tries to pull in a different direction, its proximity to the other dolls ensures that it doesn’t get very far. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:45 PM
08.02.13

Are You Losing Inside the Box?
IF you're losing inside the box, don't bother trying to compete outside the box. If you don't have the basics in place or more to the point, if you aren't excelling at the basics, then no one cares about your uniqueness or your wow factor. Joe Calloway is one of those people that cuts through the clutter and gets to the core issue. His book Be the Best at What Matters Most is full of that—what matters most. He makes a point that is important on a number of levels. For businesses, the wow factor is nice but what is more important is to "deliver on your promise every time, with every customer, with amazing consistency." He adds, "You want to constantly innovate and improve for one purpose: to win inside the box. By 'inside the box,' I mean those things that matter most to the marketplace. These are the basic expectations of your customers." Calloway says that we should take another look at the basics of our business and be sure that we are hitting 10 on a scale of 1 to 10 inside the box before we start thinking about how we can surprise our customers. "The battle is won and lost inside the box." Regarding the random acts of wow that we hear about from time to time, Calloway says that they are wonderful and we should do them. "But that's not where you'll win or lose the game. Don't think that some once-a-year special thing that you do ever takes the place of consistently being the best at what matters most. Put your energy, effort, and focus into doing a really, really great job on the basics and into consistency of performance. That determines how you treat your customers." This is great material and it also applies in terms of your leadership. Are you losing inside the box? It's tempting to try to put on the showier aspects of leadership and ignore the hard-won aspects of trust, communication and character. We want the choicest assignments and the most visible trappings of leadership. It's nice to be the superhero. But great leadership is won and lost inside the box. Are you generous with information? Are you respectful? Do you listen? Do you communicate? Do you take the time to build others? Do you set a proper example? Can you follow when necessary? Can you set your ego aside? Are you accountable? Do you understand that it's not about you? It's fun to be spectacular and to be seen. You may be very competent, charismatic, and eloquent, but if you are not getting the basics right, then you're a liability, not an asset. Leader's derail quickly when they make it about them; when the organization exists to serve them and their agenda. I've seen more than a few leaders derail because they forgot to develop and sustain one or two of the basic practices of good leadership inside the box. They looked good on the outside but it was the day-to-day that they struggled with and never addressed. The real work of leadership is often the unsung, behind-the-scenes work of serving others that must be done on a daily basis. It may not give us that temporary ego boost, but it is the most rewarding work and has the biggest payoff in the long run. So, the real question is, are we working to improve the basics on a daily basis? Are we hitting 10 on a scale of 1 to 10 inside the box?

Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:48 AM
06.26.13

Seven Disciplines that Make Leadership Development Stick
LEADERS don't always finish well or finish what they start. Leadership sustainability isn't easy. Given the fact that we all know leaders that haven't finished well, it's surprising how many of us have no plan in place to consciously and specifically improve our leadership abilities. Most of the time we wing it. Leadership sustainability is about the commitment to change and growth that is consistent with shifting requirements, not just individually but for the organization as a whole. In Leadership Sustainability, authors Dave Ulrich and Norm Smallwood have defined seven leadership practices that instill sustainability. It begins with "recognition that what matters most is the impact of the leader's actions on others—not just the actions themselves or the rationale behind them." Yet that's not something that we often feel we have time to consider. Our leadership is experienced in our actions and not our intentions. In brief, the seven disciplines to incorporate into your leadership plan to help make your best intentions stick are: Simplicity. Focus on what matters most. Tells stories with impact. Leadership sustainability requires that we find simplicity in the face of complexity and replace concept clutter with simple resolve. It entails prioritizing on the behaviors that matter most. Time. Manage your calendar to reflect your priorities. Put desired behaviors into your calendar. Employees see what leaders do more than listen to what they say. Leadership sustainability shows up in who we spend time with, what issues we spend time on, where we spend our time, and how we spend our time. Recognize routines and modify as necessary. Accountability. Take personal responsibility for doing what you say you will do and hold others accountable as well. "We see too many leadership points of view that are more rhetorical than resolve, more aspiration than action, and more hopeful than real. Leadership wish lists need to be replaced with leadership vows." Be consistent with personal values and brand. Resources. Leaders dedicate resources in order to support their desired changes with coaching and infrastructure. Use a coach. Get coaching and institutional support to become a better leader. "Leaders acting alone, even with great desire and good intentions, are unlikely to sustain their desired changes." Tracking. Move from general to specific measures. Measure what's important and not what's easy. Tie to consequences. Unless desired leadership behaviors and changes are operationalized, quantified, and tracked, they are nice to do, but not likely to be done. Melioration. Leadership sustainability requires that leaders master the principles of learning: to experiment frequently, to reflect always, to become resilient, to face failure, to not be calloused to success, and to improvise continually. Emotion. Know why you lead. Connect change with personal and organizational values. Recognize your impact on others. Celebrate success. "Some leaders work to hide their feelings and avoid becoming too personal with others. These leaders end up distancing and isolating themselves. Leaders who are emotionally vulnerable and transparent will be more likely to sustain change." The authors have provided videos, tools and assessments on their web site to help you to achieve leadership sustainability.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:05 PM
05.07.13

11 Ground Rules that Leaders Ought to Know
PHILLIP VAN HOOSER has condensed his leadership experience down to 11 ground rules that Leaders Ought to Know. Van Hooser begins with the fact that leaders are made: Leadership is a choice, reinforced by individual effort. In his earlier days, he was moved by a comment that Deming wrote in Out of the Crisis:Long-term commitment to new learning and new philosophy is required of any management that seeks transformation. The timid and the fainthearted, and the people that expect quick results, are doomed to disappointment. His choice to be a leader has proven to be his most important professional decision. And it could be yours too. But as Deming noted it takes deliberate work and is not a quick transformation. It is the choice to make the effort that makes a leader. The choice can be made by anyone anywhere because leadership is not a title. It is, as he states in ground rule 2, the ability to offer service and the willingness to take action—especially on those things we already know we should be doing, but aren't. He continues with ground rules on earning respect, integrity, motivation, preventive leadership, courage, leadership pitfalls, and some good commonsense. Ground Rule 3: Leaders cannot function in a vacuum; Leadership requires willing and able followers.
Van Hooser on keeping your distance: You can be a supervisor or manager without getting close to your followers; however, you cannot be a leader unless you get close to your followers. Van Hooser was given this advice on parenting: "You may not always be able to predict what your child will do, or say, or think. But you're the father; your child must always be able to predict with certainty what you will do, or say, or think. That way, he can adapt and adjust his behavior to yours." He relates it to leadership: A leader's consistency provides a predictive foundation from which followers can begin to think, decide, and act. If a leader does not establish that foundation, he or she—albeit unintentionally—creates confusion, uncertainty, and potentially chaos in the followers' minds. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:21 PM
03.27.13

5 Leadership Lessons: Avoiding the "Mediocre Me" Mindset Act boldly in shaping outcomes in our spheres of influence. Become the best version of yourself possible by exercising the creativity of thought, diversity of perspective, and depth of conviction to do what we can, when we can, where we can to try and make our part of the world a little better tomorrow than we found it today. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:12 PM
03.18.13

Fred 2.0 – Leadership in ActionYou are no doubt familiar with Fred, first introduced to us in The Fred Factor by Mark Sanborn. Fred exemplified an attitude of exceptional service delivered consistently with creativity and passion in a way that values other people.Now Fred 2.0 brings us fresh insights, deeper understanding and wider application of the Fred Principles—and an update on the life of the real Fred Shea. Fred 2.0 is about a specific way of approaching life and business. It’s an attitude that extends far beyond customer service. It comes from within and says I will do extraordinary things because that’s who I am. It’s not a feeling—it’s who you are. It is not dependent on the performance of anyone else. Why Would You Live this Way? Sanborn says it’s because being a Fred enriches others, expands you, puts more life into your living, breaks the bonds of self-absorption, makes you more employable, offers you a better way to live, creates a positive influence, and is more fun. “Creativity is an essential ingredient in delivering extraordinary results,” writes Sanborn. Being creative is doing something different that adds value. More often than not, it’s the little things we notice that can be done better. This applies not only to the “things” we do, but also to our relationships; how we respond and interact to those around us. Sanborn shows very specifically how to build better relationships, elevate the experience for those we come into contact with, how to build a team of Freds and how to instill the Fred approach in your kids philosophy of life. The Fred Philosophy is Good Leadership The Fred philosophy is ultimately what good leadership is all about. It’s a battle against mediocrity says Sanborn. The first job of leadership is to help people see their significance. Leaders recognize that those who feel insignificant rarely make significant contributions. An effective leader is able to show people that they are significant in ways they may not realize.The Fred philosophy means: • Leading by example • Starting with what’s right instead of what’s wrong • Encouraging people to try • Asking for and sharing good ideas • Removing barriers and obstacles • Being a champion of those around you • Giving people the freedom they need • Teaching the Fred philosophy consistently • Recognizing and rewarding • Make the process enjoyable “It’s our choice whether we’ll use our time, effort, and talents to turn ordinary work into something extraordinary.” writes Sanborn. It begins as always, with integrity. If you value it, those around you will too. Fred 2.0 will show you the thinking behind extraordinary leadership and apply it in every area of your life. “When you know what is important to you in your life and work, you should apportion your talents and efforts so you can give the best you have to those things.” Love what you do and love the people you do it with.
SPECIAL OFFER: Visit Mark Sanborn's Fred 2.0 web site now to learn more and gain instant access to a Fred 2.0 “EXTRAordinary Results” Resource Kit, free with purchase of Fred 2.0. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:17 PM
03.12.13

Leadership and the Art of Struggle: 5 Things You Can Do
STRUGGLE is a part of any human endeavor and leadership is no different. The problem is we view struggle as a negative. But struggle is how we grow. Without them we can’t reach our full potential as leaders. We like to think of our leaders as flawless. We like to be perceived as flawless—or at least we like people to think we have everything under control. But as Joe Badaracco has pointed out, “leadership is a struggle by flawed human beings to make some important human values real and effective in the world as it is.”It may sound counterintuitive, but considering the benefits illuminated by Stephen Snyder in Leadership and the Art of Struggle, we should welcome it as an important element of the leadership process and our own personal development. Snyder writes that we should face struggle “head on—not hiding from it or feeling shame—because struggle is the gateway to learning and growth.” It can also help us to discover our purpose and meaning and develop the adaptive energy necessary to sustain our leadership for a lifetime. Struggles have three defining characteristics:
In the world we live in today, this is a common occurrence often leading to burnout unless we learn to see struggle through a different lens. Snyder recommends: Adopt a growth mindset. The first step in accomplishing this is through reflection—being aware of what is going on around you. Snyder’s former colleague at Microsoft, Frank Gaudette, used to say: “I reserve the right to wake up smarter every day.” A good mantra to make our own. Center your mind, body and spirit. We all need some way to anchor ourselves and gain perspective that we practice daily like exercise and diet, prayer, connecting with nature, meditation, and/or journaling. Build your support community. “Create a community of people whom you can connect and bond with and from whom you can seek advice and feedback.” Overcome your blind spots. Blind spots by their very nature are hard to recognize. And they are frustrating because they blind us from seeing why people may be responding to us in counterproductive ways—leading us to finger pointing rather than personal responsibility. “Blind spots,” writes Snyder, “are the product of an overactive automatic mind and an underactive reflective mind.” A fairly common blind spot Snyder calls the Conflict Blind Spot. This blind spot can cause someone to interpret every interaction through a distorted lens. It reinforces the perception that the other person is wrong and we are right. Recommit, pivot, or leap. When we struggle we have essentially three options. The first is to recommit and stay the course. The second is to pivot and make a course correction. And third is to leap into uncharted territory far beyond our comfort zone. Choosing the right option requires that we examine ourselves and determine which choice is most consistent with our personal values or mission statement. Every struggle is a chance to learn and to confront who we are and what we are becoming. Seen in that light, they are a gift. And our ability to deal with our own struggles effectively has an impact on those around us. Not only does it create a more positive environment to function in, but it provides a constructive example for others to follow. Snyder has written an outstanding and practical book to help us to rethink the challenges and problems we face along the way. One of the best you’ll ever read on the topic. (The Adaptive Leader Profile is available from Snyder Leadership Group.)

Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:27 PM
01.10.13

The Secret to Leadership Growth
THE NUMBER ONE way leaders grow is by listening. Leadership feels like a talking role, but it is predominately a listening role. That can be hard to accept. It feels counterintuitive. A leadership role often makes us feel like we should be talking all the time; like we’re the most important person in the room. We’re not. Listening takes us outside our own heads. It gives us a chance to see things from a different perspective. It creates options. It creates the space for serendipity. Listening takes us beyond our egos. Without it we begin to miss very elementary things. When we miss elementary things we crash and burn in a self-made morass of complexity. Listening clarifies. Listening renews and refreshes. Without it we get stuck and tedious. When we help others grow, we grow. Leaders guide people and then listen. Listening is the best way to turn someone from a victim (of your talk) to a supporter of your idea. Listening gives others the chance to take ownership. Listening is the catalyst for making individuals a community. Listening creates the space for leadership.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:53 AM
12.12.12

The Leader’s Pocket Guide
WHAT I LIKE most about the work of John Baldoni is that it is very practical. His advice is relatable, practical, and gets to the core of the issue. In article after article, book after book, he hits the nail on the head. The Leader’s Pocket Guide is the next best thing to having John as your own personal coach. He shares the lessons he’s learned coaching others. Without a doubt, it’s a handy reference guide when you’re stuck, but if you use this book like a leadership development program, you can pull out its real value. “When we are no longer able to change a situation, we are challenged to change ourselves.” Leadership development is not easy. Facing yourself as a leader is the most difficult part. Appropriately, he begins with “How to Know Yourself Better.” Leaders continually need to compare where they are developmentally to where they want to be. It’s critically important to their growth. John suggests that we ask ourselves and others three questions: What more do I need to be doing more or less of? What else should I be doing—what should I be asking others to do? and How do I accept feedback? Inside you will find 100 more ideas related to leading yourself, leading others and leading an organization. Each leadership essay is clear and to the point. Reflection questions are asked throughout the book that you can take advantage of. As you read each topic, ask if you are where you want to be on that topic. And importantly, ask others for feedback because how you are perceived gives you a more accurate view of your leadership effectiveness than your intentions. The Leader’s Pocket Guide is a useful book for both new and seasoned leaders. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:47 PM
12.03.12

The Character Based LeaderCharisma: helpfulCompetence: important Character: Priceless The greatest threat to any leader comes not from without, but from within. It is who we are, more than anything else, that will derail us. The traits we so value in great leaders is a matter of character. And it is through this character that our leadership is manifested. It creates the space in which we lead. Good leadership rests upon good character. It’s not by chance then that Mike Henry Sr., founder of the Lead Change Group, has gathered together twenty leadership experts to write The Character Based Leader about the importance of and the need for character and the challenge of leading from it. They hope, through the pages of this book, to inspire leaders to look inside themselves so that they might lead beyond themselves in the service of others. They define character-based leadership as leading from who you are rather than from power or position. These twenty-one dedicated experts—Tara Alemany, Chad Balthrop, Meghan M. Biro, S. Max Brown, Page Cole, Heather Coleman – Voss, Deborah Costello, Monica Diaz, Sonia DiMaulo, Georgia Feiste, Chery Gegelman, Christina Haxton, Mike Henry Sr., Will Lukang, Susan Mazza, Jennifer Miller, Jane Perdue, Lisa Petrilli, Dan Rockwell, Mary Schaefer, and Dan Shapiro—cover topics such as humility, communication, service, passion, discipline, trust, leading from our strengths, the power of character, and how we demonstrate good character every day. The Character Based Leader is both instructional and inspirational. It’s a good book to read chapter by chapter and reflect on the implications in your own life. The message is on-target and the best place to begin any leadership development program. It’s a call to make the choice to develop yourself so that you can lead with greater influence for the benefit of others. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:33 PM
11.19.12

Does This Doorframe Make My Head Look Big?Failure is not an option. And we learn a lot if we take the time to learn from our mistakes. But gain much more when we can learn from the mistakes of others before we find ourselves confronted with the same issues.The Wisdom of Failure by Laurance Weinzimmer and Jim McConoughey, examines the lessons learned by studying thousands of executives in hundreds of companies. They have discovered three areas where aspiring leaders fail: Unbalanced Orchestration (leadership failures at the organizational level)
The goal of the self-absorbed leader “isn’t necessarily status, position, or promotion. Rather, their goal is to have things work out the way they think they should work, because, well, they are the greatest.” This is an easy mindset to slip into. And unfortunately, it is almost impossible for a self-absorbed leader to recognize that they are just that. They need outside help, but when confronted, they are sure that the observation is of course, wrong. Underneath is all, self-absorption is “rooted in low self-esteem and a feeling of insecurity, as well as a profound discomfort with or disregard for what others bring to the table.” It is marked by “talking big, a sense of entitlement, a sense of infallibility, a lack of empathy for others, an intense desire to win at all costs, one-upmanship, a know-it-all attitude, and an inability to listen.” Michael Bryant, CEO of Centra Health explained it this way: “A good leader is like a coach of a basketball team. It is not important for the leader to score the points. It is important for his team to score the points. It’s not rocket science! So the one key to being an egoless leader is to understand the paradox….Self-absorbed leaders never get the paradox.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:55 PM
11.12.12

The Eight Pillars of Trust
EVERYTHING of value is built on trust. The Trust Edge explains how you and your organization can become trusted. A lack of trust is your biggest expense. It is the currency of business and life. Author David Horsager, explains that trust is tangible, learnable, and measureable. Trust is a confident belief in someone or something to do what is right, deliver what is promised, and to be the same every time in spite of circumstances. Horsager identifies twelve barriers to trust: conflict of interest, threat of litigation, lack of loyalty, increasing examples of others untrustworthiness, threat of exposure, lack of control over technology, fear of the unknown, negative experiences, individualism, differences between people, desire for instant gratification, and a focus on the negative.
The eight pillars of trust form the framework for learning to build trust and overcoming the twelve barriers. These all take time and are not quick fixes for any trust issue. Trust is built over time. Clarity. Clarity starts with honesty. People trust the clear and distrust the vague. Communicate clearly and frequently. Compassion. Think beyond yourself. There are four keys ways we show we care: listen, show appreciation, be engaged, and serve others. Character. Have high morals and be consistent in your thoughts, words, and actions. Always ask, “Am I doing the right thing?” Competency. Humility is the first step in learning. Create a regular plan for staying competent and capable. Commitment. Great leadership demands sacrifice. The people who stick with you when things are tough are the ones you can really trust. Connection. Trust is about relationships. In every interaction we increase or decrease trust. Be genuine, be grateful and avoid gossip. Contribution. You must deliver results to be trusted. Give attention, resources, time, opportunity, and help. Consistency. Probably the most important pillar of all as it gives meaning to all of the other pillars. You will never get one big chance to be trusted in your life; you will get thousands of small ones. Just one inconsistency can change people’s perspective. Horsager notes that in this flat world, because we can connect with so many, we have a hard time cultivating depth. Trust at its best is deep, making it difficult to gain the trust edge. In response we need to be even more intentional about developing the pillars of trust on a global level finding common ground and showing ourselves to be trustworthy.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:57 PM
08.14.12

Triple Crown Leadership
WITH far too much failed leadership on display, leaders should commit to building a different brand of leadership—Triple Crown Leadership, say authors Bob and Gregg Vanourek. Triple Crown leaders have the goal of building and sustaining organizations that are excellent (high performance), ethical (do the right thing), and enduring (stand the test of time). As with the Triple Crown in thoroughbred horseracing, it is an epic quest that is audacious but not impossible. Triple Crown leaders integrate five practices that build excellent, ethical, and enduring organizations: Seek “head and heart.” The first step is putting together a triple crown team. Typically we look for people with the right “head” skills (experience, education, expertise), but they must have the intangible “heart” qualities (character, integrity, courage). Post “colors.” An organization’s “colors” are its purpose, values, and vision. Leaders must engage all in developing the colors through a collaborative process, thereby increasing ownership and buy-in. People are free to act as long as they do so in accordance with the colors. Flex between “steel and velvet.” Triple Crown leaders cannot remain stuck in their normal style of leadership. They lead by flexing between the hard and soft edges of leadership, sometimes in command, other times willingly soliciting and following the leadership of others. If your actions are consistent with the colors—purpose, values, and vision—you will not appear inconsistent in your approach. Unleash “stewards.” Stewardship is everyone’s responsibility. It’s not empowerment handed down from the top but a culture where the freedom to act is expected as long as they act in accordance with the shared values and vision of the organization. It’s automatic. “Triple Crown leadership ebbs and flows dynamically from person to person—up, down, and around—depending on the person’s knowledge, skills, passion, and the nature and urgency of the challenge at hand.” (Look on pages 114 to 123 for lists of specific ideas on how boards, CEOs, managers, and people without authority can become Triple Crown stewards.) “Align.” Alignment builds trust. Alignment speeds up the process. Alignment should be collaborative, start where you are and cascade, and be flexible. It requires some finesse to get people on the same page while protecting the innovative mavericks and creating the conditions for operating in a state of flow. There is a big difference between completing an alignment exercise at a one-shot retreat and actually creating an aligned organization, between having a purpose statement and being purpose-driven, between having values and upholding them when the pressure is on, between saying you are vying for the triple crown and actually aligning the enterprise to achieve it. The five triple crown leadership practices are related and mutually reinforcing. Building excellent, ethical, and enduring organizations requires a commitment from many people over many years, and the view that leaders exist at all levels. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:31 PM
07.27.12

The Titleless LeaderLeading without a title is about taking personal responsibility. We—the world—is in desperate need of people who will choose to lead whenever and wherever they can. In The Titleless Leader, Nan Russell describes where we are:Everything isn’t alright in our workplaces. People are frustrated, angry, disillusioned, tired, and afraid. Not to mention skeptical, cynical, and distrustful. And those plaques touting people as the most important asset should be taken down. They’re a hypocritical reminder of last century’s failed promise. Not everywhere, of course, but in far too many organizations.But we have a choice. We can continue the de-motivating spiral of self-indulgent, unaligned leaders, or we can decide to create tomorrow’s workplaces through a new kind of leadership. It’s the kind that doesn’t come with a title. It’s not determined by rank, responsibilities, or position. No one needs to appoint you, promote you, or nominate you. You decide.What Russell is talking about here is a different kind of leadership that starts with what all good leadership begins with: self-discipline. It is taking responsibility for the outcomes in your area. It’s setting an example of behaviors that are aligned with values. For Russell, titleless leadership is based on four cornerstones: Self-Alignment: Behavioral integrity. People remember what you are. Possibility Seeds: Encourages and nurtures others. Titleless leaders plant possibility seeds “not because there’s a mentoring- or succession-planning program, but because they’re operating with a better together approach.” Soul Courage: Step-up and offer your best self. Push outside your comfort zone to do the right thing. and Winning Philosophies: It’s only when we’re all winning that we truly all win. Focus on group wins and not the politics of individual wins. The Titleless Leader is a handbook of behaviors and thinking to help you lead from where you are. Certainly, they’re not easy and require some change in perspective, but they will create more meaning and value in your workplace and more importantly, in your life. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:58 PM
07.25.12

If It's Important, Be There
IN Contented Cows Still Give Better Milk, authors Bill Catlette and Richard Hadden make the point that organizations with contented employees understand that one of the most fundamental precepts in the whole workplace arena is that “the person who started for them this morning is as close to a ‘model employee’ as they’re ever going to get.” So the best companies do something about it. They are fanatical about training people not only with skills they need, but they also carefully train them in the organization’s traditions, values, and philosophies. But this is the part (too) many leaders just don’t get: “People want to know that the training course they’re taking the time to sit through is as important to senior management as it is supposed to be to them.” How do you communicate that? “This often requires senior management to ride along with them—not in their own condensed mini-versions, but alongside everyone else.” Catlette and Hadden go on to say, “There should be no executive parking spaces when it comes to training. Managers must participate enthusiastically and, more important, be able to demonstrate the skills they expect everyone else to learn.” The message is clear. If it’s important to you, it will be important to them. It’s quite common to hear, “If this is so important, where are they?” Without the visible support of the leadership, commitment to the training is compromised. Leaders need to visibly communicate: “This is important—so important that I went through it before you did. I’m using it, and now I want and expect you to do the same. That’s why I’m here." 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:49 PM
07.11.12

Having an Informed FaithWhether developing an organization or (especially) an individual, having an informed faith is essential. We value seeing things as they are—seeing reality. But potential is as much as part of reality as cold hard facts. Being able to see where an organization or an individual could go is vital for any leader.The authors of Higher Ambition put it this way: it’s the “ability to envision and believe in a company’s potential and to understand, within an environment often characterized by confusion, crisis, and underperformance, the real possibilities of success.” This is even harder to do when applying this idea to developing people. It’s easier to give up on people than to take the time to help them over their hurdles. To see what is and to see what could be. The combination is essential for leadership. They add, “On the one hand, these executives see the reality with clarity. This keeps them from being easily deluded or distracted, builds the confidence and trust of those around them that they ‘get it,’ and motivates them to make difficult decisions about which activities to pursue and which to jettison, as well as which people to retain and which to encourage into other endeavors. But they also see the potential with real excitement and enthusiasm. “As Roger Dickhout, co-founder and CEO of Pineridge Group, put it: ‘It’s believing in the potential of what you want to be, as opposed to describing what you are. That intention attracts opportunities to you.’” Make potential part of your reality. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:26 AM
06.15.12

What’s Wrong with Leadership Training Today? IT’S A DIFFICULT TIME for leaders. “Our familiarity with and disrespect for our leaders,” writes Harvard professor, Barbara Kellerman in The End of Leadership, “coupled with our feeling entitled and being emboldened, saps their authority, which then drains their power and influence.”
IT’S A DIFFICULT TIME for leaders. “Our familiarity with and disrespect for our leaders,” writes Harvard professor, Barbara Kellerman in The End of Leadership, “coupled with our feeling entitled and being emboldened, saps their authority, which then drains their power and influence.”
Commenting on the 2011 budget-ceiling talks she finds that Barack Obama’s followers are “more disposed to resist him than to support him….No one was able to lead…and no one was willing to follow.” Perhaps no one was able to lead because no one was willing to follow. Leading in America is now more difficult than ever “not only because we have too many bad leaders, but because we have too many bad followers.” Kellerman cites lack of involvement as the culprit, but it goes further than that. We have never been taught how to support a leader in the right way. Followership is as important a skill as leadership. Kellerman notes that the contract—you lead, I’ll follow—between leaders and followers has been undermined “because of the information to which followers now have access, too many leaders are judged by too many followers to be unethical or incompetent or both.” Familiarity with our leaders had bred contempt. Technology has changed the social landscape providing us with so much more information. But it has, I would argue, informed us more broadly, but for the most part, not more deeply—if we even had the time or the inclination to go more deeply. I would also suggest that we are not, at times, very good judges. We lack facts and context much of the time. What frames our judgments are often selfish concerns—just like our leaders. And too, we rarely judge others in the manner that we would like to be judged. The End of Leadership offers a report on the state of leadership and followership today. Kellerman has surveyed the history of leadership to pinpoint a trend—the diminishing power and influence of leaders and people in authority and the increase of power and influence of ordinary people—followers. In recent years, communications technology has played a large part. “The effect on leaders is to diminish them. The more we know about how leaders and managers manage, the more they tend to shrink.” The contract between leader and follower has changed. The assumptions on which it was based has changed because first, “the old justifications for having power, authority, and influence are no longer so persuasive and second because people in the present think of themselves are more important, more entitled than did people in the past.” Kurt Anderson asked in New York magazine, Is Democracy Killing Democracy? He writes: So now we have a country absolutely teeming with irregular passions and artful misrepresentations, whipped up to an unprecedented pitch and volume by the fundamentally new means of 24/7 cable and the hyperdemocratic web. [There is ] the misapprehension that democratic governing is supposed to be the same as democratic discourse, that elected officials are virtuous to the extent that they too default to unbudging, sky-is-falling recalcitrance and refusal. And the elected officials, as never before, are indulging that populist fantasy. Just as the founders feared, American democracy has gotten way too democratic. I wonder if we have—in our radical shift to the entitlement of followers and the bad leadership that encourages it—sowed the seeds for an overcorrection in the other direction. Perhaps we will find ourselves welcoming a society governed by extremely self-deferential leaders to sort it out. History shows us that when societies get to the point that they can’t properly govern themselves, they don’t get more disciplined and make the necessary corrections, they instead get behind anyone that will make all the “bad” go away—usually with negative consequences. Because we have been able to “do” leadership in a way that has been less respectful of the follower and get away with it, doesn’t mean we were doing it right. While old methods of leadership are not tolerated at the present time, it doesn’t mean leadership itself has changed. The “right” way of leading people has never changed; our approach to leading people just swings back and forth from ditch to ditch. History shows us that we rarely get it “right.” Kellerman observes that in the world in which we actually live, “leaders tend to put self-interest ahead of the public interest.” How true. The idea that our leaders reflect who we are should give us pause. Much of the problem with leadership training, in my view, is that we are trying to develop something in leaders long after the train has already left the station. It’s not that it can’t be done. It’ is just much harder. Good leadership development begins much earlier in life. Given our situation, Kellerman asks, how do we learn to lead in the twenty-first century? How to learn to lead when leaders are diminished from what they were, even in the recent past? How to learn to lead when resources such as power, authority, and influence are scarcer than before—and when any number of followers is as likely to be resistant as deferent? And, finally, how to learn to lead when the context itself is fraught with complexity and constraint? Could we develop betters leaders if we developed better followers and would better followers create a pool of better leaders? Should we be training for followership? Should we be teaching the right kind of followership is leadership? The End of Leadership is a vitally important book that every leader/follower should read and consider, but it is the tip of a much larger discussion about leadership, followership and society. Kellerman writes that “it is meant as a caution about the future of leadership in the twenty-first century. For nearly everywhere, leaders are found wanting, followers are restive, and the context is changing—sometimes at warp speed. So unless we get a grip, the prognosis is grim.” Kellerman says that the leadership industry must make at least four changes:
Kellerman lays the foundation with this: “We need to think of leadership as a creative act—for which leaders and followers both are educated, for which leaders and followers both are prepared over a lifetime of learning….There are ways to educate women and men so they learn to be good, smart followers as well as good, smart leaders, and develop as large capacity for contextual intelligence as for emotional intelligence.” Absolutely.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:19 PM
05.21.12

The Twelve Absolutes of Leadership
Gary Burnison considers leadership to be a privilege. Most people like the idea of leadership but few count the cost. He says, “To lead is to be all in, transparent and accessible, calm in the face of upset and even crisis, and always mindful that you are a steward of something bigger than yourself.” That’s not easy. To whom much is given much is required. That’s the part that easily trips us up. His book, The Twelve Absolutes of Leadership offers insight from his lifetime in leadership, interacting with some of the world's top leaders in the C-suite and boardrooms, as well as heads of state. He offers a framework based on fundamental human truths and the essential elements of leadership. The “Absolutes” are building blocks that must be present regardless of your leadership style or approach. Here are the 12 Absolutes with Burnison’s thoughts on each:
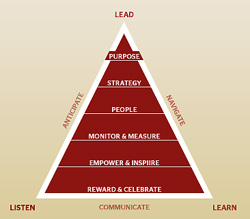
Burnison reminds us that leadership is about people. “To lead,” he writes, “is to make an emotional connection on a very real and human level in every interaction.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:47 PM
05.16.12

Real Leaders Don’t Boss
RICH EICH says that Real Leaders Don’t Boss. “Real leaders are rare in today’s fast-moving, financially driven world. In their place are fast-track wannabes and imposters, intent on instant gratification in the form of quick (and unsustainable) bottom-line results.” As Eich observes, there are far too many bosses and not enough leaders. Bosses who are too narrowly focused, see employees as tools, are respecters of position, controls rather than empowers, and sets expectations for others that they wouldn’t wish on themselves. Eich identifies and then dedicates a chapter to each of eight essentials of effective leadership:
These eight essentials are about treating people right. They also reflect an extended range of responses to people and situations that “bosses” either don’t possess or exercise. “Real” leaders inspire others to lead wherever they find themselves in the organization. They help them to find meaning in their own lives. Leadership isn’t something you are born with, it is something that is thoughtfully developed throughout life. Eich notes, “Most real leaders aren’t born with some innate ability transforming them into magnets that attract others to follow them. They may have expectations placed on them to rise above their present situation or environment; they may even have an inborn strong desire to serve others and accomplish something unique. In most cases, however, leadership skills are developed and honed in the battlefield of life, where leaders discover their drive, passion, and wisdom.” It is these opportunities to rise above our present situation and environment that we should be seeking out and providing for our children—the next generation of leaders. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:14 PM
04.02.12

A Leader’s Most Dangerous Thought Leadership is demanding. It takes a personal toll and if we are not careful, we can begin to make it about us. It’s not a difficult position to rationalize. The problem with “I deserve” is that it changes our perspective. We see our contribution as more important than anyone else’s contribution. It creates a lack of proportion. It leads to a wrong motivation for leadership: leadership as a means to better get what we want. We see this all the time—the hypocrisy of leadership—seeking positions of power while denying the real nature of leadership. Service. And it is why we have seen far too many leaders derail. “I deserve” thinking threatens our ability to lead. It diminishes our influence because it takes us out of the community; out of the narrative. We no longer lead for the cause but only as a means to serve ourselves. Side effects include distrust, cynicism, the wrong kind competition and isolated thinking. Good leadership creates connections and avoids points of disconnect. The opposite of “I deserve” isn’t denying ourselves. We must take care of our needs in the same way we take of the needs of others or we will not be able to properly serve others. The antidote is remembering that leadership is not a position but a role. It’s a gift and it is temporary. It’s channeling all that we are for the benefit of others. Leadership is something we live, for others.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:00 PM
03.07.12

8 Essential Principles of Effective LeadershipGayle Beebe has written a book on how effective and moral leaders develop and more importantly, how they must continue to develop. Too often leaders think they have made it and stop working on themselves. Eventually they become leaders in title only. He writes in The Shaping of an Effective Leader:Our understanding of leadership does not come to us all at once. It takes time. In our instant-oriented culture we often want to short-circuit the thinking, reflecting and acting that mark our progressive development as leaders. Understanding how leaders develop and why they matter requires discernment, wisdom and insight.Leadership development is a process. Seeking instant results and ladder-climbing can leave us little to show for our efforts. Some leaders “penchant for moving on has allowed them to avoid facing the consequences of their decisions” thereby restricting their development. “They have changed responsibility so often that they have failed to undergo the development that comes from facing mistakes.” Then too, some leaders are so busy “fixing problems” with personnel changes that they never really face the core issue—themselves. Beebe draws heavily on Peter Drucker’s teachings and writings. The implementation of these eight principles will have a profound impact on your leadership: The Necessity of Character. “The formation of our character creates predictability to our leadership. Predictability, dependability and consistency: these three qualities ensure that our leadership is reliable and motivates people to place their confidence in us.” The Importance of Competence. “Drucker emphasized the importance of a liberal arts education, which he believed was the best training for learning how to synthesize discrete pieces of information into a meaningful whole….All knowledge must be brought to bear on our challenges.” The Advantage of Team Chemistry. Generosity builds teams. Greed destroys them. “Eventually it leads to a lack of respect for the needs and ambitions of others because our own needs and ambitions overrun all normal boundaries and expectations….It is made manifest by an excessive need for acclaim, attention or compensation. It also is evident in an inability to share the limelight. Malice and thoughtlessness are twin manifestations of this same inner drive.” The Interplay of Culture and Context. Cultures shape people. “An appropriate structure (culture) is the one best suited to maximize the performance of our people.” In addition, “culture is also shaped and influenced by the environmental context in which it exists….One of the biggest mistakes a company can make...is when it operates on the basis of what it prefers and how it believes a society should function, rather than how the society actually operates.” The Strength of Compatibility and Coherence. “We have to know ourselves well enough and understand ourselves deeply enough to enter into the kind of human communities that will sustain us.” The Guidance of Convictions. “An individual must balance a strong self-understanding and self-esteem with the necessity of confronting all issues both objectively and subjectively….A self-differentiated leader is one who has a head (intellectual capacity) from which he speaks with conviction while having a heart (empathetic capacity) with which he stays connected to people.” The Significance of Maintaining Our Connections. “Remaining connected to our work associates even when we make hard decisions is only possible if we maintain personal integrity, display competence, create team chemistry, develop a great culture, retain a level of compatibility that motivates, and display a level of conviction and predictability that people trust.” The Opportunity to Make an Ultimate Contribution. The ultimate contribution is in our quest for meaning. “Work, meaningful as it may be, can lose its appeal….Drucker advocated developing a second interest long before we exhaust our first interest. This parallel career becomes not only our lifeblood for meaningful work and service opportunities in the future, but also a source of great support if we were to experience major setbacks in the present.” Beebe writes, “These principles do not operate separately from one another. Indeed, they build on each other, and their effect is cumulative.” These eight principles will improve our contribution as leaders if we are mindful of them on a daily basis throughout the rest of our lives. At each level our character is tested and developed. Effective leadership is built on moral authority grounded in character. Leadership is a privilege that we earn every day. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:36 PM
02.15.12

The Inner World of the Leader: On the Couch with Manfred Kets de Vries
WHY do organizations attempt to function on the basis that executives are logical, rational, dependable human beings? Kets de Vries is a clinical professor of leadership development at INSEAD. His background in economics, management, and psychoanalysis, adds a great deal of richness and context to the study of leadership. Over the last three years Jossey-Bass has published a mostly revised and updated collection of his rather large body of thoughtful-provoking writing in this series of three books. The opinion of one of the power holders in the [Harvard Business School] Organizational Behavior department was that I would never write anything. That particular person must have had a very good understanding of human behavior. One of the small pleasures of life is doing something people say you will never do. I believe that [Reflections on Character and Leadership] is my twenty-ninth book. I have always thought that academics are masters in character assassination.Kets de Vries begins the series with Reflections on Character and Leadership. In it he examines some of the major issues about leadership. What makes a leader? What is good leadership? And what is bad? What happens to organizations if a leader derails? What are the impacts of successful and failed leadership on followers and organizations? Every leader needs someone who is willing to speak out and tell the leader how it is in order to create checks and balances—the counterweight of the person in power. Without such people leaders easily derail and organizations can become paralyzed by fear, mistrust and insecurity. He explains how leaders construct organizations that are great places to work. The era of the highly structured organization is past….Clearly, some executives may not be able to deal with the ambiguities that this new kind of networking, boundary-less organization entails—the external boundaries in an organization can be removed fairly easily, but the boundaries inside people’s heads are more difficult to dissolve. Weaning some leaders away from their need for authority, structures, and controls may take considerable time and effort. In the long run, however, it will be well worth it. Eventually, they will enjoy their work more, and be more effective.Kets de Vries says that narcissism is an inescapable aspect of human nature—and leadership. It has had a generally bad press. “There is such a thing as a healthy dose and it lies somewhere on a wide spectrum that ranges from grandiosity and showmanship to denigration and coldness.” He begins Reflections on Leadership and Career Development by discussing narcissism and leadership. Leadership can be pathologically destructive or intensely inspirational. But what is it about the leaders themselves that causes them to be one or the other? I believe the answer lies in the degree of narcissism in the personality of the leader in question. He discusses the qualities characterize great leaders and the interactions, both positive and dysfunctional, between leaders and followers. “The truly effective leader “is the one who knows how to balance reflection and action by using self-insight as a restraining force when the sirens of power start singing.” He takes a look at leadership archetypes and how they operate within organizations—and how to deal with them. He concludes with an examination of the issues, anxieties, and opportunities that we face at midlife and beyond. How can we alter our perspective on life to become “twice-born”? Finally in Reflections on Groups and Organizations, Kets de Vries looks at leadership issues in the context of groups and organizations. He examines various ways in which neurotic individuals create neurotic organizations. He describes how folie à duex—literally “madness shared by two”—works in an organizational setting; how individuals’ activity or passivity and tendency toward conformism can contribute to the process and what checks and balances could be used to forestall and manage dysfunctional leader-follower relationships.Kets de Vries doesn’t believe leaders are born. While some seem to have a head start, leadership potential can be developed. “Leadership potential is a delicate interplay between nature and nurture.” An effective leader is someone, says Kets de Vries, “who is a little like a Zen riddle, or kōan—a paradox who is comfortable dealing with paradoxes. Because a leader has to be active and reflective, an introvert and an extrovert, engaged in both divergent and convergent thinking. A leader needs IQ, but also EQ. A leader has to think atomistically, but also holistically, for the short term and the long term. Anyone who can balance these contradictions effectively will do well.” He advocates the building of an organization wide coaching culture ad discuss how it can be implemented. There are several basic things that any leader has to do: provide focus, understand what makes their people tick, set an example, and make things happen. However, the distinguishing factor between mediocre and great leadership is always the same: the creation of meaning….When it comes down to it, people are searching for meaning. This series of books cannot be read quickly. Each book in the series seeks to understand leaders, human nature and its vicissitudes. They need to be reflected on. They will challenge your thinking, widen your perspective and inspire you to do better.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:08 PM
01.16.12

12 Reasons You Will Be a Better Leader this Year
1. Because you are generous with information. You know it enables and values others. 2. Because you eschew the trappings of power. You respect your position too much to let yourself become self-absorbed and disconnected from those you serve. 3. Because you know leadership isn’t about how well you are appreciated, but it’s about endlessly showing your appreciation of others. Leadership isn’t about how you feel, but how you make others feel. 4. Because you are honored to lead, you genuinely respect and care for the people you serve. 5. Because you avoid the trivial and stay focused on your core values and the vision they enable. You will always pay attention to what matters most and you communicate it tirelessly and with clarity. 6. Because you are driven to produce and are accountable for it and expect the same from others. 7. Because you take time to reflect to keep yourself aligned and to continually evaluate your impact. 8. Because you exercise. You know that regular exercise not only makes you feel better physically and it has a profound impact on your cognitive abilities and mental health. 9. Because you are curious, you are committed to being a lifelong learner and building a learning culture within your team and organization. You won’t rely on what worked for you in the past. 10. Because you are humble enough to know that you don’t have all the answers and it doesn’t have to be your way and it is in fact, unhealthy for you to insist on it. 11. Because you are committed to building others greater than yourself. You are validated not by your own knowledge and accomplishments but by those you help to succeed. You are passionate about and energized by the people you serve. 12. Because you know that you are setting an example for others to follow. Everything you do matters. You know it’s not about you.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:02 AM
12.07.11

True North Groups
YOU can’t do it alone. We often try to, imagining that we can see and know the things we need to know without the discerning eye of an outside point of view. Bill George and Doug Baker remind us in True North Groups that, “We need people around us to whom we can look for support and advice, who can help us develop as human beings. We need them to help us become better leaders in our work, our communities, and our families.” It’s easy to get off track. “Most of us know what our True North is, but we are constantly pressured from external sources to deviate from it. Or we are seduced by extrinsic rewards like money, power, and recognition that cause us to detour from our True North.” A True North Group is comprised of six to eight trusted peers who meet on a regular basis to discuss the important questions of their lives and to support each other during difficult times. At various times, each person in the group will serve as a mentor or coach to others. True North Groups are not just about having a place to go to help you with your challenges. Done well, a group will encourage you to make the necessary course corrections that will help you to avoid the avoidable problems we all can get ourselves into. Save us from ourselves so to speak. It’s also a place to share successes.At stake is our own vulnerability. Even if we are afraid of the idea, it’s not difficult to see the value in it. George and Baker have been doing this for decades and share the nuts and bolts of creating your own group. It begins with picking the right people and that may not include your close friends. It’s based on trust and a commitment to personal growth. The authors list the following characteristics of ideal group members:
Next steps include, Norming (establishing how the group functions), Storming (behaviors that may impede your group), Performing (maintaining and renewing your group) and Reforming (the need to restructure and start again). The appendix provides topics for discussion to get your group going and thinking in the right direction. You’ll also find Member Contracts, Ground Rules and other valuable resources for your own True North Group.>/p>

Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:27 PM
11.14.11

Do You Have Moral Overconfidence?In a recent Bloomberg Businessweek article, Harvard Business School Dean, Nitin Nohria stated that because we all suffer from “moral overconfidence,” the most important thing business schools could be teaching is humility. He writes:Many people view “character” as an immutable trait formed during childhood and adolescence. I believe character development is similar to the development of knowledge or wisdom—it’s a lifelong process. The world isn’t neatly divided into good people and bad people. Most will behave well or poorly, depending on the context….Business leaders need to remember that most of us have too much confidence in our strength of character.Nohria is exactly correct. Good leadership is humble leadership. Humility is living in truth. The truth about our limitations and an understanding of our proper relationship with others. And do we share with each other a moral overconfidence—a certain naiveté about ourselves that carries with it the seeds of our own destruction. Humility gives us a better understanding of how we are to treat each other. Without it we operate from only one perspective—our own. This kills influence. As leaders, we are to work with people, not over them. It is far too tempting to think hierarchically and not relationally. In Leading Without Power, Max De Pree says that “Leaders belong to their followers.” Too many leaders try to create a buffer between themselves and their followers, when instead, they need to be leading from among their followers. A humble leader will close the gap between themselves and others. Humility manifests itself in understanding the need to learn. Authority disciplined by humility is teachable. It is arrogant to think that once we have the position or a title, we’ve arrived. We never arrive. It is merely an opportunity to learn from another perspective. If you stop learning, you stop leading. It’s something we need to stay on top of because if we don’t, life has a way of bringing us up short in an effort to get us to wake-up and start learning. Leadership has a way of revealing our weaknesses.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:07 PM
11.07.11

3 Self-Limiting Mindsets that Will Hold You Back at Work
THE workplace has enough challenges and obstacles without us getting in our own way. But too often, we sabotage ourselves. Whether it’s internal forces that cause us to sell ourselves short or it’s a matter of having been conditioned not to “toot our own horn,” people have a marked tendency to avoid the limelight when in truth, they belong in it. What’s more, if you’ve always been the ‘unsung hero,’ management wants to know who you are. In my executive coaching business, I’ve worked with scores of clients over the years to help them overcome self-limiting mindsets that were holding them back in the workplace. Here are some of the most common issues:
Remember, if you don’t take credit for your own success, someone else will. That doesn’t serve your own interests. And if you think about it, it doesn’t serve the long-term interests of the company. You have a professional duty to yourself as well as your company to make sure your accomplishments are recognized and credited to you.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:11 AM
11.04.11

If You Will Lead ... WellIf You Will Lead by Doug Moran, is a good book for reading chapter by chapter and stopping to reflect on each one. Based on Kipling’s poem “If–,” Moran has created the “If” Sixteen Leadership Framework to help us answer four important questions:1. Who am I, and what do I believe? 2. What do I want? 3. How will I attract and motivate others? 4. How will I earn and retrain the privilege to lead? Combining historical lessons with examples of his contemporaries, Moran effectively communicates the sixteen attributes: character, authenticity, integrity, self-efficacy, ambition, vision, boldness, resilience, inspiration, courage, selflessness, stamina, composure, patience, enthusiasm, and accountability. Leadership is a choice and how well you will lead is up to you. “The greatest uncertainties associated with leadership,” writes Moran, “are how we use the skills and abilities we have, how hard we work to acquire and build those we don’t, and how well we create positive change by inspiring and motivating others. We reduce the uncertainty by becoming more aware of what it takes to lead well. We reduce uncertainty further by choosing to invest and commit ourselves to our development.”

Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:58 PM
10.28.11

No Fear of Failure
GARY BURNISON, CEO of Korn/Ferry International, shares one-on-one conversations with a dozen successful leaders in No Fear of Failure. He found a common theme in these conversations: they each “exhibited tremendous courage around the possibility, and even the inevitability at times, of failure. In the face of uncertainty, they draw on an inner strength that allows them to strive for what is possible rather than become paralyzed by the risk of failure.” Indra Nooyi, chairman, and CEO of PepsiCo, on Learning: “The one thing I have learned as a CEO is that leadership at various levels is vastly different….As you move up the organization, the requirements for leading that organization doesn’t grow vertically; they grow exponentially….If you want to improve the organization, you have to improve yourself and the organization gets pulled up with you….Just because you are a CEO, don’t think you have landed. You must continually increase your learning, the way you think, and the way you approach the organization.” Vicente Fox, former president of Mexico, on Humility: “The higher leaders rise, the further they move from where they began. The danger is that success will undermine their humility, leaving them out of touch and disconnected….There are so many temptations that would undermine your humility. You have to develop that part, work on it all your life. It’s easy to fall on the other side, especially when you are in power and have a position.” Daniel Vasella, MD, chairman of Novartis AG on Stewardship: A vineyard owner pointed to a stone wall and explained how his grandfather had started building it and then his father added to it as did he. Vasella “found this to be a fascinating analogy. It’s like no great cathedral was build in one generation. There are several implications. First, you’re not here to take advantage but rather to add. Second, you will not finish. Third, it is very important that the overall vision of what is being built be shared by several people over time.” Coach John McKissick, the “winningest” coach in football on Coaching: “I don’t coach football, I coach kids.” His code is “to live clean, think clean, and stop doing all the things that will destroy them physically, mentally, and morally, and to start doing things that will make them cleaner, finer, and more competent. That’s not a sacrifice. I tell them that all the time. ‘I’m helping you be a better person and a better player.’” One of the most important leadership lessons Burnison learned in his career was that “leadership is all about the other person. No matter the topic—whether someone is being fired or has just told you about a serious health issue—that person should leave your office feeling better than when he or she entered.… For the CEO there is no off-the-cuff remark. Leadership demands introspection and an understanding of the clout that one’s words and actions carry.” The conversations Burnison shares will influence your leadership in profound ways. As leaders, we need to keep learning. It’s key to our success. It’s sad how many leaders do not actively pursue their own leadership development. This book will help. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:49 AM
10.26.11

It’s Not About You It’s Not About You (Reissued as The Go-Giver Leader) by Bob Burg and John David Mann, is the story of a leader’s journey. A journey any good leader has to take.
It’s Not About You (Reissued as The Go-Giver Leader) by Bob Burg and John David Mann, is the story of a leader’s journey. A journey any good leader has to take.
Ben begins with an agenda. His job is to convince or if necessary, to steamroll a manufacturer of high-quality chairs to accepting a merger. Ben’s company believes it to be a good thing, but the target company is not so sure. Ben’s mindset as he starts out is: “how do I get them to do what I want them to do.” Somewhere between getting people to understand him and slowing-down long enough to understand them, he found his answer. Through a series of encounters with a mentor—Aunt Elle—and a lot of reflection Ben comes to understand that it is not about him. His journey causes him to reflect on five lessons: Lesson #1: Hold the Vision. The hard part isn’t coming up with the vision, it’s holding on to the vision. “As a leader, your job is to hold fast to the big picture, to keep seeing it in your mind’s eye, with crystal clarity, where it is you are going—that place that right at this moment exists only in your mind's eye. And to keep seeing that, even when nobody else does.” Lesson #2: Build Your People. “People have all sorts of amazing qualities and natural abilities trapped inside them. With the wood, it’s knowing how to apply the heat. With people, it’s applying your belief.” If you give people something great to live up to, they usually will. “How influential you are, comes down to your intention. What are you focused on? Your benefit, or theirs?” The more you yield, the more power you have. Lesson #3: Do the Work. Be humble and stay grounded. Aunt Elle said, “People who achieve great things that the world will never forget, start out by accomplishing small things the world will never see.” Lesson #4: Stand for Something. Lead from who you are. People will figure it out anyway. People need to trust your competence, but they need to trust your character more. “Competence is simply the baseline, the thing that puts you in the game. It matters, but honestly, it’s a dime a dozen.” The authors remind us that you can only lead as far as you grow. Aunt Elle says, “What you have to give, you offer least of all through what you say; in greater part through what you do; but in greatest part through who you are.” Lesson #5: Share the Mantle. It’s not about you. “You are not their dreams, you are only the steward of those dreams. And leaders often get it backwards and start thinking they not only hold the best of others but they are the best….The moment you start thinking it’s all about you, that you’re the deal, is the moment you begin losing your capacity to positively influence others’ lives.” Whatever great parenting looks like, it is not about the parent. The Go-Giver Leader is a great presentation of solid life lessons. A book to be read and passed around. Unfortunately, “it’s not about you,” is not the kind of lesson that once learned, is always remembered. If it was, fewer great leaders would finish poorly after so many years of outstanding service. This is an issue that we face over and over again, but hopefully in ever diminishing frequency and intensity as our leadership matures. This book is a great reminder of the power of the right kind of leadership; leadership that comes from an inner strength of understanding, service and outgoing concern for others.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:29 PM
10.10.11

Maxwell's 5 Levels of Leadership
OVER 30 years ago, John Maxwell began developing the 5 Levels of Leadership. It has been presented before but never to this depth and completeness. The 5 Levels express a way to understand and organize your leadership growth. Each of the levels builds on the previous one and you can only progress to the next level once you have mastered the previous level. As you go higher it is easier to lead because your influence grows as well, as your leadership becomes more service-oriented. Maxwell says it takes longer than you think to get to the top level—and many never do. At the same time, you can go down very quickly. But if you have developed the right kinds of relationships with others, they will support you through your missteps and fumbles. As shown below, the first level is POSITION. At this level, people follow you because they have to. Your influence comes from your position. While that’s not bad—you probably got the position because of your leadership potential—you don’t want to stay here. Leadership is about relationships and leaders will make it their business to develop them. The second level is PERMISSION. People follow you because they want to. Permission is about building relationships. It focuses on the value of each person and opens up communication. Connecting with others begins with connecting with and growing yourself. Understanding that the first person I must get along with is me, the first person to cause me problems is me, the first person that must change is me, and the first person that can make a difference is me. Level three – PRODUCTION – recognizes that relationships alone are not enough. A leader is tasked with getting things done. Production level leaders are followed because of what they have done for the organization. They get things done. Their credibility is based on their example. The ability to get results alone doesn’t make you a leader. Leaders are measured by what the entire group accomplishes and not by the individual efforts of the person in charge. Leaders develop their people into a team to get results. To get to the next level you must develop your people. The fourth level is PEOPLE DEVELOPMENT. Leaders become great because they empower others. They develop more leaders. “Production may win games, but People Development wins championships.” People development assures that growth can be sustained. Self-centered, insecure leaders neglect this stage in their development. Maxwell estimates that less than 1 percent of all leaders ever reach Level 5 – THE PINNACLE. Leaders at this level understand that the highest goal of leadership is to develop more leaders, not to gain followers or do work. Level 5 leaders develop Level 4 leaders. Developing leaders that can, in turn, develop leaders is hard work and takes a great deal of skill, focus, and a lifetime commitment. But those leaders that do create Level 5 organizations. They create opportunities that other leaders don’t. Level 5 leaders leverage their own leadership through others. People follow these leaders because of what they are and what they represent. “When you lead an organization, you can’t be focused on just fulfilling the vision or getting work done.” 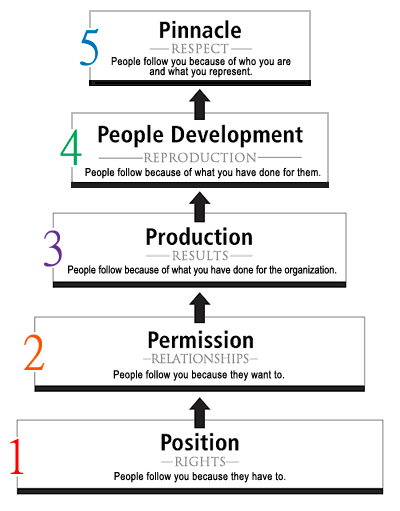 In addition to describing each of the Levels in detail, Maxwell shares upside and downside of each Level, how the 21 Irrefutable Laws of Leadership relate to each Level, an assessment to gauge your current level of leadership, and most practical, a growth guide to help you understand the mindset needed to move from one level to the next.

Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:26 AM
09.16.11

Too Many Bosses, Too Few LeadersRajeev Peshawaria says ironically, even though leadership hasn’t changed, we have Too Many Bosses, Too Few Leaders. The difference between mere bosses and leaders is that “leaders find the energy to stay on and fight, and energize others around them, while nonleaders give up.”“Superior leadership requires incredible amounts of emotional energy—the power to stay the course despite the most formidable of obstacles.” This energy comes from discovering your purpose and values. One of the biggest reasons we have many poor leaders is that too many of them get into leadership for the wrong reasons—personal fame, fortune or glory—or are given positions based on competence alone. Peshawaria cautions that “accepting a leadership position without carefully considering what you really want for yourself and for the people around you is a very dangerous proposition.” Real leadership is not easy or glamorous, but before you make the decision to lead, you should ask yourself six questions:
As a leader you need to focus on what he calls brains, bones, and nerves or setting direction, execution, and organizational culture. The trick of course is staying focused on these issues and not becoming distracted with all of the work you should be delegating. To lead, says Peshawaria, “leaders must first uncover their own sources of leadership energy—their purpose and values—then enlist a few co-leaders and align their energy toward a common purpose. Finally, the leader and her co-workers must galvanize the energy of the rest of the organization by shaping and managing the brains, bones, and nerves of the enterprise.” In his view then, leadership development programs should help participants to become more self-aware—who they are and what they want. Peshawaria notes IMD Switzerland professor George Kohlrieser’s thought that “when development focuses too much on presenting the ‘how-to’s,’ the result is not deep enough to change the inner life of a leader.” For the most part, most leaders know enough to lead, what is often lacking is the emotional intelligence to use it appropriately. In light of the rapidly changing world, Peshawaria raises an important question: Does it still make sense to identify a few, anoint them as high potentials, and invest disproportionately in their development? As leaders, we are not good stewards of people if we don’t give everyone a “similar development diet” and let the “cream rise to the top on its own. Peshawaria asks, “What if the world changes in ways that require a totally different type of potential in five years compared with the benchmarks used to identify today’s high potentials? What about late bloomers—those who may not show early brilliance, but might become very valuable later on? And what about the negative impact on the morale of those not chosen as high potentials? It might be time to rethink the ‘best practice’ of identifying and developing a pool of high potentials.” Amen. Then too, we also might want to rethink what it means to be a leader and stop developing functional leaders and instead develop true leaders that can lead in changing contexts. That’s an entirely different focus.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:01 AM
09.07.11

The Anywhere Leader
IN an environment of uncertainty and disruption, a successful leader must become what Mike Thompson calls an Anywhere Leader. The anywhere leader is the kind of leader who can land on their feet no matter what the setting or situation presents. Mike Thompson, author of The Anywhere Leader, says that “managers who have advanced their careers through tumultuous times are the ones who find a way to fit in, build trust, and contribute in any setting in which they are placed.” In order to adapt to and broker positive change in any environment, the Anywhere Leader possesses three key traits: Driven for Progress: Driven more by progress than politics. This means that they are discerning, daring, and determined. Because they are driven for progress, they operate with the right and proper motives and remain determined. To become a discerning leader, you need to immerse yourself in a constant state of evaluation…. Because these leaders never view their decisions as static, they aren’t consumed by trying to make the perfect call. They can confidently move forward, knowing that they can, and will, make adjustments as they go. Sensationally Curious: Having an exploratory mindset. They are consummate learners, who continue to grow and improve themselves, their team, and their work. Corollary strengths include being reflective, receptive, and perceptive. Anywhere Leaders have a distinctive ability to go deep with their own personal insights—calling upon their experiences, connecting with them, and forming some pretty strong opinions from them—yet put their egos aside and be open to the opinions of others. These leaders aren’t afraid to shift their thinking. They are in pursuit of the best idea regardless of whether it comes from them or from someone else. Vastly Resourceful: Able to get the most out of whatever you have to work with. Related strengths include being imaginative, inclusive and inventive. Because they are resourceful, they never get stuck in uncertainty, but invent their way through setbacks and out of tough spots. Leaders who can imagine are leaders who don’t get stuck. Thompson devotes a chapter to developing each of these traits. Few have all of these traits in ample amounts but awareness creates an opportunity to develop and/or manage these qualities. Not everyone is cut out to be an Anywhere Leader, nor does everyone need to be, says Thompson. “A job for an Anywhere Leader is one that features uncertainty—the unfamiliar, the unknown, and the unpredictable nature of business.” Thompson suggests that you structure your life so that you are accessible, wired (connected), attuned, and un-nested (MBWA) so that you are transportable or able to lead effectively, anywhere and everywhere you are. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:49 PM
08.26.11

Credibility: How Leaders Gain it and Lose It
CREDIBILITY is the foundation of leadership. Unfortunately, many people today do not trust their leaders. “Many wonder if there are any leaders left who have the strength of character to sustain their trust,” write Jim Kouzes and Barry Posner in Credibility: How Leaders Gain it and Lose It – Why People Demand It. While there is no single reason for it, “there is the gnawing sense in many corridors that leaders are not competent to handle the tough challenges; that they are not telling the truth; and that they are motivated more by greed and self-interest than concerns for the customer, the employees, or the country.” The time is ripe to revisit this topic. Credibility is a wake-up call to get back to the fundamentals; to remember that leadership is about relationships. “The secret to closing the credibility gap lies in a collective willingness to get closer, to become known, and to get to know others—as human beings, not as demographic categories, psychographic profiles, voting statistics, or employee numbers.”The process of building and sustaining credibility requires six disciplines: discover your self, appreciate constituents, affirm shared values, develop capacity, serve a purpose, and sustain hope. The authors devote a chapter to each of these issues. Personal responsibility is key to building and restoring credibility. Personal responsibility means understanding not only your actions, but the likely consequences and attending to them. Kouzes and Posner suggest following the “Six A’s of Leadership Accountability”: accept, admit, apologize, act, amend, attend. Leadership isn’t easy and in a constantly changing world, things like credibility and competency can seem elusive. But if we act on a daily basis, “in ways that increase people’s belief that we are honest, competent, inspiring, and forward-looking, people will be much more likely to want to follow your direction.” When leaders walk the talk, others are more likely to follow. Some leaders think that credibility once demonstrated and earned, is complete. But it must be renewed daily in everything we do. Unfair or not, it is the life that a good leader has chosen and demonstrates the understanding that the function of leaders is to serve, not be served. Credibility is an important book to help you sustain your influence. They conclude: Renewing credibility is a continuous human struggle and the ultimate leadership struggle. Strenuous effort is required to build and strengthen the foundations of working relationships. Constituents do not owe leaders allegiance. Leaders earn it. The gift of another’s trust and confidence is well worth the struggle and essential to meeting the challenges of leading people to places they have never been before. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:46 PM
08.19.11

What to Ask the Person in the Mirror
WHILE we might like to think otherwise, here is a fact about successful leaders: Successful leaders go through significant periods of time in which they feel confused, discouraged, and unsure of themselves and their decisions. They feel as if they should be somewhere else, doing something else. And unsuccessful leaders go through the same thing. The difference, says Harvard professor Robert Kaplan, is “how they deal with these periods of confusion and uncertainty. The trick lies not in avoiding these difficult periods; it lies in knowing how to step back, diagnose, regroup, and move forward.” This means not having all the right answers, but learning to ask the right questions. The challenge will be asking the right questions and making to the time to reflect on them. Reflecting is the key ingredient here and what many of us are short on. In his timeless book, What to Ask the Person in the Mirror, Kaplan offers seven basic types of inquiry or areas of focus—actually a system of inquiry that ties the leadership function together—that you should be looking at on a regular basis:Vision and Priorities. In this foundational area we need to be very clear and communicate it in a way that helps others to be able to determine where to focus their own efforts. Have you developed a clear vision and have you identified three to five clear priorities to achieve that vision? Managing Your Time. Your vision and priorities are reflected in the way you use your time. Track your time for two weeks. How does this compare to your key priorities? Giving and Getting Feedback. Most leaders do not effectively coach their subordinates, and also fail to get the critical coaching that they themselves need in order to excel. Do you cultivate advisors who are able to confront you with criticisms that you may not want to hear? Succession Planning and Delegation. When leaders fail to actively plan for succession, they do not delegate sufficiently and may become decision-making bottlenecks. Have you identified potential successors for your job? Why not? Evaluation and Alignment. It is often extremely difficult as an insider to see where you and the organization have drifted out of alignment. If you had to start again, how would you do it? Would you be doing the same things? Does the design of your organization, your incentive systems, your culture, and even your approach to leading still fit the needs of the organization? The Leader as Role Model. Many leaders fail to appreciate that their actions speak louder than their words. Self-awareness is critically important. Write down two or three key messages you believe you send with your behavior. Seek advice from key subordinates and advisors who directly observe your behavior, in order to answer this question: is there a “disconnect” between the messages you wish to send and those you are in fact sending? Reaching Your Potential. Know and learn to manage your strengths, weaknesses, and passions, not only to bring out your best, but also to create this same environment and aspiration among your staff. It’s not uncommon to find leaders that just stick to what they know best and not address those areas where they feel uncomfortable or insecure. All of these areas need to be reflected on as they each have an impact on the other. Taking the time to reflect is not easy and “doesn’t sound like fun, and may not sound as important as the fifty other things you have to fit into your day—but it works.” And be sure to take the time to reflect on these issues with your team as well. With many down-to-earth examples, Kaplan will expand the range of questions you should be asking yourself. What to Ask the Person in the Mirror will help you to rethink unsustainable behaviors that are damaging to both you and your organization and help you to mature and grow in your leadership role. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:57 PM
07.13.11

Who’s the Real Leader in Your Office? How often have you wondered who the real leader is in your office? Maybe you need to delegate a critical project, and you can’t afford to put your faith in someone who is not up to the job. Or maybe you work under several managers, and you want to make sure that you are building rapport with the one who counts. Or maybe you’d like to do some self-inventory in order to gauge how far you might rise after four or five additional years. All of these are good reasons for wondering how to accurately assess leadership potential. Unfortunately, most people have been taught to think about this issue in all the wrong ways. As a society, we rely on some rather misguided ideas about leadership success. As a result, when it comes to leadership selection decisions, we commit some pretty big errors. The first mistake stems from not knowing what qualities to seek in potential leaders. For decades we have been told that a charismatic personality, or Ivy-League training, or certain style, make all the difference. They don’t. None of these factors is a reliable predictor of leadership effectiveness. Other times we focus on qualities that do matter, but we don’t go far enough to seek a healthy balance. For example, we gravitate toward individuals who possess enormous passion and vision, but who lack solid character. Or we promote people with impressive courage, but who lack enough empathy to handle sticky social situations. The second big mistake we make when trying to judge leadership potential is the use of insufficient assessment techniques. In other words, even when we know what to look for, we don’t know how to look. We rely on backward looking interview questions, or inappropriate personality tests, or letters of reference from those who simply cannot predict how a person will perform in a fundamentally new position. Even the perennial favorite among promotion criteria – prior performance – is not a good indicator of future leadership success. At best, it tells only half the story. A solid manager with ten years of experience in sales, for example, might be poorly suited for a generalist role that will require her to lead an entire division. In our book Why Are We Bad at Picking Good Leaders? the two of us answer these crucial “what” and “how” questions. Based on more than fifteen years of experience working with premiere executive education programs and some of the best organizations in the world, we explain how to identify the very best leaders. Here are some highlights that will help you make your own determination: • Focus on the Qualities that Count. There are seven essential attributes of leadership success—integrity, empathy, emotional intelligence, vision, judgment, courage and passion. Take away just one, and a person who is called upon to lead will eventually fail. For example, former BP CEO Tony Hayward successfully climbed the corporate ladder for more than 25 years. But when the Deepwater Horizon exploded in 2010, his leadership faced a stiff challenge. In particular, he needed a strong sense of empathy to deal with an outraged public and a diverse set of competing constituents. Unfortunately, he was not up to the task. During an early interview, he claimed that the oil spill was “relatively tiny” compared with the “very big ocean,” and he consistently underestimated the extent of the leak. Obviously the spill wasn’t tiny from the vantage point of the Gulf Coast fishermen who lived nearby. Worse was the comment Hayward posted on Facebook to the effect that more than anyone else, he wanted the crisis to be over because, he said, “I want my life back.” This quip was widely seen as insensitive to the men whose lives had been lost in the explosion. President Obama responded, “He wouldn’t be working for me after any of those statements,” and although his days were probably already numbered, that was the last straw. Hayward lacked the kind of empathy that leaders need to survive. • Use the Right Assessment Techniques. Not too long ago, we met with a Fortune 500 president who was reeling from a poor hiring decision. Just six months after filling a key position, the company had to terminate its new hire and start a search all over again. When we asked the president how he and his team chose the person who was originally selected, he said: “He [the candidate who was hired] had great experience in the industry, a track record of turning around underperforming business, and already had relationships with several of our largest customers.” In addition, the company hired a search firm that conducted extensive background referencing, and all signs were positive. The candidate was results-oriented, friendly, well liked, and driven. While these findings sounded good, further investigation on our part revealed that the president fell into some classic assessment traps. The most serious mistake he made was relying on an evaluation process that was essentially backward looking. The president spent large amounts of time going over the candidate’s résumé and credentials: he asked about prior successes and failures, he asked others how the candidate performed, and so on. But this backward-looking investigation has limited predictive value when trying to determine a candidate’s likely success in a fundamentally new position. In our assessment practice, we overcome this obstacle by using a variety of different techniques, including simulations and case studies, direct observation in group settings, and specially created hypothetical scenarios that test a candidate’s leadership potential. This last technique is critical because it is forward looking. Unlike a typical interview question that asks candidates to discuss what happened in the past, these hypothetical situations present candidates with unfamiliar and challenging leadership situations. No amount of preparation or interview savvy will enable a candidate to fudge her answer or game the interview process. For more information on how the best companies in the world find first-rate leaders, including how to order Why Are We Bad at Picking Good Leaders? visit PickingBetterLeaders.com or email the authors directly at jcohn@liag-advisors.com and jmoran@liag-advisors.com.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:48 PM
06.17.11

42 Rules for Your New Leadership RoleWhether you have just been given a new leadership role, are currently in a leadership role, or have consciously decided to begin to lead from where you are, Pam Fox Rollin has created a concise guide for doing it successfully. 42 Rules for Your New Leadership Role gives you a starting point to work from to help prevent costly errors from occurring and will also aid in improving one's overall leadership experience.In all the busyness that surrounds a new role, it’s easy to forget the essential little things that make all the difference. We easily get caught up in the activity and don’t slow down enough to think about what it is we really need to be doing. New roles bring with it new expectations and that means doing things differently than we have done them before. 42 Rules will help you to gather your thoughts and lead thoughtfully. A quick daily review will help to keep you focused on the agenda that really matters. The book is divided into seven sections: Set Yourself up for Success: Take charge of your start. New roles require new starts. “When brains are overloaded, people tend to rely on what they’ve done before, even when that didn’t work very well or is out of place in the new context. Ironically, this tunnel vision and rigidity is especially true of leaders who have experienced success.” Map the Terrain: Investigate what matters. “If you’re going to deliver for someone, make it your priority to deliver up. That gives you breathing room to deliver for everyone else.” Common mistakes: Seeing smoke and running off to chase fires; Adopting other people’s agendas with insufficient data and thought; Becoming buried under the pent-up piles of tasks. Show up Wisely: Know yourself. Use your strengths, but avoid diagnosing problems to suit your strengths—dragging the problem into your comfort zone. “If you're good at running numbers, be aware that you may frame problems quantitatively, when lack of strategic insight is at the root of the problem. Seeing problems as they really are—rather than as you are—is especially essential in your first months on the job.” Start your Wins: You will feel the pressure to start with something dramatic. Pick smart quick wins. “The quick wins you choose will signal to others what matters to you….Bold moves in the second and third quarters of your tenure tend to accelerate your career.” Create your Management System: Define your own processes. At the same time, “lighten up on talking about ‘your leadership style’ and think more about what you could do that would be truly useful for your team members and colleagues.” Spotlight your team and grow more leaders. Stay Smart: Keep learning. “If you neglect to stay smart, seek feedback, and build your network, no one is likely to mention the gap. You’ll just become less valuable.” Set You and Your Team to Thrive: “Many people can drive themselves and their teams to exceed expectations for a quarter or two. The real challenge is to build a team—and a life—that sustains high performance.” “Extend a hand to the next round of leaders by sharing what you’ve learned.” What rules have helped you in your leadership role? 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:36 PM
05.26.11

5 Leadership Lessons: Redesigning Leadership
JOHN MAEDA is the president of the Rhode Island School of Design. In Redesigning Leadership, he—with co-author Becky Bermont—pulls the leadership lessons from the ups and downs of his time there. In his transition from MIT to RISD he found that the two words “free pizza” were a powerful motivator to convene large numbers of students. “Making people work together can be fairly challenging, but getting them to eat together is somehow vastly easier. A meal is often a catalyst for a conversation that can lead to a collaboration, and a meal is a natural happening to signify closure when the collaboration has been completed.” Leadership is never easy and it is made more difficult by what I perceive is a growing sense of entitlement we all feel in our culture. It’s not all good or bad, but it is something to deal with. Redesigning Leadership is a slim book, but it is full of great thoughts like these:

Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:52 AM
05.13.11

7 Essential Attributes for Picking Good Leaders
WE complain about our leaders. So we eventually get rid of them and we move on to the next one with the hope that it will be different this time. But it’s not. And we’re back where we started. Jeffrey Cohn and Jay Moran ask Why Are We Bad at Picking Good Leaders? “For starters,” they write, “because selecting the right people can be very, very, hard.” It’s easy to say that if we had better choices, we would pick better leaders. But that means that we are promoting the wrong people through the system. “If the only candidates with experience are simultaneously not qualified to lead, how did they get in the running for leadership positions?” Good question.To me, it’s obvious we are looking for the wrong things in our leaders and the right things are difficult to judge. Often the things that first attract us to a leader are not the attributes that make a good leader in the long term. “The truth is that most of us like a little bit of rock star in our leaders. We respond to their magnetism, their celebrity.” Charisma and smooth talk just aren’t enough.
These seven are the basic building blocks of a leader and other aspects of leadership flow from them. For example, innovation “requires the imagination to conceive of a new vision, the judgment to ensure this vision is practical and can be implemented, the empathy to anticipate how others will react to the new idea and to garner their support, and the courage to stick with a plan despite inevitable bumps in the road.” (They note that because innovation draws on so many of the seven attributes it is a rare quality among many leaders.) They are:
Each attribute is discussed in detail—with examples of leaders who have it and those who don’t—and they suggest practical ways to access their presence in potential leaders—or yourself for that matter. This exercise should help you better understand which aspects of your own leadership might be holding you back and should be addressed. This book is a valuable tool for evaluating the efficacy of your own leadership development program. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:39 PM
05.10.11

Can I Lead? Yes. But…There is a danger in selling leadership to everyone.Serious practitioners of leadership know that there is a lot of work that goes into being a good leader (dictators of any variety, not so much). Competence in your chosen context for leadership aside, the life-long inside work of leadership—figuring out what you won’t do before you figure out what you will do—is sometimes gut-wrenching and sometimes the most thrilling feeling you can experience. Character usually isn’t explicitly stated in the sales pitch. Instead, leadership is quite often seen as a way to be heard, to advance your own agenda and to put yourself out front. It is no surprise that Alan Webber recently wrote in the Washington Post: You will be told that you have a responsibility to be leaders. That what the world needs more than ever are leaders. That we suffer from a lack of leadership. That with your education, your values, your ability to apply social media, your global vision, your youthful idealism, you will be the next generation of leaders!Choosing to lead is one of the most rewarding decisions you may ever make. But it’s not about you. Yes, you will bring your unique and much needed gifts to the world, but not for your own sake. Your job is to use your gifts to help others express, make known and fulfill their potential. Influencing others with a purpose, a calling, and with opportunities they never imagined they had. It’s a mindset of service. It’s a mindset of continual learning. It’s a mindset of growth. The single biggest truth of leadership is that we build who we are by building up others. That doesn’t come naturally to us, but it’s your calling, if you would be a leader.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:15 PM
04.22.11

5 Leadership Lessons: What You Need to Know about Developing Teen Leadership
DAN APPLEMAN has written a handbook for developing teen leadership. Based on over 20 years of real world experience, you will find ideas, techniques, examples and even sample statements to guide you. Developing Teen Leadership will not only help you develop leadership skills in yourself and others, but you will find ways to help teens help other teens on their leadership journey. The challenge for most parents, teachers and teen advisors is first understanding what they believe about leadership. If we think leadership is telling people what to do, it is difficult to guide their understanding of what real leadership is. They learn best by example. Appleman offers over 50 valuable thoughts that impact your effectiveness with teens. Here are just five:
This is not a book about teens. It is a book about how we as adults relate to teens. Because the only tool we have to teach leadership skills (or anything) to teens is the control we have over our own actions. You can spend hours worrying about what the teens are doing or their attitude, but we can only control the things we do and our own attitude. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:10 PM
04.12.11

From Values to Action
FORMER chairman and chief executive officer of Baxter International, Harry Kraemer, has written a genuine, back-to-basics book on value-based leadership: From Values to Action. He presents four interconnected principles that build on and contribute to each other: Self-Reflection is the most important and is central to your leadership. “If you are not self-reflective, how can you truly know yourself?” writes Kraemer. “If you do not know yourself, how can you lead yourself? If you cannot lead yourself, how can you possibly lead others?” Self-reflection allows you to transform activity into productivity for all the right reasons. It means “you are surprised less frequently.” It is essential in setting priorities. You can’t do everything. So reflection makes it possible to answer key questions like What is most important? and What should we be doing? in a way that is in line with your strengths and values and organizational goals. Engaging in self-reflection on a regular, ongoing basis (preferably daily) keeps you from becoming so caught up in the momentum of the situation that you get carried away and consider actions and decisions that are not aligned with who you are and what you want to do with your life. Balance and Perspective is the ability to understand all sides of an issue. Pursuing balance means you will have to grasp the fact that leaders don’t have all the answers. Kraemer says, “My task was to recognize when a particular perspective offered by one of my team members was the best answer….Leadership is not a democracy. My job as the leader is to seek input, not consensus.” Because he believes we are more effective if we balance all areas of our life, he prefers the term “life balance” over “work-life balance.” It’s not an either-or proposition. “When you identify too closely with your work, you can easily lose perspective and become unable to look at all angles in a situation.” He recommends implementing a “life-grid” to keep track of where you are spending your time and to hold yourself accountable. True Self-Confidence is know what you know and you don’t know; to be comfortable with who you are while acknowledging that you still need to develop in certain areas. (Comfortable not complacent.) Why TRUE self-confidence? There are people who adopt a persona that might make others think that they have self-confidence, but they are not the real deal. Instead, they possess false self-confidence, which is really just an act without any substance. These individuals are full of bravado and are dominating. They believe they have all the answers and are quick to cut off any discussion that veers in a direction that runs contrary to their opinions. They dismiss debate as being a complete waste of time. They always need to be right—which means proving everyone else wrong. Genuine Humility is born of self-knowledge. Never forget where you started. “Genuine humility helps you recognize that you are neither better nor worse than anyone else, that you ought to respect everyone equally and not treat anyone differently just because of a job title.”
Kraemer describes a values-based leader well: “Self-reflection increases his self-awareness. Balance encourages him to seek out different perspectives from all team members and to change his mind when appropriate in order to make the best possible decisions. With true self-confidence, he does not have to be right, and he easily shares credit with his team. Genuine humility allows him to connect with everyone because no one is more important than anyone else.” From Values to Action is an outstanding book and filled with important concepts that any would-be leader would benefit from. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:13 PM
03.10.11

A Case for Reconsidering the Way We’ve Always Done It
S SOCIETY that doesn’t train their children to think critically, to be aware of those around them, and to serve, must create more rules and regulations than can be accounted for. There will never be enough rules—there are too many variables—especially when people begin to direct their creativity in dysfunctional ways. The challenge is to develop sound minds. As Kant determined, a person with a sound mind is one that can think for oneself, is able to place oneself in the place and viewpoint of others, and can think consistently and coherently. But it‘s easier, in the short term, to create rules. And we pay a price. To be sure, I am not advocating anarchy—we absolutely must have rules—and some rules unquestionably make possible the learning process, but when the rules we have in place reflect our lack of engagement, they become disrespectful and de-motivating. It’s easier to lay down the law or set up a checklist than it is to explain the why; to communicate where we’re headed with this idea. From time to time, it is good to think about the rules we have created (or have had handed down to us), that are impeding progress, relevance, imagination, and growth both for ourselves and others. Here are a few thoughts to guide that process: I am a big advocate of tradition, but when “that’s the way we’ve always done it” or “that’s how I learned to do it” gets in the way of relevance or growth, we need to take a step back and reconsider our stand. What we have done may have served us well in a particular place and time, but may only be an irritation here and now. Rules can reveal a lack of trust. “I don’t trust you to be as smart—considerate or creative—as I am.” And they never will be if not given the chance. As leaders, we need to be aware of where we are blanketing people with rules and procedures that do nothing more than to serve us and not the people it is our intention to serve. We need to consider that perhaps we have implemented rules to create a comfort zone for ourselves. A world where people act and think like we do. A world of clones. A world on autopilot that requires less of us. Often our need for rules and procedures is just masking our fear of the unknown. Our attempt to manage a world that is changing faster than we are learning. No leader can do it on their own and rules are no substitute for not trusting, growing and building relationships with people. Where are we hiding behind rules? Rules, for the most part, do not leverage other people’s strengths and thinking, they mostly mirror our own. Given the chance, people will surprise us with new, different, and better ways to push our agenda forward.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:43 AM
02.22.11

Leading As One: Generating Collective BehaviorTo be successful in the world we’re entering, we will need a new set of mental models. While these new models should not exclude the possibility of commanding and controlling, they need to encompass a much wider range of possibilities.The challenge facing any leader is turning individual action into collective power. In short, getting people to act as one. As One by Mehrdad Baghai and James Quigley, is the result of a two year research project conducted by Deloitte Touche Tohmatsu Limited, to understand this common leadership challenge and to answer the question, “What leads to effective collaborations in a wide range of fields?” Not just working together, but working as one. As we talk about leadership it is easy to confuse ends and means and seek collaboration for collaborations sake. The authors note that collaboration "is a means to an end, not an end in itself, and that because the purposes might be different you might need different styles" of collaboration for different situations. Thus we find successful leadership comes in many different shapes and sizes. They believe real leadership is about productivity, people and purpose—or As One Leadership—“leadership that results in a cohesive group of people working together effectively toward a common goal or purpose.” Initially the task is identifying which people need to be involved (the Who) and what purpose they need to satisfy (the What) and then How do we need to collaborate to get the results we seek. 
What emerged from the As One Flagship Project was the identification of eight models or archetypes of As One behavior. Arranged around two axes: a vertical axis that describes how power is exercised in an organization from emergent to directive and a horizontal axis that conveys the nature of individual’s tasks and outlines how work is organized from highly scripted and uniform to highly creative. 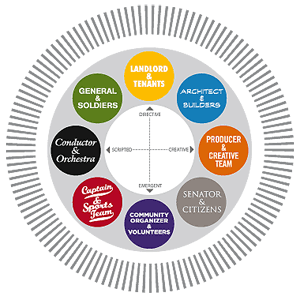 Not surprisingly, these archetypes reflect both top-down and bottom-up styles. The analysis is very balanced. In the descriptions that follow, you can see that different kinds of organizations or situations with different kinds of objectives call for different kinds of leadership. It is enlightening to identify your type of organization and the related leadership approach. The book presents case studies of each type, an explanation of the key characteristics, and a discussion of what you can do to be better at that type. Not surprisingly, these archetypes reflect both top-down and bottom-up styles. The analysis is very balanced. In the descriptions that follow, you can see that different kinds of organizations or situations with different kinds of objectives call for different kinds of leadership. It is enlightening to identify your type of organization and the related leadership approach. The book presents case studies of each type, an explanation of the key characteristics, and a discussion of what you can do to be better at that type.
The Deloitte Center for Collective Leadership was launched in January to advance the study of the As One Collective Leadership discipline and As One behavior. Through research, data collection, and analysis, this center will help define and increase knowledge in the exciting and dynamic field of collective leadership. If you are wondering what your model is, they have created an online As One Classifier tool to figure out which archetype is closest to your current situation. THE EIGHT ARCHETYPES The four main archetypes are: Landlord & Tenants: The Landlord & Tenants pairing is based on landlords’ top-down driven strategy and power: they control access to highly valuable or scarce resources. Landlords decide how to generate the most value for themselves and dictate the terms of participation for the tenants. Tenants voluntarily decide to join landlords, and it’s usually in their best interests to do so. However, once they do, landlords define the rules of participation. Landlords maintain their power by ensuring the best tenants are rewarded, so that, over time, as the number of tenants grows, the landlords’ power increases. Community Organizer & Volunteers: The Community Organizer & Volunteers pairing is based on volunteers’ bottom-up, autonomous, independent, decision-making ability and their desire to voice their opinions. Community Organizers ignite volunteers’ interest through compelling storytelling and opportunities for volunteers to join in. They may have little direct power over the volunteers, but they can tap into volunteers’ interests by gaining their trust, promoting a strong brand, and understanding their motivations. Volunteers themselves are drawn together by a rallying cry, or out of a sense of enlightened self-interest; they gain their power through a strength-in-numbers approach. Conductor & Orchestra: The Conductor & Orchestra pairing is based on highly scripted and clearly defined roles that focus on precision and efficiency in execution as defined by the conductor. The orchestra members, who have similar backgrounds, need to be fully trained to comply with the requirements of the job, and, therefore, must be carefully selected to ensure they fit the strict culture and scripted tasks. Belonging to the orchestra provides members with the best way to make a living while focusing on tasks at which they excel. Producer & Creative Team: The Producer & Creative Team pairing is typically about producers providing their creative team with the freedom to do their best work and reach their natural potential. This pairing is led by legendary, charismatic producers who bring together a team of highly inventive and skilled independent individuals to achieve the producers’ objective. Producers guide the vision and overall progress, while the creative team develops ideas through frequent meetings and interactions using an open culture of collaboration. Dissent is used to push creative boundaries. To maintain longevity in their industry, producers and creative teams need to continuously produce new and innovative ideas. The four hybrid archetypes combine the characteristics of the adjacent pairings and occupy the spaces between the axes. General & Soldiers: The General & Soldiers pairing has a command-and-control-type culture combined with a multi-level hierarchy organized around the general’s clear and compelling mission. Soldiers’ activities focus on clearly defined and scripted tasks. They are motivated by advancing up the hierarchy through well-defined roles at all levels. Soldiers undergo extensive training to understand the army and its culture, and to learn specific skills. They are committed to the mission, the overall institution, and each other, while the general provides strong top-down authoritarian direction to motivate and direct them. Architect & Builders: The Architect & Builders pairing focuses on the creative collaboration between groups of diverse builders that have been recruited by visionary architects to bring a seemingly impossible dream to life. Their visions are so innovative and ambitious that they can’t be achieved simply by using conventional means, so builders often need to reinvent and rethink ways to achieve them. Builders strive to meet ambitious deadlines and milestones mapped to deliberate workcycles. As each milestone is completed, the builders become one step closer to bringing the architect’s dream to reality. The Architect & Builders hero story is based on the development of the world’s cheapest car, the Tata Nano. Captain & Sports Team: The Captain & Sports Team pairing operates with minimal hierarchy and acts like a single cohesive and dynamic organism, adapting to new strategies and challenges with great agility as they appear. Members of the sports team have a strong shared identity. They have extensive and networked communication channels, and carry out the same highly scripted, repeatable tasks. There is strong camaraderie and trust among the sports team – the collective good outweighs the needs of the individual – while captains are there, on the field as part of the team, to motivate and encourage. Senator & Citizens: The Senator & Citizens pairing is based on a strong sense of responsibility to abide by the values or constitution of the community, which have been outlined by the senators. Sovereignty is held by both senators and citizens, and the citizens thrive on the values of democracy, freedom of expression, and autonomy. Since citizens are autonomous, the community structure is flexible. There is no set framework or direction organizing the citizens. Instead, much of their direction is emergent as they gather ideas and collaborate with other citizens. Senators are the guiding intelligence for the citizens and oversee decision making for the community. There is no one size fits all archetype and each archetype is more nuanced than described. Putting As One into practice consists of three steps: First, a diagnostic to assess the who and to do what and then determine the how or what archetype is being used. Second, determine the type of intervention to strengthen the archetype being used or to create a new approach and third to adopt the approach across the organization and applying different archetypes in different situations even in the same organization. It is an interesting study that begins to create a broader understanding of what it takes to lead at all levels as opposed to the common polarizing either/or discussions of command and control versus collaborative leadership. It also helps to dispel the myth that top-down leadership is synonymous with command and control. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:11 AM
02.18.11

Making the Transition From Bud to Boss
OFTEN, when we are given a formal leadership role a couple of questions come to mind: Will they take me seriously? and How can I develop the influence I need to do this job? A promotion changes the scope of the kinds of things we have to think about. It changes the degree to which we have to regulate our behaviors, conversation and opinions. In short, it changes our relationship with everyone around us. How will we handle it? What about old friendships? They’re all watching us. It can make us feel a little anxious and insecure. From Bud to Boss is written for that moment. It is designed to get you pointed in the right direction and engaging in productive behaviors and thinking. Authors Kevin Eikenberry and Guy Harris have organized this book around six key areas of concern:
What they offer isn’t counterintuitive, they’re just things that we forget to do or find difficult to do and so we don’t. But ignoring them affects our ability to lead. This is an action-oriented book and is extensively supported by the Bud to Boss community on the Internet. To help you get your foundation for leadership in balance, Eikenberry and Harris discuss the impact of your leadership style: In your leadership style, you probably have a natural “lean” that is a little more toward getting things done or toward people and relationships. One major key to leadership success lies in learning to compensate for the way you learn so that you stay balanced between getting things done and building relationships. This is a key point. You need to become more self-aware. You will be judged for results, but if you try to get those results without maintaining the respect of those around you, you will ultimately fail as a leader. So often when we get into a position of authority we begin to think, “How can I get these people to do what I want?” The question seems innocuous enough, but the danger is that it can lead us to focus on controlling others and forget that the task of leadership is to influence others. The authors suggest turning the focus of the question around: “How do I change my words and behaviors so that I communicate with my team more effectively?” or This kind of thinking places responsibility where it should rightfully be. You. They write, “Control what you can. Influence who you can.” From Bud to Boss provides direction and tools that will allow you to take the right action and build confidence—the essential forward momentum you need to be successful. It should go without saying, but it is said, so I’ll mention it. No book, speech, or coach will ever be able to cover everything you could need to know. Because the players are all different, it isn’t possible to address everything specifically. So the trick for us is to get the general principles down and learn to apply them. That’s really what good books, speakers, and coaches try to do; give you principles and tools that you can learn to apply properly in the situations you face as they come up. That’s what From Bud to Boss does well. The rest is up to you. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:35 AM
02.16.11

Frances Hesselbein: To Serve is To Live
FRANCES HESSELBEIN is a remarkable leader because she doesn’t try to get others to think of her as a leader, she tries to get others to think of themselves as leaders. Reading her autobiography, My Life in Leadership, I was struck by the importance she places on inclusion, respect, civility, decency, honor, honesty and faithfulness. It’s not surprising then, that she never thought of herself as a “woman leader,” but always as “a leader who is a woman.” Hesselbein didn’t start out to be a leader, but she became one by expressing her best self in all that she did. An example for all would-be leaders to follow. Her mantra is, “to serve is to live.” Her father was her hero and when he died, she dropped out of college to help support her family. Later she married and raised a family with no intention of leaving her hometown in Pennsylvania. Later to help out, she volunteered to serve as a Girl Scout Troop leader. Eventually, as doors opened for both her and her husband, she was asked to head the Girl Scouts of the USA which she did from 1976 to 1990. From her contribution there, she was named “Best Nonprofit Manager in America” by Fortune Magazine. In 1998 she was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom in recognition of her exemplary leadership as CEO of Girl Scouts of the USA, her role as the founding president of the Drucker Foundation, and her service as “a pioneer for women volunteerism, diversity, and opportunity.” My Life in Leadership is full of lessons. Here are just five of the lessons she has learned along the way. I’m certain you’ll find at least one that will improve your leadership approach and thinking. “If we value diversity and inclusion, then we must ask, ‘When they look at us, can they find themselves?’ This is the powerful question that uncovers whether an organization practices what it preaches.” At the Girl Scouts of the USA, she worked hard to make sure people of all races and backgrounds could find themselves in the organization. She writes: “One of the most important parts of transforming a large and complex organization is inclusion: engaging all of the people every step of the way... Inclusion is a powerful value: when we open up the organization, dispersing the leadership, including people from across the enterprise, there is a new energy, a new synergy.” At one point she asked her staff to introduce themselves to each other at a meeting. She shares the story of a staff member that understands what it means to think like a leader—be a leader—no matter where you find yourself in an organization: “My name is Troy. I work in the mail room, and I like to think of myself as the heart of the organization. Everything that comes into the organization comes through me. Everything that goes out of the organization goes through me. I am the heart of the organization!” She adds, “Troy’s ‘heart’ brought to us new insight about the importance of every person and every position. I’ve never forgotten Troy and that moment.” When making a decision about change you can’t stall in indecision but you can’t run over people either. She explains how she handled a touchy situation and then writes: “When does the sled take off? Is the question for all leaders, knowing that we can fail if the sled leaves too early with too few people on it, or we can wait too long, and someone else will have filled the need and eaten our lunch…. It takes managerial courage to decide that it is time for the sled to take off when many are hesitant to climb on board. A leader respects their opinions and their positions, but cannot be deterred by them. Later these people may change their minds and join you, but if you act in a dismissive way that diminishes them, they never come back. Save the face and the dignity of the people who oppose the initiative. That is a key principle in managing change and mobilizing people around that change.” In 1981, at a GSA meeting, Peter Drucker told them: “You do not see yourself life size. You do not appreciate the significance of the work you do, for we live in a society that pretends to care about its children, and it does not.” Hesselbein said, “I wanted to refute this, but could think of nothing to say. Drucker continued, “And for a little while, you give a girl a chance to be a girl in a society that forces her to grow up all too soon.” Hesselbein adds, “We took him seriously.” How many of us see what we do “life size?” Hesselbein says the number one element of listening is “banish the but.” She writes: If we want people to listen, we must banish “but” from our vocabulary. How many times have we had someone tell us how well we performed—and we were feeling good about the feedback, listening carefully—then we heard “but,” and the positive, energizing part of the feedback was lost in the “but” and what followed it. “But” is nobody’s friend—listener or speaker. “And” provides the graceful transition, the non-threatening bridge to mutual appreciation, the communication that builds effective relationships. Hesselbein believes that “in the end, it’s the quality and character of the leader that determines the performance.” As President and CEO of the Peter Drucker Foundation for Nonprofit Management (now the Leader to Leader Institute), she was asked what the two most powerful messages were that he left with her. She said, “Think first, speak last” and, “the leader of the future asks; the leader of the past tells. Ask, don’t tell.” In the foreword, Jim Collins sums up well the example of Frances Hesselbein: No matter what knocks you down, you get up and go forward. You might be appalled by horrifying events, but never discouraged. You might need to deal with mean-spirited and petty people along the way but never lose your own gracious manner. You might need to confront a litany of brutal facts and destabilizing uncertainties, but it is your responsibility, as a leader to always shine a light.   
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:00 PM
12.29.10

Leadership: Artistry Unleashed
The executive functions … are feeling, judgment, sense, proportion, balance, [and] appropriateness. It is a matter of art rather than science, and is aesthetic rather than logical.Leadership is an art. But what does that really mean? Leadership can be taught in the way that art can be taught. There are techniques and principles that need to be understood. Seeds that can be planted. But ultimately it has to be practiced and experienced. There is the part that really matters, as Georges Braque observed, that can’t be explained. That is the art; the ever-changing context of leadership and the dance between leaders and followers that molds and shapes both the leader and follower. There is an art to bringing leadership teaching into the nuance of life. Leadership practiced, is artistry unleashed. Hilary Austen does a masterful job of explaining, even if indirectly, the art of leadership in Artistry Unleashed. She takes design thinking beyond the surface concerns of practical design and to the processes behind it. These are important issues for leaders as we face what Austen terms enigmatic problems: those that push us to the edge of what we know. “Our best solutions to such problems lie not just in better analytical tools but in a fundamentally different approach to our work—an approach that follows from cultivating qualitative intelligence in our given profession or medium.” Any more quantitative approaches alone won’t work. She explains the difference: “Quantitative thinking allows us to be precise and to share understanding; we use it to define fairness and rationality and effectiveness. It’s this utility that has led so many people to equate quantitative thinking with intelligence.” “A qualitative approach embraces the unexpected, the subtle, the open-ended, the unique, the poetic; it escapes rules, single answers, or single perspectives. These features are by their very nature hard to pin down and can be quite unnerving to people who want precise information and specific answers. The quantitative approach gives us the means to predict and control what we can measure, to record and codify what can be clearly defined, to collect sharable facts, and to identify universal rules and laws. To be sure, Austen is not advocating one or the other. “Each has its own set of purposes, and developing one does not mean abandoning the other. Achieving artistry means being able to use qualities to help you work when that’s what the situation demands; it doesn’t mean rejecting quantitative methods.” We gravitate to quantitative thinking. We like things nailed down. Numbered. Labeled. Defined. It gives us some certainty. It makes us comfortable. We can check it off and move on confident that we’ve done the “right thing.” Unfortunately, life is messier than that. Austen cites Ted Sorenson’s observation from his book Decision-Making in the White House: “White House decision-making is not a science but an art. It requires not calculation but judgment….Every decision a president makes involves uncertainty.” Qualitative thinking is less about imposing an answer and more about shaping an answer from awareness of the present and feedback from the application of knowledge to it, when predetermined steps and measurable goals are absent. The present and the possible are considered at the same time so that ends and means influence each other as they occur. Austen writes, the “interdependent relationship between ends and means is a hallmark of artistic work. As your effort to solve an enigmatic problem proceeds, the ends evolve as means are generated. Likewise, as means unfold, new ends become possible; these may, in turn, demand new means.” It means managing the tension between mastery and originality in search of the possible. “The forces that drive mastery are conservative. Mastery brings predictability and control to action. By contrast, originality is driven by often unpredictable responses to immediate experience. Finding originality means leaving behind some of what you know. Artistry is driven forward by the interplay of these two competing forces.” New York University professor David Ecker’s six phases of qualitative problem solving developed from the work of John Dewey, described in Artistry Unleashed by Austen is helpful: In the first phase, artists engage what Ecker calls the presented or initial relationship between existing qualities….Some of these relationships may be problematic, others intriguing, and so they attract the artist’s attention. Different practitioners may see different qualities and make sense of what they see differently, depending on the ideals, concepts, and sensibilities they bring to bear on the situation.A leader’s function is to create the disequilibrium needed to go from the known to the unknown possibilities. Qualitative thinking is important to the leader because without it we can easily impose answers rather than exploring possibilities. We can too, get in our own way by overvaluing the importance of our own experience and thought and thereby limit possible outcomes. Austen develops a Knowledge System model comprised of the interdependency of Experiential Knowledge, Conceptual Knowledge, and Directional Knowledge, that can be used to help anyone develop and apply qualitative thinking. The cursory view I present here of the connection between business and art, she more fully develops in her book. The examples she gives dramatically demonstrate this important connection and essential understanding needed by leaders of every type. Related Interest:   
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:21 AM
12.23.10

Managing Yourself First Checklist
MAKE sure that the first person you are managing every day is yourself. Take good care of yourself outside of work so that you can bring your best self to work every day. Arrive a little early to work and stay a little late. Focus on playing the role assigned to you before trying to reach beyond that role. Focus on doing your tasks, responsibilities, and projects very well, very fast, all day long. If you want to carry weight with your boss, that should be your primary focus. Be a problem-solver, not a complainer. Commit to continuous improvement through rigorous self-evaluation. Think about context and figure out where you fit in every situation. Continually ask yourself, “Where do I fit in this picture? Why am I here? What is at stake for me? What is my appropriate role in relation to the other people in the group? What is my appropriate role in relation to the mission?” Concentrate on playing these roles 110 percent. Contribute your very best thoughts, words, and actions. No matter how lowly or mundane or repetitive or minor your tasks and responsibilities might seem in relation to the overall mission, play your role to the max. Attitude matters—a lot. Effort matters—a lot. Start mastering the art of human relations. Approach every relationship by focusing on what you have to offer the other person rather than on what you might want or need. Be a model of trust. Remove your ego. Listen carefully. Empathize. Exhibit respect and kindness. Speak up and make yourself understood. Be a motivator. Celebrate the success of others. Make yourself a great workplace citizen. Under-promise and over-deliver. Don’t bad mouth others, and try not to speak about others unless they are present. Keep your word. Keep your confidences. Be an accurate source of information. Don’t keep other people waiting. Instead of under-dressing, overdress. Practice old-fashioned good manners. Adapted from It’s Okay to Manage Your Boss by Bruce Tulgan. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:13 AM
12.21.10

quickpoint: The Benefits of Hardship in Character Development Adversity and hardship contribute to character development when they cause personal reflection and introspection about a leader’s behavior and influence. Hardship can cause leaders to look inside themselves, asking questions the answers to which can result in huge learnings and behavioral adjustments. Hardship can reveal a leader’s behavioral blind spots, inconsistencies, weaknesses, personal limitations, ad ineffective or bad behaviors. Adversity and hardship contribute to character development when they cause personal reflection and introspection about a leader’s behavior and influence. Hardship can cause leaders to look inside themselves, asking questions the answers to which can result in huge learnings and behavioral adjustments. Hardship can reveal a leader’s behavioral blind spots, inconsistencies, weaknesses, personal limitations, ad ineffective or bad behaviors.
Hardship and adversity can also be cleansing. They can have a refining effect. Through suffering, the dross of one’s personality can be removed. It can cause a leader to look at personal behavioral challenges related to anger, impatience, fear, selfishness, and so on. Adversity can also produce a clearer focus and concentration on what is important in life and what is not. There is also a maturing element to hardship. Mature means being seasoned, tested, hardened, weathered, ready, and fully developed. Thus, adversity and hardships can take each of us to a higher level of character development. (Adapted from: Building Character: Strengthening the Heart of Good Leadership by Gene Klann)
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:45 AM
12.13.10

Bury My Heart at Conference Room BIn Bury My Heart at Conference Room B, Stan Slap cuts through a lot of the dancing around that occurs in many leadership discussions.It should go without saying that emotional commitment improves organizational performance. If in doubt, Slap spells it out in the first third of the book. The way to get that emotional commitment, says Slap, is for you to live your own deepest values in your work environment. While any organization should encourage this, most often they don’t. “What companies want most from their managers is what they most stop their managers from giving. What managers want most from their jobs is what they most stop themselves from doing.” So, it’s up to you. The process of managing this tension what Bury My Heart is all about. The underlying problem is this: Companies can’t get emotional commitment from their managers because the company believes it needs to be the dominant organism in the relationship, which causes managers to have to repress their own values—and so causes them to detach emotionally from their jobs.Fear drives this tension: Are we going to survive as an organization if we are not in control? Slap says the only sustainable solution is leadership. “Leaders are people who live their deepest personal values without compromise” and because they do, “they’re essentially self-medicated—the pressure’s off the company to provide the deepest motivational fulfillment.” Slap insists that this isn’t licensing chaos but insuring control. Paradoxically, “there is no more reliable way for the company to become the cause than by not always insisting on being the cause.” Allow people to live their values at work. This isn’t a self-indulgent free-for-all. “Freedom to pursue your values come with responsibility to protect the company’s values.” It becomes an issue of trust between the organization and the individual. “Your job as a manager requires achieving results through others. Leadership is the single best method to do that. As long as your vision doesn’t violate the basic objectives and principles of your organization, those results will be hard for anyone to argue with.” Your leadership begins by understanding your own values—what is important to you—so you can sell those values to others. Beyond envisioning a “Better Place” of your creation, the people you lead have to see it too. What does life look like for them in this Better Place? Help them to get what they want as they head toward the Better Place. Slap writes: = Live better. If they believe it, they’ll do it. Of course, not everyone you lead will have the same values as you, but if you have communicated them well, “they’ll support yours if yours have positive impact for them.” Leadership happens to you as soon as you understand your own values and understand how to enroll others in supporting them. Instead of waiting for a leader you can believe in, try this: Become a leader you can believe in.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:47 PM
11.08.10

Congratulations, You’ve Reached the Next LevelYou’ve moved up to the next level. You’ve been promoted to the executive ranks. “You should be uncomfortable,” says Scott Eblin in The Next Level. “If you’re not, you are probably underestimating what’s ahead of you.” Statistically, many do. As high as 40% of new executives fail within the first eighteen months of being named to their positions.New positions carry with them greater expectations even if those expectations are not clearly stated. You are left to navigate uncharted territory. The single most important thing to remember is that what got you there may not serve you well in your new position. Going to the next level says Eblin, is “about developing consciousness around what is and isn’t serving you as you take those steps. It’s about retaining what is working, staying open to picking up new skills and mind-sets, and having the courage to let go of the behaviors and beliefs that brought you this far when they no longer serve you on your journey.” Eblin has developed an Executive Presence model that focuses on nine behaviors in three areas that a successful executive should develop on the one hand and drop on the other:
Eblin covers each of these behaviors in detail with insights, interviews, coaching tips and research. But in an important foundational chapter, he talks about grounded confidence. That is, add value but know what you are talking about. “It is critical for your success that you not dwell on thoughts and self-assessments that cause you to doubt your capacity to contribute. There is a certain amount of insecurity that comes with any new position, but “insecure people make lousy leaders.” Insecurity causes us to behave in a lot of counterproductive ways: indecisiveness, micromanaging and control, taking undeserved credit and passing blame, lack of teachability. Eblin says that developing strong relationships with your peers is essential to your success. “Your success in managing relationships will stem from the confidence you have in yourself and your ability to work well with others to make things happen.” This is an area where you need to move quickly. Your new role brings with it an expectation of your involvement in a wider range of issues. This means projecting confidence in your judgment that “extends beyond functional or technical knowledge.” This means also, more listening and less talking. Being teachable. Getting feedback. Of course, there is a lot of confidence to be gained by being prepared—being intentional. Eblin’s approach is to begin with the end in mind. You need to consistently ask yourself two questions: “What do I want to accomplish?” “How do I need to show up to accomplish that?” Practicing new and unfamiliar behaviors can be uncomfortable and seem artificial, but executed repeatedly these behaviors will become ingrained into your character and make them your own. As Aristotle said, “We are what we repeatedly do. Excellence, then, is not an act but a habit.” Feedback Tip: Ask your colleagues this question—What’s your best advice for anyone who is working on team reliance versus self-reliance (or whatever your working on)? Experience shows that it’s useful to ask the question in this format instead of asking, for example—What should I do to be better at team reliance? Asking the question in a less personal way makes it easier for your colleagues to be candid in their feedback. The Next Level is an excellent coaching reference book that makes it an indispensable companion guide to any change in responsibility. Keep it handy and bookmark the Situations Solutions Guide that contains practical solutions to scores of situations that predictably occur in most executive careers.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:40 AM
09.24.10

It’s All About You???In another fine offering from Bob Sutton—Good Boss, Bad Boss—he makes this attention grabbing statement: “To be a great boss you’ve got to think and act as if it is all about you. Your success depends on being fixated on yourself.” What?Ironically, great leaders know that it’s all about them because it isn’t. Great leaders focus on developing themselves so they can develop others. They know themselves first so they can understand others better. They check their own ego so they can build others. They take responsibility for their own actions before they consider looking at others. They have taken an inventory of their strengths and weaknesses so that they know where they need to check themselves and where they need to partner with others. They understand their own failings so that they are more understanding of others. They are appreciative of the room they have been given to grow and make certain they create this space for others. It’s about self-awareness. A self-aware leader is in a better position to lead others with authenticity and benevolent concern. Self-aware leaders know how they are coming across to those they lead. Sutton writes, “If you are a boss, your success depends on staying in tune with how others think, feel, and react to you.” Sutton offers two acid tests for bosses:
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:25 PM
08.10.10

Ten Truths about Leadership
IN the last 30 years James Kouzes and Barry Posner, authors of the highly regarded leadership classic The Leadership Challenge, have studied leaders all over the world. They understand leadership. The question they get time and time again is “What’s new in leadership?” They answer that while the context of leadership as changed dramatically, “the content of leadership has not changed much at all. The fundamental behaviors, actions, and practices of leaders have remained essentially the same since we first began researching and writing about leadership over three decades ago. Much has changed, but there’s a whole lot more that’s stayed the same.” That is probably the fundamental truth of leadership development. With that understanding, we can develop leaders in all contexts and weed out fact from fiction.Based on thirty years of research—more than one million responses to their leadership assessment—Kouzes and Posner have gathered together in The Truth about Leadership, the ten truths that have stood the test of time and they hold true both globally and cross-generationally. They devote a chapter to each of these ten concepts: Truth #1 You Make a Difference. Before you lead you have to believe that you can have a positive impact on others. When you believe you can make a difference, you position yourself to hear the call to lead. Truth #2 Credibility Is the Foundation of Leadership. If people don’t believe in you, they won’t willingly follow you. You must do what you say you are going to do. This means being so clear about your beliefs that you can live them every day. Truth #3 Values Drive Commitment. You need to know what you believe in because you can only fully commit to the organization or cause when there is a good fit between what you value and the organization values. This is true too, for the people you lead. Truth #4 Focusing on the Future Sets Leaders Apart. You have to be forward looking; it’s the quality that most differentiates leaders from individual contributors. You need to spend time reflecting on the future. Big dreams that resonate with others inspire and energize. Truth #5 You Can’t Do It Alone. Leadership is a team sport, and you need to engage others in the cause. You need to enable others to be even better than they already are. Truth #6 Trust Rules. To enlist others, you need trust. Build mutual trust; you must trust others too. Truth #7 Challenge Is the Crucible of Greatness. Great achievements don’t happen when you keep things the same. Change invariably involves challenge, and challenge tests you. It introduces you to yourself. It brings you face-to-face with your level of commitment, your grittiness, and your values. It reveals your mindset about change. Truth #8 You Either Lead by Example or You Don’t Lead at All. You have to go first as a leader. That’s what it takes to get others to follow your lead. Truth #9 The Best Leaders Are the Best Learners. Learning is the master skill of leadership. Leaders are constant improvement fanatics. Truth #10 Leadership Is an Affair of the Heart. Leaders love what they’re doing and those they lead. Leaders make others feel great themselves and are gracious in showing their appreciation. These truths should form the basis of any leadership development program. Even more, they are the motivation behind the right kinds of behaviors that go into the formation of good and sustainable leadership. There are no shortages of problems and opportunities…. Leadership is not about telling others they ought to solve these problems. It’s about seeing a problem and accepting personal responsibility for doing something about it. And it’s about holding yourself accountable for the actions that you take. The next time you see a problem and say “Why doesn’t someone do something about this?” take a look in the mirror and say instead, “I’ll be the someone to do something about it.” 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:09 AM
08.04.10

Are You a Hundred Percent Leader?Research done by Leadership IQ indicates that 77% of leaders believe their employees are not giving 100%. Employees don’t seem to argue the point. 72% of employees admit that they in fact aren’t giving 100%.If you want your employees to give 100%, you need to be the kind of leader that creates Hundred Percenters—a 100% Leader. In Hundred Percenters, Mark Murphy, CEO of Leadership IQ, says that the “two most important differentiating factors in separating exceptional from average leaders are Challenge and Connection.” Challenge is the extent to which a leader pushes his or her people. Connection is the strength of the emotional connection they build with their people. You need to decide how much you want to challenge your people and how tight an emotional bond you want to build with them. The age-old question plaguing leaders is whether it’s better to be loved or feared. What our research seems to suggest is that while fear doesn’t lead to superior results, it’s also true that if being loved means you don’t push people, that’s not so great either. The balance seems to be that leaders should be loved, but they should be loved for pushing people to give 100%, not for coddling or appeasing them.The degree to which you challenge and connect with your people will determine the results you get. Based on their research, Murphy has divided leaders into four basic types: Appeaser, Avoider, Intimidator and 100% Leader. With the challenges leaders face, appeasing, avoiding or intimidating can seem like necessary approaches; the path of least resistance. But they don’t produce fully engaged and accountable people. In practice, the four types are described this way: 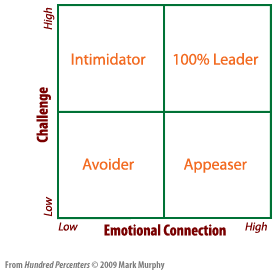 Working for the Appeaser. You’re given enjoyable assignments, you’re allowed to spend most of your time on work that plays to your strengths, your boss gives you lots of positive feedback, and your boss seems to care most about making sure you’re really happy. Working for the Intimidator. You’re given seemingly impossible assignments; you don’t feel like you’ve got all the skills you need to complete those assignments; when your boss gives you feedback, it’s usually pretty harsh and critical; and your boss seems to care most about achieving his goals no matter who’s with him at the end. Working for the Avoider. Your boss doesn’t really force too many assignments on you, you’re not really required to learn new skills, your boss lets you figure out for yourself how you’re doing, and your boss seems to care most about not getting in your way. Working for the 100% Leader. You’re given really challenging assignments, you’re required to learn new skills even in areas you might not consider to be your natural strengths, your boss gives you lots of constructive and positive feedback, and your boss seems to care most about pushing you to maximize every ounce of your potential. What kind of leader are you?
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:34 PM
08.02.10

Bootstrap Leadership: Creating a Blueprint for Your Leadership DevelopmentLeadership is difficult but it is not complex. The most difficult part is you and me; getting ourselves to do what we know we need to be doing; interacting with people the way we know we should, but for all kinds of “good” and easily “justifiable” reasons don’t.The hardest person you will ever lead is yourself. Changing your personal behaviors and consequently your leadership style is not easy. It requires reflection, a vision of what should be and a plan, but it is ultimately up to you to make the changes. Bootstrap Leadership by Steve Arneson is an effort to guide you into doing just that. One of the most important capabilities of a leader is self-awareness. That is where this book rightfully begins by asking, “How are you showing up as a leader?” Arneson believes you need to begin with a definition of what good leadership means to you. “If you don’t know how to define the very thing you’re trying to do, how can you be successful at it?” Unfortunately, many leaders don’t know how to adequately define their role. He says that once you have created your own definition of leadership, you need to “become an evangelist for leadership” and share it with others. To start pulling yourself up by your own bootstraps and developing a customized leadership development plan, Arneson has provided a self-assessment of 50 statements that correspond to a chapter dealing with that particular need. After determining the areas you need to work on, he recommends that you tackle one each week. Bootstrap Leadership provides a very doable plan for improving your leadership. By looking at each of the 50 ideas, you will see areas where you can improve your weaknesses and refine and leverage your strengths. It is also valuable in helping others to develop their leadership potential. Invest these 50 ideas in yourself and others. Resist the temptation to say: “OK, I applied a few of the techniques this year, I’m good for awhile.” Keep stretching yourself.The best leadership advice? Become a better listener. “If you do nothing else to develop yourself, work on becoming a better listener.” It’s one of the “most effective ways to improve your leadership brand."
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:46 PM
06.29.10

Multipliers: How the Best Leaders Make Everyone Smarter
MUCH OF WHAT constitutes good leadership can be summarized in two words: respect and selflessness. How we relate to those two words will determine how we lead. Consider two assumptions that lie at the opposite ends of the spectrum: • Really intelligent people are a rare breed and I am one of the few really smart people. People will never be able to figure things out without me. I need to have all the answers. • Smart people are everywhere and will figure things out and get even smarter in the process. My job is to ask the right questions. What you believe has a big impact on the performance, engagement, loyalty and the transparency you find with those you lead and interact with. In Multipliers: How the Best Leaders Make Everyone Smarter, authors Liz Wiseman and Greg McKeown refer to those with the mindset represented by the first assumption as Diminshers and those with the mindset represented by the second assumption as Multipliers. It explains why some leaders create intelligence around them, while others diminish it. The value of Multipliers is that is shows what these assumptions about people look like in practice and how they are reflected in your behavior. How would you approach your job differently if you believed that people are smart and can figure it out? With a Multiplier mindset, people will surprise you. They will give more. You will learn more. What kind of solutions could we generate if you could access the underutilized brainpower in the world? How much more could you accomplish? It’s not that Diminishers don’t get things done. They do. It’s just that the people around them feel drained, overworked and underutilized. Some leaders seem to drain the “intelligence and capability out of the people around them. Their focus on their own intelligence and their resolve to be the smartest person in the room [has] a diminishing effect on everyone else. For them to look smart, other people had to end up looking dumb.” In short, Diminishers are absorbed in their own intelligence, stifle others, and deplete the organization of crucial intelligence and capability. Multipliers get more done by leveraging (using more) of the intelligence and capabilities of the people around them. They respect others. “Multipliers are leaders who look beyond their own genius and focus their energy on extracting and extending the genius of others.” These are not “feel good” leaders. “They are tough and exacting managers who see a lot of capacity in others and want to utilize that potential to the fullest.” The authors have identified five key behaviors or disciplines that distinguish Multipliers from Diminishers. You are not either/or but are somewhere along a continuum. These are all learned behaviors and have everything to do with how you view people. We don’t have to be great in all disciplines to be a Multiplier, but we have to be at least neutral in those disciplines we struggle with.
They have developed an assessment tool you can use to see where you are. Importantly, the first place to begin is with your assumptions about people. If you don’t have that straight the rest is just manipulation. As with most behaviors, we do them because we feel we have to. They are self-perpetuating. We jump in where we shouldn’t and come to the rescue. Under our “help” (domination) people hold back thereby reaffirming our belief that they just couldn’t do it without us. And they can’t or rather won’t. Instead they quit while still working for us or move on. We see this in ourselves, in others and in organizations of all types. Leaders are especially prone to run over people, because after all, they have the vision, the know-how and the desire to get it done. We have to slow down and remember that we are not there just to get the job done, but to develop others to get the job done. They can (and need to be able to) do it without us. It’s our job to show them how. In many ways, as leaders, we can become accidental Diminishers. The skills that got us into a position of leadership, are not the same skills we need to lead. Leadership requires a shift in our thinking. Wiseman and McKeown write, “Most of the Diminishers had grown up praised for their personal intelligence and had moved up the management ranks on account of personal—and often intellectual—merit. When they become ‘the boss,’ they assumed it was their job to be the smartest and to manage a set of ‘subordinates.’" Here are some thoughts—out of context—from the book that will get you thinking: “Marguerite is so capable she could do virtually any aspect of girl’s camp herself.” But what is interesting about Marguerite isn’t that she could—it is that she doesn’t. Instead, she leads like a Multiplier, invoking brilliance and dedication in the other fifty-nine leaders who make this camp a reality. One leader had a sign on her door: “Ignore me as needed to get your job done.” She told new staff members, “Yes, there will be a few times when I get agitated because I would have done it differently, but I’ll get over it. I’d rather you trust your judgment, keep moving, and get the job done.” The path of least resistance for most smart, driven leaders is to become a Tyrant. Even Michael said, “it’s not like it isn’t tempting to be tyrannical when you can.” Policies—established to create order—often unintentionally keep people from thinking. At best, these policies limit intellectual range of motion as they straitjacket the thinking of the followers. At worst these systems shut down thinking entirely. “It is just easier to hold back and let Kate do the thinking.” [They resign: “Whatever!”] It is a small victory to create space for others to contribute. But it is a huge victory to maintain that space and resist the temptation to jump back in and consume it yourself. An unsafe environment yields only the safest ideas. [Multipliers] ask questions so immense that people can’t answer them based on their current knowledge or where they currently stand. To answer these questions, the organization must learn. His greatest value was not his intelligence, but how he invested his intelligence in others. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:28 PM
05.17.10

Serve to Lead: Make Your Life a Masterpiece of Service Everyone can be great because everyone can serve. You don’t have to have a college degree to serve. You don’t have to make your subject and your verb agree to serve…. You only need a heart full of grace, a soul generated by love.“Everyone can lead because everyone can serve,” says James Strock. “When service is the basis of leadership, everyone can be a leader.” What’s more, “We’re in a new era, with new rules, new ways to serve—and much greater accountability.” In a new edition, Serve to Lead 2.0 puts the focus of leadership where it should be. Too often, people think of leadership as being about the leader. A leader who serves has greater influence. Service—not control—leads to trust and increased influence. In an excellent chapter on management, Strock helps to place management and leadership in perspective and explains some of the nuances of tough love and accountability. “Management is encompassed within leadership.” As leaders, we must develop management skills. “Ultimately, management is a key to extraordinary service. Individual performance has the limitations of an individual. You may be a virtuoso. Yet, if you are determined to express your individuality in a more expansive way, you must develop management skills and engage others in a larger enterprise.Filled with examples and quotes, Serve to Lead 2.0 is well thought out and one of the best books you’ll read on how to think about service and how to get your leadership to be one of service. Strock urges us to make our life a masterpiece of service. It begins by asking the question—who am I serving—throughout our life, minute by minute, hour by hour, day by day. Importantly, it is not a question that we should apply to only one area of our life. It should be an approach we take in all areas of our life—our time, our money, our relationships, and thoughts. As an ongoing practice, he suggests we continually ask ourselves four questions: Who am I serving? How can I best serve? Am I making my unique contribution? Am I getting better every day? Service isn’t easy. It doesn’t always get noticed, but it is what leading is all about. If that is hard to swallow, you need to ask yourself, why do I want to lead? How many people are trapped in their everyday habits: part numb, part frightened, part indifferent? To have a better life we must keep choosing how we’re living.   
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:42 PM
04.14.10

The Little BIG Things
IN many ways leadership is about taking an oath of excellence. To a leader, excellence matters. Excellence requires “re-imagining” (to borrow a Peters’ term) your world done excellent. Leaders see things differently and this difference can be taught. Teaching excellence—one behavior at a time—is what The Little Big Things by Tom Peters, is all about. Some of what you will read in TLBT has been presented on the Tom Peters blog over the years. But for this book, the posts have been edited, revised, organized and conveniently packaged. It’s a compilation of 163 behaviors you can put into practice to achieve excellence in any endeavor. As such, it is not meant to be read straight through. Jump in anywhere it looks interesting. The process here is: read—consider—implement—repeat. Tom, as we’ve said here before, is good at boiling things down to basics. You’ll find opportunities to pursue excellence in basic insights that produce big results. Courtesies of a small and trivial character are the ones which strike deepest in the grateful and appreciating heart. Sometimes the little-big-things can seem too “soft” or beneath the demands of business. Tom explains: “Ideas like conscientiously showing appreciation are matchless signs of humanity—and the practice thereof, in my opinion, doubtless makes you a better person, a person behaving decently in a hurried and harried world….Acts of appreciation, to stick with my theme of the moment, are masterful, even peerless, ways of enthusing staff and partner and client alike, and, hence, greasing the way to rapid implementation of damn near anything. That is, ‘Soft is hard’ is wholly pragmatic—and more often than not, effectively implemented, makes the bottom line blossom!” Excellence has to be challenged into existence. The Little Big Things does just that. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:00 AM
03.10.10

How to Decommoditize Your LeadershipAll leaders want to make a difference; be transformational. And some do and some really don’t. We’ve all known leaders that are easily replaced. And (hopefully) we’ve known some that we can’t imagine doing without.The difference begins with the bond we create by integrating who we are with what we do. Making a difference has a lot to do with how completely we integrate what we are (our character, values and attitudes) with what we do (our competencies). All leaders have to set direction, give orders, and display competence. But if that’s all they’re doing, they’re replaceable. What sets one leader apart from another, what makes an order compelling rather than coercive, is the kind of spirit that accompanies their actions; a commanding what-can-I-get-from-them approach or a servant what-can-I-give-them value system. But either way, what makes us take notice is their authenticity—their uniqueness. Are they being themselves or worse still, trying to be something they’re not? It is in the visible world that our “invisible” inner world is manifested. When we integrate our whole person, we create the potential for meaning in our work, trust with those we lead, and in turn, we build our uniqueness as a leader. In Rework, they write about building uniqueness in a business: “If you’re successful, people will try to copy what you do. It’s just a fact of life. But there’s a great way to protect yourself from copycats: Make you part of your product or service. Inject what’s unique about the way you think into what you sell. Decommoditize your product. Make it something no one else can offer.” The same is true on an individual level. You are your product. When you put more of you into the equation, you make yourself unique—even indispensable. When you add in humility, you create meaning that people can get behind. [In Seth Godin parlance: Indispensable + Humility = a Linchpin you can live with]
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:25 PM
02.21.10

What Organizations Value in Leaders Bloomberg BusinessWeek.com and Hay Group have released the results of their annual survey which ranks the best companies for leadership and examines how those companies develop leaders. Last year the quality that the Top 20 companies valued most in their leaders was execution—the ability of leaders to achieve results through others. This year, the most valued quality is strategic thinking. "This year's emphasis on strategic thinking suggests that, like an individual recovering from a personal upheaval, businesses today are taking stock: reviewing their options, rethinking their strategies, considering new opportunities and innovations." It also suggests more long-term thinking. 
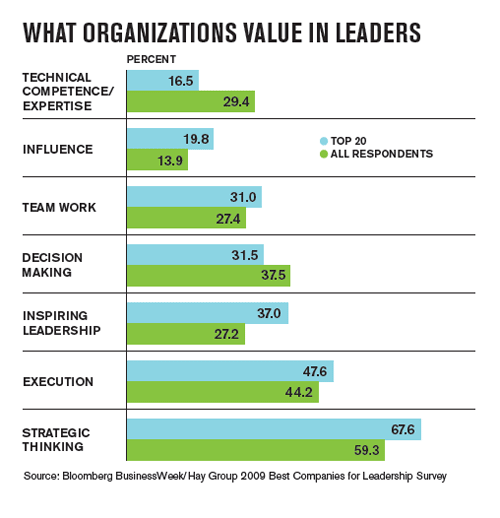 "While the data suggest there is no one best way to grow leaders, the companies that do it best share certain key characteristics. The top 20 companies address leadership development on multiple fronts, from articulating how leadership behavior needs to change to meet the challenges of the future to managing their pools of successors for mission-critical roles. And, despite the chaotic, crisis-strewn atmosphere of the past year, they've continued to make leadership a top priority."
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:39 AM
01.28.10

What Kind of Leadership Will Work in 2010?The Work Foundation, a British think-tank, released a reaffirming report on the principles of outstanding leadership. They concluded that outstanding leaders do three things:
“Not too many leaders can place a tick by all four of these requirements. Cynical or disillusioned leaders will just add that list to the pile of other leadership theories, which have urged them to become “servant leaders”, “coaches”, “player managers”, and so on. Meanwhile, the disillusionment and dissatisfaction of those who are led grows. And we do not seem much nearer to establishing a clearer idea of what sort of leadership will work in the cynical and confused world of 2010.” He adds this closing anecdote: During the British general election of 1959, the journalist Geoffrey Goodman spent the campaign following the deputy leader of the Labour party, Aneurin Bevan, around the country. He made a record of Bevan’s many memorable speeches. One quotation in particular stands out. Contemplating the world’s increasingly interlinked problems, and the leadership that was on offer to deal with them, Bevan summed up what he saw in these terms: “Smaller and smaller men, strutting across narrower and narrower stages.”In another highlight from the Work Foundation study, they made this observation about the process of becoming an outstanding leader: Becoming an outstanding leader is likely to depend a great deal on maturity, self-awareness and self-development within the job. Some of the outstanding leaders featured in the research did not originally have a people-focused approach, but realised the impact they were having on people and therefore adjusted their style accordingly. They arrived at this point through experience, maturity and reflection. They had a very sophisticated understanding of cause and effect and how their actions can dramatically affect outcomes.I would suggest that “maturity, self-awareness and self-development” will help us to adjust our leadership to the context we now find ourselves working within.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:09 AM
12.14.09

Lift: How to Be a Positive Force in Any Situation
TO OVERCOME the force of gravity—that which pulls us down—we have to generate an opposing force greater than gravity. That force is lift. Any opposition to lift is called drag. In the same way that we use the laws of physical science to lift a plane off the ground, we can use social science to lift “ourselves and others up to greater heights of achievement, integrity, learning, and love,” thereby becoming a positive force in any situation. It’s the pressures of daily living that drag us down. Instead of experiencing lift we fall back into our comfort zones, become reactive, self-centered and fatalistic. To intentionally experience lift and to be a positive influence for others, we have to make a conscious choice. In Lift: Becoming a Positive Force in Any Situation, authors Ryan and Robert Quinn present this fitting metaphor, to explain how we can intentionally experience lift, to rise above the constraints of everyday life and lift the people around us. “All of us have a choice: we can choose to be the kind of people who drag others down or to be the kind of people who lift…. We are relational beings. Who we are at any time depends on who the people around us are, and who they are depends on who we are.” That last sentence can’t be overemphasized. It carries with it a great deal of responsibility, especially for us as leaders. The authors describe lift as “a psychological state in which a person is purpose-centered, internally directed, other-focused, and externally open.” What exactly are these four characteristics of lift? In a very relatable and revealing example—the parenting of a young son, Mason—the authors show how this plays out in real life. I can’t reproduce the example here, but I think from the inferences you will get the idea the authors are trying to convey. The following is paraphrased from their work: Purpose-centered is the opposite of being comfort-centered. The desire to stay comfortable is a characteristic of a normal psychological state. My son Mason’s behaviors were comfortable for me. In my desire for comfort, what had not occurred to me was the possibility that perhaps Mason was behaving differently because of the changes that had happened recently in his life. We need to ask, “Are the results I am trying to create about me and what I am comfortable with or are they about what is best for the other person?” Internally directed is when people experience the dignity and integrity that comes with exercising the self-control necessary to live up to the values that they expect of others. External direction, on the other hand, is a characteristic of a normal psychological state. If Mason was building with his Legos or playing a game when I asked him to do something, I expected him to put those things aside and do it. Yet, if I was involved in an activity and Mason interrupted me, I would expect him to wait until I was done with my activity before I did what he asked. I expected him to show respect to me, but I was not doing the same for him...When people are externally directed, they let circumstances (such as the need to get Mason to clean up or go to bed) drive their behavior instead of their values (such as respect for others’ time and activities). Other-focused is to be open to other people’s feelings and needs. We then empathize with them and feel impulses to be compassionate. When we are self-focused, we are concerned only with our own needs, feelings, and wants. We see other people as objects that either helps us or impede us in our goals. In my case, Mason was an object that was preventing me from my goal of showing that I was a good father. Externally open is openness to external cues. When we are open we learn, grow and adapt ourselves to the situation unfolding before us. When we are internally closed, we ignore and deny feedback. We ignore or deny feedback out of fear that the feedback says something about our worth as human beings. So as a result, we tend to get angry. Again with Mason, I was not showing him the respect that I wanted him to show me. As I opened myself to the possibility that I might be wrong, I also opened myself up to what Mason was feeling, and to what his needs might be and became other-focused. Using scientific research to provide “insight into why lift is important, what the characteristics of lift are, and how our psychological states influence others,” they formulated four questions that capture the nuances required to intentionally move ourselves from a normal state into lift.
This post is getting long, but I would like to share several more thoughts for you to contemplate: When a new situation disrupts our previous expectations, though, it is more productive to change our expectations than to try to make the world conform to our old expectations. The book is full of great examples and scientific evidence to back their perspective. The scientific evidence is really just icing on the cake. The relational principles at work here are sound, but they require much thought and self-examination. This is a book that needs to be read and re-read. Inertia is our biggest enemy. Inertia will keep us from benefiting from this book and becoming a positive force; the kind of leaders that provide lift in our own lives and those we influence. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:10 PM
11.23.09

Do the Leaders within Your Organization Have the Skills They Need To Be Successful In the Future? Do the leaders within your organization have the skills they need to be successful in the future? This is the basic question that the Center for Creative Leadership asked 2,200 leaders from 15 organizations, in three countries between 2006 and 2008. Do the leaders within your organization have the skills they need to be successful in the future? This is the basic question that the Center for Creative Leadership asked 2,200 leaders from 15 organizations, in three countries between 2006 and 2008.
The findings from this research project identified the following seven leadership skills as most critical for success, now and in the future:
However, what I found interesting in the report was the following comment: “These data show that many leaders’ strengths are not in areas that are most important for success. Organizations report greater bench strength in areas ofThe above listed five skills were categorized as over-investments or competencies that are strengths but not considered important. (Additionally, confronting people, putting people at ease, managing one’s career were considered to be competencies that are not strengths and not considered important.) This finding struck me as rather odd for two reasons. First, these competencies are areas where we find people continually getting themselves into trouble and secondly, most of the nine competencies listed have a direct and even causal effect on the seven competencies that the participants found to be insufficient to meet future leadership requirements. Respecting individual differences and lack of self-awareness are two popular weapons of self-destruction. The fact that we think we have these skills sufficiently mastered to render them unimportant suggests that we have blind spots that have not been fully explored. Consultant Wally Bock rightly observed, “The ‘important’ list includes ‘leading people’ and ‘inspiring commitment.’ Those two are among the competencies that the respondents thought they were not good at. Maybe there wouldn’t be a gap on those competencies if they thought things like ‘building and maintaining relationships’ were important.” Absolutely correct. If leadership is about anything, it is about relationships. All our hopes, dreams, goals, metrics, sales, market share and aspirations are going to be accomplished through people. The “important” skills are founded on the “unimportant” skills. Learning how the nine “unimportant” competencies impact and drive the seven “important” competencies will help to fill the leadership gap now and for decades to come.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:32 AM
07.30.09

Emotional Intelligence: Self-Awareness
WITHOUT self-awareness leadership becomes just another exercise in ego gratification. Self-awareness allows for self-discipline and control of the ego. Without it the ego runs amok looking after itself and only incidentally in the service of others if the needs of both happen to align. Self-awareness is the ability to see when an emotion or a perception is influencing your thinking and behavior and, if necessary, do something about it. Gaining control over the state of your mind will pay big dividends in terms of your leadership effectiveness. What is going on beneath the surface? It is the blind spot of leadership. Being able to step back and see both the positive and negative aspects about yourself, to see how you affect others, and to see how you are behaving in real-time, is critical to your success as a leader. Emotional Intelligence 2.0 offers some good strategies to develop your self-awareness as part of an overall EQ skill development program. Self-awareness is a bigger problem than one might think. The book reports that “only 36 percent of the people tested were able to accurately identify their emotions as they happen. This means that two-thirds of us are typically controlled by our emotions and are not yet skilled at spotting them and using them to our benefit.” A proper and healthy self-awareness facilitates an essential other-awareness that is vital to good leadership. You can not manage the behaviors of others without first getting a handle on your own.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:33 PM
07.09.09

The Natural Authority that Comes From Being AuthenticA thoughtful framework from which to view leadership was revealed in an interview and presented in Leading for Success by Andrew and Nada Kakabadse and Linda Lee-Davies. Sr. Judith Zoebelein, a Franciscan Sister of the Eucharist, makes a clear statement about the dynamics of authentic leadership. It also underscores the fact that no one can or should be the “leader” all the time. She states:I do believe that everybody has authority. Living in communities you really come to recognize the gifts and the leadership of each person in different areas. That person may not be the superior and in charge of the house, but if for example, I need someone to come out and help feed goats, I know exactly who I am going to ask, because that Sister has a giftedness with animals. She has the knowledge and intuitive sense about animals that perhaps I don’t have. We call this “authority,” an authority that is authoring life, opening up a new awareness in others. When I work with her, I gain a lot; understand through her something new which is not natively mine to understand.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:03 PM
07.03.09

What You Need to be Doing NowGeoff Colvin, Fortune’s senior editor at large and author of The Upside of the Downturn, offers much to savor and chew on, but his list of five things this recession demands from a leader are essential.One of those behaviors is Be Decisive. He writes, “Leaders in a crisis must not lose their rare opportunity to act. The difficulty is that just when decisions are most easily accepted, they’re hardest to make. All business decisions are made with incomplete information, and that’s especially true in the heat of a crisis. At the same time the stakes are higher than usual. Every instinct tells you to decide more slowly than usual, yet it’s vital that you decide more quickly.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:42 PM
03.23.09

MBA Arrogance and the Myth of Leadership
PHILIP Delves Broughton, author of Ahead of The Curve: Two Years at Harvard Business School, writes in the Financial Times about MBA Arrogance and the Myth of Leadership. Broughton observes: What business schools can teach is organisational behaviour. They can teach compensation systems and recruitment processes. They can offer classes on cash and non-cash incentives, on training, promotion and the value of a corporate culture. They can offer frameworks for negotiations, strategy decisions and implementing change. But when they bundle this up and call it leadership, they risk leaving their students with the faulty impression that they are now qualified, if not obliged, to go into the world and lead. It breeds the arrogance for which MBAs are mocked. It is the merit of Broughton to remind readers of the problems of surrounding leadership education. He is right. Business schools are best at teaching the competencies that business leaders need when performing their tasks. And at this point in time, they are probably rethinking what that means. Teaching leadership – as in take these classes and read these books and you are a leader – is something else. Broughton correctly asserts that MBA students often walk out into the world thinking that they are uniquely equipped to lead the world. It’s an arrogance that is rarely appreciated in the real world and an approach that does not serve them well in the long-term. Books and lectures do not make you a leader, but they can give you the tools to become a leader through the practice of leadership. They point you in the right direction. They fast-track your awareness. They are extremely valuable but they do not make you a leader. That label is earned, not taught. Broughton states, “Not all MBAs can be leaders, nor need they be. Every business needs followers: people who are good at what they do, who are able to implement the plans laid out by leaders.” Here is where discussions of leadership often derail. Broughton is confusing leadership with position. Position is the brass ring and there are a limited number of those to go around. Most people will be left out. He’s right. We can’t all have position, but we can all be leaders. Likewise, we are all – regardless of our position – followers. The idea that “I’m a leader, not a follower” is a foolish notion and belies the ignorance of what leadership really is by anyone who states it. Leadership is intentional influence. Basic to a proper understanding of leadership is the understanding that leadership is not position and does not make you a leader. There was a time when management was just management, the science of providing organizational support for innovators and salespeople to win customers and revenue. No, business schools need leadership courses. They just need better ones. They need courses with a proper emphasis about leadership. I appreciate his phrasing – “this super-sizing of management” – but management and leadership go together. They are often separated so that we can, by pulling them apart, see how they fit together. We need both and we need to be practicing both. One is not better than the other. A good leader manages. A good manager leads. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:50 AM
02.18.09

Goldsmith's Gold: You Are Under the Microscope
In his excellent Succession from Harvard’s Memo to the CEO series, he explains: Let’s face it: your successor, like you, will spend hour after hour listening to potentially boring PowerPoint presentations—on topics that he has already been briefed on. He needs to realize that those presentations may be the summary of months of effort by employees at all levels in your organization. He needs to understand how much these employees care about their CEO’s reaction. He will need to actively listen—and communicate with caring, interest, and enthusiasm—no matter how tired he may feel on the inside. He needs to realize that everyone will not only be listening to his words—everyone will be watching his face. Signs of boredom or indifference that may be ignored if coming from peers can be demoralizing when coming from CEOs. Signs of recognition and support can validate employees and provide needed recognition and inspiration after a great effort. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:22 AM
01.09.09

The Accountable Leader
BRIAN DIVE tells us in The Accountable Leader that many organizations have difficulty developing leaders and fostering effective leadership because they have never considered the context they must lead in. The organization must be structured, Dive contends, so that all leadership roles from top to bottom have well-defined decision rights. In other words, accountability needs to be structured into the very fiber of the organizational architecture at all levels. Accountability, organizational design, and leadership are three inextricably linked factors. An organization is in flow, or in a state of equilibrium, when the required number of management layers (vertical architecture) matches the effective reach (or span of control) over the relevant resources that the organization needs in order to achieve its purpose. After briefly explaining the problem and the key concepts used in correcting it, he begins to present the practical application of his ideas for creating accountability within an organization. He addresses questions such as: How many layers of management are necessary? How do leadership requirements change at different levels? How can potential leaders be identified? How can they be developed? How should people be rewarded?Beyond the useful correctives to organization architecture and accountability, Dive also makes an important distinction between Managerial leadership (operational in nature) and Strategic leadership (changing the organization) for leadership development. Each requires different abilities and approaches in decision-making style and accountability. “Operational accountability is ensuring that existing assets and resources continue to perform better. The resources are given. Problem-solving remains related to actual events, rather than the abstract.” With Strategic accountability, “problem-solving moves into the abstract domain. Solutions have to be found that require mental modeling, as they do not yet physically exist.” On leadership development, Dive writes that “many organizations still confuse values, skills, and competencies” and “it is one of the main reasons why so many leadership development programs fail.” Here are several thoughts in this regard: Although values and skills, especially technical skills, play an important role in who should work in an organization, they are not reliable guides for the assessment of potential and who should be promoted. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:01 AM
12.17.08

Preparing to Lead: Things You Should Be Thinking About NowThe Secrets of CEOs is a valuable tool for reference, inspiration and guidance. Authors Steve Tappin and Andrew Cave have assembled 150 interviews with chief executives and woven them into a lucid and absorbing guidebook on some of today’s big issues. Some of the chief executives they interviewed provided their perspective on what you need to keep in mind as you prepare to lead:Adopt the Mindset of a CEO Approach this from two levels: from the bottom up and from the top down. “From the bottom up, assume the mindset of a CEO in your core work activities: deliver first, but take a broader view on how to help the wider business be more successful. From the top down, learn to assess the business from the point of view of the CEO.” Develop Winning Habits, but Know How to Lose Most CEOs believe that their experience with serious failure or very difficult situations, were some of their most valuable experiences. Lord Browne put it, “Everything adds up to you: a book read, a business, traveling to somewhere that you fail. Experiences build character and you grow your intelligence, skill and judgment.” When CEO of Aurigo Management, Archie Norman hires people, he wants to know, “What has been that moment that you have stared into the cavern? What did you have to do where you had to confront really difficult people, people you just didn’t get along with or you didn’t like?” Be a Student of Personal Development Try to pick up a coach and a mentor pretty early on. Hone your strengths and work on your weakness where you can. Have a Life CEO Mitch Garber says, “It’s important to have not just strategic and business leadership experiences but a broad enough experience of life. For me life experience has included my marriage, bringing up my kids, setting up a shop at 14, being a lawyer, being a professional skier, and my interests in food and travel. It is diverse experiences which allow me to talk to and relate to employees at all levels.” Learn to Celebrate Your Success Take the time to celebrate successes; it will energize you to tackle the next goal. Show Total Commitment but Ruthlessly Change Role if You’re Not Being Stretched “A number of CEOs said that it was vital to absorb everything you can from every role before moving on; do not only excel in your job, but observe how the business you’re in works and what’s going on around you….Move on without regret only when you’ve sucked the experience dry.” Be True to Yourself Ben Verwaayen, former CEO of BT observes, “Authenticity is only possible with confidence because the temptation to be conformist is enormous.” The authors add, “In short, be yourself. When push comes to shove, you have to make all you big decisions with your heart; you can’t lead if you’re acting.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:59 PM
12.10.08

Exploring the Five Key Roles Used by Effective Leaders IN Making Sense of Leadership, authors Esther Cameron and Mike Green asked if leadership is making something happen that would not have otherwise happened, what is it that leaders must pay attention to? They came up with five naturally occurring areas of concern:
IN Making Sense of Leadership, authors Esther Cameron and Mike Green asked if leadership is making something happen that would not have otherwise happened, what is it that leaders must pay attention to? They came up with five naturally occurring areas of concern:
• Discomfort: What’s not working? Where is the organization hurting?
These areas of focus were then paired with five shifting roles used by leaders to deal with each of these areas of concern. Leaders must draw their cues from the environment in which they lead. These roles are: • Edgy Catalyser: Focuses on discomfort, asks difficult questions, spots dysfunction and resistance, creates tension for change.
The authors discuss each of the five roles in detail and show in what context they can be used. They offer a valuable self-assessment and demonstrate ways to expand your role repertoire. Knowing which role or roles you tend to gravitate to is important in a number of ways. Understanding your own tendencies helps you to know which areas you can build on and what you can expect to achieve. It also helps you to know which roles you could develop to make yourself more flexible, but more importantly, it helps you to know the kinds of leaders you should surround yourself with to accomplish your organizational goals. Leaders don’t all have to be highly dominate people; they don’t all have to be interpersonal wizards. It’s not essential for all leaders to be electrifying speakers and leading-edge thinkers. Neither is it essential for every single leader to be superbly organized…but it does help to be at least some of these things. And leaders have to learn to develop the right mix of role to match their personality, the organizational situation and the people around them. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:36 PM
12.04.08

What is the Secret of Great Performers?
MALCOLM GLADWELL tells us in Outliers that when it comes to success, context is everything. Only by asking where a person comes from can we understand who succeeds and who doesn’t. Geoff Colvin would agree but there’s more. In Talent is Overrated, Colvin rightly asserts that “great performance is in our hands far more than most of us ever suspected.” When many people never become outstandingly good at what they do, no matter how many years they spend doing it, why do some people become excellent at what they do? Colvin convincingly argues that in general, it’s not innate gifts or intelligence, but what researchers call deliberate practice that creates world-class performers. A study by Anders Ericsson and his associates concluded that “the differences between expert performers and normal adults reflect a life-long period of deliberate effort to improve performance in a specific domain.” Deliberate practice is not your normal practice. It contains several important elements: it’s designed specifically to improve performance (usually with a teacher or coach), it can be repeated ad nauseam, feedback on results are continuously available, it’s highly demanding mentally (focus and concentration), and it isn’t much fun. Add passion and the good news is that great performance is not reserved for a preordained few. It is available to everyone. Colvin’s homework makes a great case for the idea that leaders are developed. What is alarming is Colvin's observation that “At most companies—as well as most educational institutions and many nonprofit organizations—the fundamentals of great performance are mainly unrecognized or ignored.” He writes that organizations that apply the principles of great performance follow several major rules:
Talent is Overrated is the most readable and pragmatic book on the topic. The examples and relevant research cited are compelling and his application of great performance principles to self-development, business development, and innovation are thought-provoking. Related Interest:

Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:29 AM
11.21.08

8 Dangers Every Leader Must Face and Overcome Don Schmincke writes, "here, climbers resemble corporate professionals. They live passionately while confronting impossible odds. Some are deeply humble while others are psychotic narcissists. They come with all levels of competence; from naive wannabes to elite athletes. And when put to the test, climbers react like professionals: sometimes heroically, other times self-destructively." Don Schmincke chose this environment to answer the question, when it comes to job, career, or personal success, why do some professionals excel while others flounder even with the same methods? To study those who lead teams in the riskiest and most extremely challenging situations encountered in death zone environments, he tuned to mountaineering expedition leader and founder of Earth Treks, Chris Warner. In High Altitude Leadership, Don Schmincke and Chris Warner offer lessons from the death zone that any leader can use to achieve something much higher than they currently feel possible. Where people can die or business can fail, high altitude leadership—people who produce peak performance in the face of extreme challenges—is needed. Leadership is a sweet delusion: so fragile, so easily sabotaged. Whether on a mountain or at work, leading others can quickly become difficult and dangerous. You want badly to influence positive change in your organization. You accept the title of leadership and purposefully trek upward, propelled by hope. In this exciting journey, you seek to be a great leader leading a great company to great altitudes.Schmincke and Warner have identified eight dangers that can sabotage anyone at some point in their journey and put at risk careers, projects, or even companies. Overcoming these dangers requires implementing specific survival tips that are outlined below:
Here at sea level, these dangers don’t seem to pose a very big threat. But it’s deceptive. We figure we can get by. At sea level the margin for error is greater and the consequences often take longer to be realized. In the end, they will destroy you just the same.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:45 PM
11.04.08

Lead By Example
LEADING BY EXAMPLE is one of those things we know and remember to do on our way to do something else. The problem is that it requires a lot more inner work than we are willing to put in, but it leverages our leadership more than any other thing we can do. Unfortunately, it is the norm that leaders don’t know themselves well enough to set an example. Tolstoy once remarked, “Everyone dreams of changing humanity but no one dreams of changing himself.” Yet that’s what it takes to lead by example. John Baldoni has written an excellent and practical book that addresses areas that leaders need to look at in order to be the kind of person that people will want to follow. Lead by Example contains 50 short chapters that pinpoint an area of concern and how to tackle it. It “demonstrates how leaders leverage their best attributes to overcome their shortcomings in order to build trust and drive results.” Baldoni breaks up the 50 chapters into four sections that he describes this way: Set the Right Example
Act the Part
Handle the Tough Stuff
Put the Team First
The way this book is organized makes it a great reference tool that you can refer to when you are faced with leadership—people—issues. It’s also a good book to put in the hands of those who are seeking to lead in your organization. The thinking and behaviors addressed in this book will pay dividends. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:23 AM
09.15.08

Developing Diamonds in the RoughNancy Ortberg is an alumnus of Willow Creek Community Church and is a founding partner of TeamWorx2, a business and leadership consulting firm to businesses, schools, nonprofits, and churches. She has made a important observation concerning leadership development in her book, Unleashing the Power of Rubber Bands. Often in our search for new leaders we go looking for the finished product. She refers to Andy Stanley's comment that leaders always think that they can do a better job than you are doing. So that's a good place to start (unless we are taking ourselves too seriously). A leader's responsibility is to develop these diamonds in the rough. Ortberg writes:We need to keep our eyes open for leadership qualities: energy, dissatisfaction, new ideas, mistakes, and perhaps even a bit of cynicism. These are the raw materials in the making of a leader, not the finished product. Leadership development doe not necessarily start with strong leadership qualities like discipleship, maturity and wisdom. Those are the end products. We need to be looking for the drive without the experience, the vision before the patience, the energy minus the discipline. These are the building blocks, the clues that ell us there is a leader here, but so much still needs to be done.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:06 AM
09.05.08

Bill Hybels on Growing as a LeaderI have little patience with leaders who get themselves into leadership binds and then confess that they haven’t read a leadership book in years. If you’re a serious-minded leader, you will read. You will read all you can. You will read when you feel like it, and you will read when you don’t. You will do whatever you have to do to increase your leadership input, because you know as well as I do that it will make you better.I’m often asked how, in addition to reading, to get better as a leader. And if I’m in a playful mood, I’ll sometimes say with a smile, “Just lead something!” The best way for leaders to get better is to lead something besides their “main thing.” When you use different muscles, you force your body to flex and develop in new ways. Leaders must invite the same type of cross training into their leadership development regimen. The more varied the environments in which you exercise your leadership gift, the stronger that gift will become. Lead something besides your main thing. You will become a far more effective leader. Adapted from Axiom: Powerful Leadership Proverbs by Bill Hybels.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:00 AM
07.28.08

What Is Your Plan For Personal Growth?
YOU WON'T GROW to your potential without a plan. You’ll get older, but not better. Experience guarantees nothing. Growth is intentional. If you are not growing you’re just putting in time. Waiting. Crucibles of Leadership by Robert Thomas, is an important book that asks, “What is your personal learning strategy?” A PLS is “a highly individualized plan for leveraging hard-won insights about learning from adversity and using practice to improve performance.” We all have crucibles, but it’s what we do with them that is important. Thomas writes that crucibles “are like trials or tests that corner individuals and force them to answer questions about who they are and what is really important to them.” Crucibles become valuable when we intentionally mine them for lessons that make us more effective, aware and integrated. Warren Bennis points out in the foreword that the self-awareness we should gain is “the kind of deeper understanding of self that then turns outward rather than inward and results in better understanding of others and the organizations that matter to us.” Thomas says that we have to change our approach to learning. We shouldn’t wait for just the right moment to arrive, but learn in the moment—in real time—to, as he writes, “learn while doing.” Preparation is essential to learning. In order to take advantage of our crucibles, we must develop a Personal Learning Strategy (PLS). Thomas introduces a framework for crafting a PLS complete with exercises to help you properly move through each step. It begins with a little introspection—understanding why you want to lead, what motivates you to do so and understanding how you learn. Then you need to access your capability in three core areas: adaptive capacity, engaging others through shared meaning, and integrity. From here you can see areas where you need to improve and strengthen in order to reach your leadership goals. Now you can assign behaviors to each of these areas that you can consciously practice at work and at home. He suggests that you “scan your landscape at work and at home, and identify those instances and roles out of your comfort zone that will allow you to stretch into new behaviors, perspectives, and leadership capabilities.” Organizations too, can tap into the power of a PLS by adopting an experience-based approach to their leadership development program. Organizations need to recognize the importance of crucible experiences and provide the resources people need to extract insight from them in addition to the regular technical and skills training people should be receiving. Most often those resources involve creating a process that links the two learning opportunities together. One important note on a trap that people and organizations sometimes fall into in their zeal to develop character and leadership, Thomas writes, “We create enough pressures to perform that we don’t need to invent new ones just so that we can accelerate leader development. The trick is to harness the crucibles that life sets in motion so the opportunity for learning is not squandered.” Life gives us enough opportunities to learn, but often, we just need help getting the lesson we should be getting from it. Accomplished leaders say that experience is their best teacher. They learned their most meaningful and important leadership lessons—lessons that they’ve integrated into their own leadership style—through crucibles. These were critical events and experiences, times of testing and trial, failure more often than grand success, that grabbed them by the lapels and demanded to know “What do you stand for?” and “What are you going to do?” A situation arose that did not respect age, gender, generation, nationality, talent, or charisma; all it asked was that the person step up and be someone or do something they’d never been or done before. Having a Personal Learning Strategy is a way of thinking about and looking at life that allows you to proactively grow from what life throws at you, rather than being knocked out by it. You need a Personal Learning Strategy. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:06 PM
07.16.08

The Four Rules of Influence
CHRIS WIDNER’S book, The Art of Influence, gives the proper emphasis regarding the topic of influence. He says in this entertaining short story that influence is a gift followers give you because you have become the kind of person they want to follow and be influenced by. He provides four rules of influence:

Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:07 AM
06.27.08

The Offsite: A Fable to InternalizeThe Offsite is a business fable based on the principles and practices set forth in the classic leadership book, The Leadership Challenge. And it works. Using memorable characters, author Robert Thompson, has created a story that is a great introduction not only to James Kouzes’ and Barry Posner’s work, but to the practice of leadership itself.With our birds-eye view of the offsite and its main participants, we can see the mental struggles and the ah-ha experiences of the personalities as they begin to view leadership as a way of thinking and a choice that each individual must make. They begin by facing their reality and then learn to see a new way to get from where they are to where they want to be. They begin to see real leadership as helping people to discover what matters to them and helping them to connect to it. “Leadership is about people. Leadership is how you get management done. Leaders stretch others, not stress others.” Through the offsite seminar leader Charlie, Thompson presents the Five Practices of Exemplary Leaders this way: Your credibility matters so … Model the Way. How? Clarify values by finding your voice and affirming shared ideals. Set the example by aligning actions with shared values. Your voice matters so … Inspire a Shared Vision. How? Envision the future by imagining exciting and ennobling possibilities. Enlist others in a common vision by appealing to shared aspirations. Your action matters so … Challenge the Process. How? Search for opportunities by seizing the initiative and by looking outward for innovative ways to improve. Experiment and take risks by constantly generating small wins and learning from experience. Your gift matters so … Enable Others to Act. How? Foster collaboration by building trust and facilitating relationships. Strengthen others by increasing self-determination and developing competence. Your gratitude matters so … Encourage the Heart. How? Recognize contributions by showing appreciation for individual excellence. Celebrate the values and victories by creating a spirit of community. This is the kind of book you need to give to everyone on your team and to those your team interacts with. If you’ve read The Leadership Challenge (the new 4th edition will be out in paperback in August), then it’s a good reminder, if you haven’t, then it’s a great introduction. Either way, you’ll find Thompson’s story a quick read, but packed full of thoughts and concepts you’ll want to reflect on and internalize. Leadership is a way of life that takes a conscious choice to build-in to everything you do, from wherever you sit. This is a great place to begin. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 02:35 PM
05.05.08

Learning Leadership the Hard WayInnovator and leader, Dov Frohman asserts that leadership must be learned the hard way—by doing it. In Leadership the Hard Way, Frohman likens the situation confronting today’s leaders to a pilot flying through a thunderstorm.“It is precisely these forces of increased turbulence that have fueled the growing preoccupation with leadership. In such an environment, leadership isn’t a luxury. It’s a matter of survival! Yet the very forces that make leadership more critical also make teaching it virtually impossible. What it takes to lead an organization through that turbulence isn’t simple or straightforward. There is just too much uncertainty. And it takes personal courage. You don’t really know what you will do at the moment of truth. No matter how much training you have (or how many leadership books you have read), nothing quite prepares you for that moment when you enter the eye of the storm!”He believes this means embracing turbulence and crisis, not avoiding it. It means “flying through the thunderstorm.” While there are basic principles to leadership, Frohman says “there are no simple recipes. Until you have lived it, you don’t really know how to do it.” If you are going to learn to lead, you must develop a “particular frame of mind, a distinctive way of perceiving and acting. You must free yourself from habitual ways of looking at things, cultivate an independent and questioning perspective, and be ready to embrace alternative and counterintuitive points of view.” Frohman offers four resources that aspiring leaders can use to learn how to lead: 1. Stay True to Your Passion. No leader can be effective who does not identify 100 percent with the organization’s mission. Because this identification between leader and organization is so important, it’s critical for you as an aspiring leader to identify your passion – what really drives you – and to stay true to that passion through the course of your career. If you do, you will find that this passion is a powerful resource for guiding you through the challenges of leadership the hard way. 2. Get An Invisible Mentor. No aspiring leader has to wait to be assigned a mentor. Choose and invisible mentor, someone whose behavior you study from afar. Choose someone whose leadership style you relate to and admire. Study that person closely. 3. Become a Reflective Practitioner. A term coined by organizational theorist Donald Schön in his 1983 book, a reflective practitioner is one who systematically reflects on one’s own experiences. It’s the kind of learning that happens in the moment. Build systematic reflection into your everyday activity. 4. Learn From Your People. A close relationship with your people can give you a tremendous resource for bootstrapping your leadership capabilities. There are a variety of ways to develop that close bond – be present in the organization, don’t be afraid to expose one’s own mistakes to the organization, welcome dissent, and use your own behavior strategically. Aspiring leaders should get in the habit of thinking of their actions as a form of communication.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 04:01 PM
03.17.08

In Leadership, Context Is EverythingIn leadership, context is everything. As we have said before, leadership hasn’t changed—the context we operate in has changed. Russell Palmer’s book Ultimate Leadership is on target. He believes that “the principles of leadership can be effective in a wide variety of situations, but often they need to be applied in a very different manner depending on the circumstances and the constituent groups involved.”This of course, makes perfect sense, but what makes no sense is how often it isn’t applied. We tend to plow along the way we have always done things without regard to our current situation. Palmer writes, “Success or failure can often depend on modifying leadership styles to suit a different context.” While there is no single style of leadership that works in every situation, there are basic principles of leadership that apply universally. Palmer explains some of those principles such as integrity, execution, good judgment, innovation, communication and people skills among others. The core of the book provides practical, well-heeled advice on applying basic leadership principles in a variety of contexts. He discusses execution and the pros and cons of specific contexts such as top down, crisis leadership, partnership of peers, academic, entrepreneurial organizations, non-profits, government, and the military. He includes a great deal of his personal experience and interviews with thoughtful people in each of these areas. When leading “partners and peers who have relatively narrow specializations,” Palmer points out, “leaders need a broad view. In other words, they must be generalists who know a good deal about many things. One of the problems in today’s society is that we develop more and more people with narrowly specialized knowledge…. The best subject from an educational standpoint for a leader is the study of history. Reading biographies is also particularly helpful…. The best education, for instance, for a businessperson is a strong liberal arts undergraduate program and then a graduate business program.” In the end, he concludes, it’s all about people.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:12 PM
03.14.08

Good Followers Make the Best Leaders IN CASE you didn’t know it by now, let me just say, followership is the crucible of leadership. There is no better way to learn leadership than by being under someone else—leading from the second chair. As ironic as that may sound, it’s true. Learning to lead under someone else provides you with the opportunity (the necessity) to learn to lead without coercion. You learn to let your leadership speak for itself—authentically.
IN CASE you didn’t know it by now, let me just say, followership is the crucible of leadership. There is no better way to learn leadership than by being under someone else—leading from the second chair. As ironic as that may sound, it’s true. Learning to lead under someone else provides you with the opportunity (the necessity) to learn to lead without coercion. You learn to let your leadership speak for itself—authentically.
Yet we still, as Barbara Kellerman states in her important new book, Followership, overestimate the importance of leadership and underestimate the importance of followership. She argues that “thinking leadership without thinking followership is not merely misleading, it is mistaken.” Why? The context of leadership has changed. First, leaders have been demystified, in part by modern media, which demands grist for its mill 24/7; and in part by the modern culture, in which figures of authority are no longer exalted or even so much respected. Second, because the line between the leader and the led has been blurred, the led have been emboldened. She points out that much of this is cyclical. I would agree. It’s hard for human beings to find balance. Consequently, we continually find ourselves reacting to someone else’s excessive behavior. While we have spent a great deal of time distinguishing between types of leaders, we have not done the same with followers. Kellerman spends a good portion of the book explaining followers. She describes four types: Bystanders, Participants, Activists, and Diehards. She writes: “Followers are us. This does not, of course, mean that all of us follow all of the time—sometimes we lead. But all of us follow some of the time. It’s the human condition.” She advocates that followers not try to become something else, but more importantly that they change their response to their rank, their response to their superiors and to the situation at hand. She emphasizes:
What we need now is a Followership Part 2, where it is explained to followers just how one should follow. We do a disservice to followers – as we have with leaders – by requiring no character development and self-discipline. When we learn to develop better followers, we will get better leaders. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:06 AM
02.11.08

Insultants Wanted WE need people who will tell us like it is in the right way. Often we don’t like to hear what they have to say but we should never discourage them. Frequently, leaders are the last to know. Keith McFarland author of The Breakthrough Company, calls these straight-shooters insultants (inside consultants). He describes them as those people “willing to ask the tough questions that cause a company to think critically about its fundamental assumptions. The value of insultants is that they will go to great lengths to get their companies to reevaluate a position or adapt to a changing environment.”
WE need people who will tell us like it is in the right way. Often we don’t like to hear what they have to say but we should never discourage them. Frequently, leaders are the last to know. Keith McFarland author of The Breakthrough Company, calls these straight-shooters insultants (inside consultants). He describes them as those people “willing to ask the tough questions that cause a company to think critically about its fundamental assumptions. The value of insultants is that they will go to great lengths to get their companies to reevaluate a position or adapt to a changing environment.”
If you think that you welcome these people, think again. A survey showed that while 90 percent of CEOs believed that their companies regularly implemented ideas that the CEO initially didn’t like, only 60 percent of their direct reports agreed. McFarland reports that people tend to differ to authority and rank because they feel that they must know better. “But often authority figures are wrong, and if an organization doesn’t have a strong insultant culture, errors are likely to be propagated throughout the company.” If you feel you are an insultant, don't think you begin by charging in like a bull in a china shop. There is a right way and a wrong way to do things. You are trying to make the leader successful, not trying to show how smart you are or place the spotlight on yourself. Good insultants must learn to excel at relationships based on genuine care for others. McFarland offers these tips that one would do well to heed:
As a leader, you gain nothing by not knowing what people are thinking. People with ideas and challenges to your way of doing things are not necessarily being insubordinate. They are practicing leadership. Leaders can encourage a candid environment be celebrating productive failure, involving people enough in the issues that they can make intelligent contributions, focusing on both employees and customers that have left the company, and using humor to encourage frankness and trust. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:47 PM
02.04.08

Charles Handy: Are Leaders Born or Made?Charles Handy, in another thought-provoking distillation of his thoughts, Myself and Other More Important Matters, ponders the idea of getting to the bottom of who we really are and the difficulty of seeing ourselves as others see us. Throughout our lives we all play many parts and in a sense, become different people. Can we become something different from what we see ourselves as being to this point? Can we become a leader? Handy weighs in on this:One of the debates in psychology is whether we have a core identity that is sitting there in our inner self, waiting to be revealed, or whether our identity only evolves over time. One of the perennial questions that bug organizations is a derivation of that debate – are leaders born or made? The truth, as in most things, is probably a bit of both. The battery of personality tests that purport to show whether we are introvert or extravert, whether we like structured situations or a bit of chaos, are based on the idea that our real identities are formed by early adulthood and that a good life is about finding situations that fir our characteristics. There is some intuitive truth on this….We can’t escape our genes.Leadership is a possibility we can all explore. It is something we can develop if we choose to. What combination of strengths and weaknesses we have to manage will of course vary from person to person, as we are all different; we are born with different genes. And this is as it should be. Leadership development is a highly personal experience that requires self-knowledge and a willingness to confront those areas where need to improve that will make us effective with people. The traits that will make you a better leader are the same traits that will give you the capacity for success in all areas of your life. Above all, our leadership is reflected in our character. At the same time, leadership training offers the opportunity to examine our thinking in an environment where mentors are available to help us to interpret what we find and guide us to the appropriate changes we need to make in our lives. But no training will, of and by itself, make one a leader. That’s an inside job.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:22 AM
12.27.07

Qualities of Leadership Found in Wordsworth
ENGLISH poet, William Wordsworth (1770-1850) wrote in the 1815 edition of his works, what has become a famous preface simply entitled, Preface to Poems. He begins by listing the six “powers requisite for the production of poetry.” Interestingly enough, they make a good list of qualities relating to the practice of leadership. First is Observation and Description. That is “the ability to observe with accuracy things as they are in themselves, and with fidelity to describe them.” Also, to see reality “unmodified by any passion or feeling existing in the mind of the describer.” Second is Sensibility. The more refined our senses are, “the wider will be the range” of our perceptions” and “the more will he be incited to observe objects, both as they exist in themselves and as re-acted upon by his own mind.” Third is Reflection. This quality makes the leader “acquainted with the value of actions, images, thoughts, and feelings; and assists the sensibility in perceiving their connection with each other.” Fourth is Imagination and Fancy. This is the ability “to modify, to create, and to associate.” Fifth is Invention. A quality by which a plan is made “composed out of materials supplied by observation” and are “most fitted to do justice” to the vision. And finally, Judgment. That is “to decide how and where, and in what degree, each of these faculties ought to be exerted; so that the less shall not be sacrificed to the greater; nor the greater, slighting the less, arrogate, to its own injury, more than its due.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:34 AM
11.07.07

Your Leadership BrandAccording to Dave Ulrich and Norm Smallwood, leaders must live the image they want to portray to their customers (followers) and investors. That is their leadership brand. They write in Leadership Brand, “Leadership brand occurs when leaders’ knowledge, skills, and values focus employee behavior on the factors that target the issues that customers care about. Leadership brand is an extension of an organization’s brand identity because it shows up in the behaviors and results of leaders throughout the firm in a manner that bridges employee and customer commitment.” In others words, leaders must walk the talk.But it goes beyond that. It is a philosophy that should permeate the whole organization in order to build leaders for future roles in that organization in alignment with that organizations leadership brand. It is something that is done at all levels by all leaders. Leaders who produce leaders “build a leadership brand by cultivating competence, sharing decision making and authority, imparting information, and distributing rewards.” Organizationally, the process begins by asking not “What do I want to be known for?” but, “What do we want our customers to know us for?” Once determined, living that brand becomes a serious matter; one that should be taken with careful consideration. Leadership comes with a price. Leadership requires a great deal from leaders as their behavior is carefully watched and observed by others. The needs of the customers/followers come first. Accountability is not an option. This applies to any organization. Just ask Tom Haggard or Bob Nardelli. The higher up you go the more intense it becomes. The authors quote Gary Hamel who put it this way: Authenticity is a huge multiplier of individual impact. And, at it core, authenticity is not about being true to oneself (whatever that means), it is about being true to the interests of those whose lives you want to improve and change. Mercenaries, careerists, and egomaniacs are me-centered. Great leaders are you-centered. (Nicely put Gary!)What about a personal leadership brand? They take a chapter to outline this question. It begins with the question, “What do I want to be known for?” But it doesn’t stop there. Ever results oriented (Results-Based Leadership, 1999), the authors say that that question needs to be linked to a desired result so that your brand will endure. A brand statement should read something like this: “I want to be known for __________, __________, and __________, so that I can deliver __________ and __________ at work and __________ and __________ outside work.” You then need to ask yourself if your leadership brand aligns with the organization’s leadership brand. If not, something needs to give. Understanding the identity and needs of those you're leading is the driving idea behind the leadership brand. They conclude: First, focus on the outside in instead of the inside out. Outside in means that customer (and investor) expectations should frame, focus, and influence leader behaviors. When leader know and do things that add value to customers, they are more likely to be doing the right thing. Second, focus not only on the personal attributes of a noble or successful leader but on leadership, or the cadre of leaders within you company. Based on these two principles, a leadership brand bridges the firm’s identity in the mind of those outside (customers and investors) with the behavior of its employees.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:56 AM
11.05.07

The Art of Winning Others Over
If there is any secret of success, it lies in the ability to get the other person’s point of view and see things from that person’s angle as well as your own. IN The Art of Woo or "Winning Others Over," authors Richard Shell and Mario Moussa, make the case that wooing is one of the most important skills in a manager's repertoire. Research would seem to support this claim as people with strong social skills have been shown to command higher fees and salaries than equally talented but less socially adept colleagues. And they are no doubt more pleasant to be around. Winning others over is an art. It is the ability to sell “your ideas to people within the context of ongoing, important relationships.” They maintain, “If you want to be a player in your organization, a successful partner with your customers or suppliers, a leader in your community, or even a good parent, you need to woo people to your point of view by putting your ideas across in convincing, relationship-friendly ways.” To that end, they remind us that the idea in persuasion is not to defeat the other person but to win them over. The place to begin is in understanding your own persuasion style. They have identified five types—The Driver, The Promoter, The commander, The Chess Player, and The Advocate—and have included a Persuasion Style Assessment to get you started. Whatever your preferred style tends to be, the idea is to strike a balance between what the authors identify as the "self-oriented" perspective-where focus is on the persuader's credibility, and point-of-view and the "other-oriented" perspective, which focuses on the audience's needs, perceptions, and feelings. They have created a systematic strategy or Woo Process, to aid you in skillfully getting your point across. In brief, they are: Step 1: Survey Your Situation, that is
They note that authority plays a background role in most interactions and while it can be useful in some situations, it should not be relied upon especially where there are multiple stakeholders. They say, “The formal roles people occupy are the starting positions for a complex dance of organizational influence.” They also note that actually, the higher up you go in an organization, the less authority comes into play and the more important relationship and persuasion skills become. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:03 AM
10.24.07

Making Leadership Development Part of Organizational StrategyMichael Maccoby states in his book The Leaders We Need, that “In any business, good leadership may be the most essential competitive advantage a company can have.” Linking leadership and strategy then, would seem to be an organizational imperative.According to a recent study outlined in The Leadership Advantage by Robert Fulmer and Jared Bleak, leadership is the essential element in the success of any strategic change effort. “Indeed, no strategy is good enough to succeed without strong leadership.” They found that successful organizations built a strong link between business strategy and leadership-development strategy. The link between business strategy and leadership-development strategy is not haphazard, but specific and deliberate and omnipresent. The link is part of the philosophy of the organization that “permeates all organizational levels and is applicable to all employees.” In this way, an organization can keep the leadership-development strategy relevant to each business unit and to the overall business strategy in general. For example: PepsiCo’s leadership-development strategy is grounded in the belief that strong leaders are needed to be successful in the marketplace.Using senior executive to teach emerging leaders is an effective two-way street where both benefit. One of the surprising findings of this project was the degree to which senior executives practice the concept of leading by teaching. At PepsiCo, Paul Russell, vice president of executive learning & development, speaks of “the magic of leaders developing leaders.” According to Russell, the missing adult-learning principle is that “people learn best when they get to learn from someone they really want to learn from.” Russell notes that “at PepsiCo, the ‘teachers’ our executives want to learn from are our own senior leaders. They are world class, widely respected, and have proven that they can do it here!”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:26 AM
10.19.07

The Impending Leadership Vacuum The study reports that the most vulnerable companies are those in the industrial sector and those operating in the Asia Pacific region. Yet the impending leadership crisis is a worldwide issue. Driving the problem is the retirement of baby boomers and rapid growth in Asia. Baby boomers will drain companies of valuable knowledge when they retire, while multinational firms need to find people to lead their businesses in booming markets such as India and China. The crisis doesn’t end there. “Not only are companies concerned with their current leadership capacity,” the study says, “they are confronted by their inability to develop future leadership talent. Over 75 percent of companies indicate building leadership talent is a significant challenge.” Fifty-two percent of the human resources executives interviewed said their organizations may be unable to rapidly develop skills to meet current or future business needs. The report concludes: Creating an adaptable workforce requires more than a series of HR programs….It requires the ability to identify experts and foster an environment where knowledge and experience travel beyond traditional organizational boundaries. It calls for a talent model that can help companies recruit, develop and retain valued segments of the employee population….The human resources organization, by itself, cannot be expected to shoulder this entire effort. True, the HR function needs to take a lead role in providing strategic guidance on workforce issues and designing human capital programs that can enhance workforce effectiveness. However, the entire executive suite needs to play a role in improving workforce performance. This may involve providing functional expertise, taking joint responsibility for executing human capital programs or simply setting a positive example for employees within their organizations. Without this unified commitment, all bets are off….The key to building that kind of workforce lies with the leadership of the organization, facilitated in large part by HR.The ideas in Ram Charan’s upcoming book, Leaders At All Levels, while focused more at developing CEOs specifically, addresses this looming issue and leadership development in general. He has developed a new approach to leadership development that moves it from just an HR function to “an everyday activity that is fully integrated into the fabric of the business and in which line leaders play a central role.” He calls it the Apprenticeship Model. It is essentially learning by doing. In this timely and valuable book, he states that we focus on the wrong people for the wrong reasons and thus we fail to recognize and develop emerging leaders. He constructed a guide to correctly identify leadership talent early-on, called the CEO Nucleus. We’ll take a closer look at what Charan has to say on this important issue as we approach the book’s December 21 release date.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:12 AM
09.14.07

Taking It Personally“Foolish is the person that takes offense when none was intended. More foolish is the person that takes offense when it was intended.”The above statement rings true, because either way we lose. In egonomics, David Marcum and Steven Smith describe the difficulties that arise when we get our identity confused with the topic being debated—when we take things personally. When we get into a vigorous debate, it’s quite common to find that we respond to a perceived attack with behavior that indicates our ego is in trouble. When we respond to a statement or question by comparing ourselves, seeking acceptance, showcasing or getting defensive, it often means that we think our identity is under attack. In other words, we forget about the debate of ideas and respond as though who we are is being threatened and we take it personally. It’s not unusual that we have a tough time separating our ideas from our identity? Trial attorney Gerry Spence explains, “We all have a personal image that he must protect. For example, I do not want to be seen by others, and particularly my myself, as weak, as ill advised, as less than worthy, as stupid, as someone who cannot be respected. I will do whatever is necessary to preserve my personal image of myself. The more fragile my self image, the harder I will struggle to preserve it.” Marcum and Smith explain it this way: “If we can’t distinguish who we are from what we do, what we have, or who we do it with, we won’t see past our titles or tenure in a discussion. If we say to ourselves or others, ‘I’m the Vice President,’ ‘I’m the CEO,’ ‘I’m the Director of Public Relations,’ or even ‘I’m the creative one’ or ‘I’m the advocate for diversity here,’ then we’re parading our identity, and take it personally.” In egonomics, Marcum and Smith examine an exchange between Fred Rogers and Senator John Pastore at a Congressional hearing to effectively explain this point. It clearly showcases the benefits of maintaining a separation between identity and ideas and keeping your ego in check with humility. They explain, “In the intensity of debate, humility is like a two-way surge protector; it keeps us from making it personal or taking it personally.” Of course, the trick is to avoid this negative response cycle in the first place. The authors borrowed an idea from Carl Rogers to give form to an essential attitude to take when faced with a vigorous debate (or when dealing with people in general). The idea is to treat people with unconditional positive regard. That is to say that “everyone is worthy of respect and capable of contribution, even when they don’t particularly act that way or even feel that way about themselves.” We want to assure others that we aren’t trying to change who they are, but we are interested in presenting another viewpoint. If you find yourself in a situation where things have gotten beyond productive, then the author’s suggest using one of the following opening statements before we begin asking questions: “You might be right…” “Even though that’s hard to hear, I’m glad you’re saying something…” “Okay. Let’s talk that one through.” “Say a little more about that.” It doesn’t signal agreement, it expresses a mind open to understanding. Debate needs to follow understanding or people often begin to defend themselves and not their ideas. Finally, in the spirit of vigorous debate and deepened understanding, humility prompts us to ask, “Who cares if I’m right at this instant if we get it right eventually?” If we’re devoted to progress, it doesn’t matter who has the answer, but that the answers are found.In the balance of the book, Marcum and Smith show that shifting conversations from statements and judgments to exploration requires not just humility, but the relentless application of two more principles—curiosity and veracity. They maintain a good blog that is worth checking out also.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:33 AM
09.10.07

Four Warning Signs That Our Ego is Getting the Best Of UsA managed ego is an important trait of the effective person. Authors David Marcum and Steven Smith state in their compelling book egonomics: What Makes Ego Our Greatest Asset (or Most Expensive Liability), that “surprising as it may sound, many people don’t have enough ego, and that leads to insecurity and apathy that paralyze cultures and leaders.” This is an important addition to our thinking about ego and worth examining in more depth. It does sound odd as no doubt, most of us have been told that ego is a bad thing. But an unbalanced ego—either overconfident or lacking in confidence—can trap people in bad thinking resulting in poor or damaging interactions with others.egonomics offers four warning signs that our ego is getting the best of us:
Humility isn’t the opposite of ego, but it plays a vital role in keeping it in balance. Marcum and Smith created the following diagram to help us to understand the equilibrium concept of humility.  The diagram graphically illustrates the two poles of ego and the grounding effect that humility plays to pull us back into a proper perspective. The authors define humility as the “intelligent self respect which keeps us from thinking too highly or too little of ourselves. It reminds us how far we have come while at the same time helping us see how far short we are of what we can be.” Ego doesn’t suddenly pull us to the extremes and twist us overnight into egomaniacs, or lead us to believe we’re above the law. But once we’re in the habit of being off-center, we do slowly start to believe we’re above other things: reproach, being wrong, being questioned, the need to prove we’re right, having a bad idea, following the lead of others, and so on. Being consistently off-center leads us gradually toward the extremes.When we lose control of ego, we lose “trust, respect, relationships, influence, talent, careers, clients, and market share. Each of us has occasionally, perhaps unknowingly, let ego weaken our talents despite our qualifications, expertise, charisma, track record, or remarkable ability.” This is an important book that will be helpful to anyone trying to get a handle on their ego and understand it manifestations in themselves and others. egonomics is a book that every leader should read and one that we will return to again on this blog.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:32 AM
09.07.07

Be Not a Scholar Confused By Your Own Learning
AS ONE studies leadership, I am reminded of Louis Nizer’s words to be “a scholar who is not confused by his own learning.” It’s easy to get caught up in some of the theory, jargon and formulas and find the whole thing inaccessible but to the best minds. Don’t get me wrong, I believe that the books, training, and mentoring are essential to opening our minds to think in new ways. But ultimately, leadership development begins with self-knowledge and the development of a disciplined mind and character. It is specific to our varied own backgrounds and situations. There are hundreds of great tools to help you get there, but the only one that can begin the journey, is you. The late great diplomat, Abba Eban once wrote, “An ‘expert’ is a man who understands everything—but nothing else. He sometimes becomes immune to the intangible but powerful human impulses that lie beneath the surface of his discipline.” Yet, it is in the “intangible but powerful human impulses that lie beneath the surface” where you will find leadership. Fortunately, that is accessible to everyone who makes the effort. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 11:07 AM
09.05.07

Empower Yourself
IN a very practical book, Achieve Leadership Genius, authors Drea Zigarmi, Susan Fowler and Dick Lyles ask, “What if employees didn’t wait to be empowered—but empowered themselves?” Good question, one that places the responsibility for “empowerment” where it belongs. The individual. If you’re waiting for your boss to give up control and decision-making authority to turn you into a free-thinking, free-wheeling employee empowered to determine your own work rules, you’ll wait a long time. Empowerment is a good idea, but as the authors point out, it depends on self-leadership—“people who possess the ability, energy, and determination to accept responsibility for success in their work-related role.” Employee engagement suffers because organizations depend on managers to engage employees rather than developing self-leaders who recognize their responsibility and have the skill to take the initiative for success in their role. The road to empowerment begins with visualizing your ideal role. That vision is something you can begin to build your identity around. How do you see yourself? How do you want others to see you? Your identity will guide your thoughts, decisions, and actions. Keep in mind your vision should be aligned with the goals and purposes of your boss and organization, or you will get no support. The authors remind us to “Consider your role as a piece of the puzzle—one of many in an organization. It is important for you to understand the big picture and your place within it. Your efforts to envision will not only help you understand the meaning of your work, but it will also remind your boss of the vital contributions being made by you and your role.” Wise sages extol the virtue in the moment. But what happens when the challenge of the moment diminishes the energy available for moving forward? Your work-related vision acts like an emotional manager to pull you through the tough times and into a time of possibility. It provides a transition from the potentially threatening current reality to the next step of action. It empowers you to overcome the inevitable obstacles, pain, strife, exhaustion, and any number of inevitable de-motivators that could jeopardize success in your work-related role. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:20 AM
08.27.07

5 Leadership Lessons: Measure of a Leader Aubrey and James Daniels wrote a comprehensive and thoughtful book on leadership entitled, Measure of a Leader. It is a book that deserves far more attention. The premise is a new model of leadership that focuses on the behavior of followers. By becoming a better observer of human behavior we can become better leaders. They say that “most leadership writers limit their premises to the success of the leader at his or her particular venture.” There’s more to it than that. How you accomplish something is as important (if not more important) than what you accomplish. Here are a few lessons from their book:
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:48 AM
07.27.07

Remarkable Leadership: The Kevin Eikenberry Interview Part 3
THIS IS the final post of our interview with Kevin Eikenberry author of the book Remarkable Leadership. Kevin Eikenberry maintains a blog on his web site. LeadingBlog: One thing that gets bantered around a lot today is the idea of the leaderless organization. Do you think that there is such a thing?  LB: I would agree with you completely. I don't think there is such a thing as a leaderless organization in that there is nobody at any given point at the helm. It may be shared, but that there’s nobody in that role, no. KE: Remarkable Leadership isn't even out yet as we're talking now, but I'm already working on what the next book is going to be and that is Remarkable Followership. It’s that role we play as followers. If all of us are leaders then all of us are also followers. And what does it look like as a job title or whatever? How do we still be a highly productive, engaged part of the team? LB: I think that’s really important. That’s one area that I don't think people understand — even people in leadership training — because they get the idea that I'm a leader and so I'm not a follower. Either, or. But throughout the day, sometimes I'm a leader and sometimes I'm a follower. It changes depending on the situation. A good leader knows when to follow. KE: Yes. Let’s just take the microcosm of a meeting. Within a meeting, a remarkable leader, a good leader, is going to be a leader and a follower over and over and over throughout that meeting – or maybe neither and be a facilitator (neutral). So, it’s really about role and understanding that all of us have to lead and follow. If everyone is leading and no one is following then there’s really no leader either. There’s the need for both roles and I think in reality for us to be truly highly functioning professionals, we need to master both of those roles. LB: Absolutely. Finally, what do you think is the biggest factor that prevents someone from becoming a remarkable leader? KE: Oh, to me that’s easy. The biggest factor that prevents it is belief. People don't think it’s possible: “I'm not a leader.” “Someone else is good at that, that’s not me.” “That’s not the thing that I'm good at.” “I don't see myself as that.” “My Dad wasn't a leader so I can't be a leader.” It’s not about potential, it’s not about possibility – yes, there are opportunities, there are development situations where some people have had great mentors and great opportunities and that sort of thing, but in the end, even if you have been given the opportunity to work with a great leader or have a great mentor or have had an amazingly fortunate opportunity, I believe, if you don't believe it’s possible for you to become that, it’s not going to happen. You're not going to see the opportunity. You're not going to take it. So to me the number one factor is belief.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:23 AM
07.25.07

Remarkable Leadership: The Kevin Eikenberry Interview Part 2
OUR interview with Kevin Eikenberry author of the book Remarkable Leadership continues. The final part will be posted on Friday. LeadingBlog: In your book, Remarkable Leadership, you divide teams into two types — basketball teams and track and field teams. Could you explain that? Kevin Eikenberry: You obviously read the book. LB: I did.  LB: So what we're trying to do really, is force track and field participants or teams into basketball teams? KE: I think that happens far too often. I've been on teams like that and I have been in situations like that and I have seen it many times. I've tried to help individual teams and organizations think about it. Most organizations have both kinds of teams and the problem is that leaders try to treat both the same because they've never thought about the differences. LB: You wrote in your book that “remarkable leaders don't delegate, they share responsibility.” What do you mean by that? KE: Well, you know I asked a lot of people about the “delegate” word. The interesting thing that I got was, there’s not a lot of positive feelings around the word delegate. I think that maybe it’s a bit of a play on words but I think that when leaders are thinking about delegating at least in my experience—anytime I think about any book I've read about being a more effective leader or manager and it talks about delegation, it’s talking about handing things off so you can do something else—and when you think about delegating from the perspective of handing things off to others so I can do something else, you're not doing it in support of the other person. You're just doing it in a somewhat selfish way to give me time to do something different, however valuable that might be. I think that the difference is in the focus. The focus of thinking is about sharing responsibility—it's not “I'm sharing this with you, yet I'm going to be free to do something else” but “I'm sharing this with you to help you grow, to help you to get to the point where you can do my job, or that we collectively can be more productive or whatever that looks like.” But really I think its as much about what’s the underlying reason for the activity. Remarkable leaders think about it from the perspective of how’s that going to impact positively the other person and the organization. I know that if I'm thinking about it that way Michael, I'm going to do a better job of handing-off that task—whatever we're going to use to call it. If my intent is about helping the other person be more successful, building their skills, increasing their accountability, whatever that looks like, if my intent is to help them, then I'm going to be much more successful at doing it whatever I call it. So the difference is not so much about the semantics, but the intent. I'm using different words to try to help describe that intent. I may have just done a better job of describing it here than I did in the book. I don't know. LB: That caught my eye in the book because everything you read says delegate. KE: Everybody that I talked to—and that’s one of the chapters that as I was writing that I spent a lot of time calling people, calling colleagues, calling friends, (and the next book I'd be calling you—you're one of those people that I'd ask) everyone had this whole thing about delegating—both as being delegated to and delegating—not a positive thing. I'm thinking, you know, wait a minute, these are opportunities for learning and development and growth, why is it that they don't feel that way. And I tried to back into this whole idea of intent and I think that’s where the difference is. LB: Well, that makes good sense. I was wonder about delegating those tasks where we know we are weak … if you're doing it in the sense of a shared responsibility then that would make sense wouldn't it? KE: That’s exactly right. And I think remarkable leaders do recognize their strengths verses the strengths of the other people on their team. And hopefully, we are self-aware enough to know what it is that we want to be sharing based on what our strengths are. And we're aware enough of the strengths of our team members to be sharing things with them that matches their styles or strengths better. I think as remarkable leaders we recognize that we're better off when we put the right work in the hands of the people that have the strengths to handle it. It doesn't necessarily mean the experience or knowledge as much as the strengths. I think that remarkable leaders figure that out well enough and try to share the work in a way that makes the most sense. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:24 AM
07.23.07

Remarkable Leadership: The Kevin Eikenberry Interview Part 1 THIS WEEK—Monday, Wednesday and Friday—we will feature an interview with Kevin Eikenberry author of the book Remarkable Leadership. Kevin is the Chief Potential Officer of The Kevin Eikenberry Group, a learning consulting company that provides a wide range of services, including training delivery and design, facilitation, performance coaching, organizational consulting, and speaking services. Kevin believes that remarkable leaders are developed. Remarkable Leadership identifies the 13 competencies of remarkable leadership and offers a proven method for applying those competencies at any level of leadership. The book is thought-provoking and easily applied. In this interview, Kevin will share his thoughts on leadership development, lifelong learning, teamwork, delegating, followership and the biggest factor that could prevent you from becoming a remarkable leader.
THIS WEEK—Monday, Wednesday and Friday—we will feature an interview with Kevin Eikenberry author of the book Remarkable Leadership. Kevin is the Chief Potential Officer of The Kevin Eikenberry Group, a learning consulting company that provides a wide range of services, including training delivery and design, facilitation, performance coaching, organizational consulting, and speaking services. Kevin believes that remarkable leaders are developed. Remarkable Leadership identifies the 13 competencies of remarkable leadership and offers a proven method for applying those competencies at any level of leadership. The book is thought-provoking and easily applied. In this interview, Kevin will share his thoughts on leadership development, lifelong learning, teamwork, delegating, followership and the biggest factor that could prevent you from becoming a remarkable leader.
LeadingBlog: How do you define a Remarkable Leader?  LB: What is wrong with how most organizations do leadership development today? KE: The main thing that is wrong with what most organizations are doing is that they think of leadership development as being about events. We always say, “training is an event, learning is a process.” And it’s the same thing for leadership development. Organizations are looking for the magic pill, they've identified people as high performance or their next leader or “they've been a supervisor for three years so we'd better give them some training.” So leadership development looks like this event, this workshop, this seminar, this whatever, and when they've done that they've checked that box and that’s their leadership development process. I think the smartest organizations are looking at it differently. They're looking at leadership development much more holistically. They're thinking about a wider variety of activities, and experiences and processes. Anything from different sorts of assignments, different sorts of projects to application projects, to the chance to be coached or coach others, mentoring programs and a whole host of other things, put together specifically to work best for that organization. So in short, what’s wrong is that people are thinking about leadership development like they do most training and that is as events as opposed to thinking about a process in terms of what really makes learning work. LB: So more of a long term thing? KE: A long term thing, but an integrated thing. Integrated with the work. You could have training that is long term right? You could have a class this week and next month and four months from now and 21 years from now and all that sort of thing, but the real challenge is, I think, integrating it back into the work so that people can go back and really apply what they're learning. LB: You place a lot of emphasis on learning? Would you say that the ability or the desire to learn is the most fundamental skill of the remarkable leader? KE: That’s like the big softball for me. One of the early chapters in the book talks about that very thing. I do believe that the number one skill of a leader—the underlying core skill of a leader—is their ability to learn. Because, if we want all of these kinds of things in our employees or those we lead—we want flexibility and collaboration, and we want them to continually grow and we want them to develop and we want those things for them—then number one, we had better be doing those things ourselves. And secondly, if we want to continue to build our skills—as I said a remarkable leader is someone who does continue to build their skills—that means by definition, that we have to be ongoing, or as I say in the book, continual learners. To me, it is the fundamental underlying skill. And Michael, when I work with groups, I'll ask them when they think of the best leaders they've ever experienced, make me a list of their characteristics, and people will come up with a long list of great attributes, but they won't come up with the word learning. But without learning most of those other things aren't going to happen. LB: So you don't think leaders are born? KE: I don't. I don't think leaders are born. I think that all of us have a unique bundle of gifts and talents that are a part of our DNA and although there are some people that may have some innate skills that help them become some parts of the leadership process more easily—just like there are some people that innate skills that make them better mathematicians or musicians right? But I think just like those things that challenge us as a leader, is to play on our greatest strengths—to utilize our greatest strengths—to become more effective leaders. Because in the end, being a highly effective leader is about being a highly effective human. There are many different ways to lead and the challenge is finding the voice that we best lead with and build on those strengths first. LB: Good. How would you improve your learning ability? Or make the time for it? Sometimes we get so busy that we put “learning” off because we don't have time for it. KE: Absolutely. That’s why, when I started to write the book the learning competency was that remarkable leaders are continuous learners. And I don't think that that’s really true. We're not continuous learners. We're doing all sorts of things and although as human beings we are learning beings, we are not necessarily continuously, consciously learning. The kind of learning we are talking about here is conscious right? And so, I think it’s much more about being continual. On an ongoing basis as opposed to continuous—in every moment being a learner. I think that’s too high a bar to set for ourselves. I think the challenge for us all is that first of all we have to figure out how to make the time for it and the way to do that is to find opportunities. I think if I could encourage people to do just one thing that would make them a more effective continual learner—and it doesn't necessarily take a lot of time, it takes change of a couple of habits—that is that we would just take time to reflect more on our day; thinking about what worked and what didn't, what we want to repeat and what we don't want to repeat, and what we learned that we want to do differently the next time. If we would take 20 minutes every day to do that we would improve so rapidly I think it would be quite amazing. And the way we do that is to, first of all, make a conscious effort to do it. You say, “Well I don't have 20 minutes.” but yeah you do. Because you drive home from work and you listen to the radio or you take your walk and you listen to your I-pod or watch television in the evening, I think there are lots of times we can steal 15-20-30 minutes a day to do these kinds of things. It’s not like reading … having a book in hand or any of those other things. It’s just closing our mind down enough from other things to give ourselves a chance to reflect. And in the end, a learning process has to include a reflection process or we can't learn from our own experiences. I think that that is too often left out. And we're in such a rush to move from one thing to the next—from doing one tele-seminar to another interview, to do another phone call, right?—that we don't take the time to just stop take a mental deep breath and really think about what worked and what didn't. So if I'm going to do a better job in my next interview, I'd better stop and spend a little time thinking Michael, about what went well on this one or not. And I think that is the key for us to become continual learners. If I could say one thing, it would be take the time, make the time to reflect and ask those reflective questions. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 03:23 AM
05.25.07

Developing a Respectful MindHoward Gardner writes in Five Minds for the Future, "Adolescents have potentials for leadership, or for enterprise, that can be marshaled for diverse ends; it is up to their elders—parents, educators, community leaders, slightly older and more mature peers—to influence how these potentials are mobilized." This is a significant thought worthy of repeated reflection. It describes the process of character development throughout our lives. We might consider what functions we occupy and the influence we are having on others.In any event, Gardner believes that the mobilization of these potentials should progress in five directions that can be manifested in five minds. They are: the disciplined mind (a mind trained on a specific scholarly discipline, craft or profession), the synthesizing mind (a mind that can create value from information), the creating mind (a mind that can break new ground), the ethical mind (a mind that contemplates meaning in work and life and then acts on it) and the respectful mind (a mind that welcomes differences between group and individuals). Looking specifically at the respectful mind, he writes that “rather than ignoring differences, being inflamed by them, or seeking to annihilate them through love or hate, [he] would call on human beings to accept the differences, learn to live with them, and value those who belong to other cohorts.” The respectful mind, like the other four qualities of mind, Gardner believes is a kind of thinking or attitude we will need to have to thrive during the eras to come. He says “eras to come” because while we have always needed this quality of mind, it has been a kind of option. Meaning I assume, that the repercussions of not having it were better contained in times past. However, today we are so interconnected that our very survival depends on it. In a global sense he is right. While all of these minds interact with each other, the respectful mind, I believe, would seem to be the cornerstone.  Without it we limit our input—distance ourselves from reality—and virtually assure that we are not effective with others. Consequently, the respectful mind is the first mind we should seek to develop in children and demand from ourselves. Without it we limit our input—distance ourselves from reality—and virtually assure that we are not effective with others. Consequently, the respectful mind is the first mind we should seek to develop in children and demand from ourselves.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:22 AM
05.02.07

Ignition PointsHow do you lead in a situation where you are not in control? Vince Thompson asks in his book Ignited, “Can the principles [CEOs] use to run their companies really work for managers in The Middle like us—managers without the ability to reshape businesses, redirect strategies, or even (in many cases) to hire, fire, and reward employees as we see fit? The answer is a qualified no.”Working from where you are with a foundation of authenticity and self-discipline, you can help to make the necessary changes in your organization and create more purpose in your leadership role. Thompson defines seven ignition points—functions or tools you can develop and use to create unique value to your organization.  The first of these is the power of the Process Master. “One of the most powerful ways for a manager in The Middle to add value is by knowing the processes his company engages in … and knowing them cold.” In addition to specific steps in the process, “It also means knowing the individuals who handle the processes, along with their quirks, strengths, shortcomings, needs, and vulnerabilities.” A big picture thinker. Second, is the power of the Linkmaker. “Great managing is largely about Linkmaking—knowing the people around you, understanding what makes them tick, And connecting their knowledge and skills in ways that will make powerful things happen for the organization.” Third, is the power of the Translator. The translator helps people in the organization to see each others viewpoints and values to help unite them behind shared organizational goals. It’s the ability to translate organizational goals “into actionable ideas that our diverse workforces can ll relate to, buy into, and support.” Fourth, is the power of the Scout. The Scout understands the landscape—the environment, the customers and vendors—the organization is functioning in and communicates that throughout the organization. The Scout tracks people’s changing attitudes, interests and ideas and works to develop its full potential for the benefit of the organization. Fifth, is the power of the Pilot. In the role of Pilot, you need to be “looking for threatening shoals and promising open sea lanes, and working to steer your company away from the former and toward the later.” Sixth, is the power of the Bard. “The Bard is an ignited manager with the ability to record and pass on organizational history … and the evocation of relevant facts and comparisons from past events when current decisions are being weighed.” Why is this so important? Because you can “help others understand where they fit into that story.” That’s vital. Finally, he describes the power of the Healer. “Rather than treating people like cogs in a machine, smart managers empathize with the struggles and aspirations of their team members. They realize that each one is an individual with strengths, weaknesses, and emotions that must be understood fully.” The ignited manager “knows that motivating people is, in part, about nurturing their hearts and minds. The ignited manager “knows that motivating people is, in part, about nurturing their hearts and minds. Thompson begins with a short quiz to help you identify your mindset in relation to the ideas he presents in this book. He finishes with steps you can take for “getting your idea sold and ensuring that you achieve the success and recognition you’re earned.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:51 AM
04.25.07

The Acid Test of Leadership If leadership is about influence then the acid test of leadership must be the following question: If you were stripped of your title – the politics of leadership, the power to punish and reward people – would they still follow you? Would you still get results from them? It's good to ask yourself this question periodically and adjust your approach accordingly. 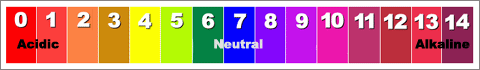
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:18 AM
04.13.07

The Courage to Initiate Relying on a single person to lead the charge reflects a dysfunctional concept of leadership. It sets up expectations that can’t be met. No one person can do everything. No wise leader would. Leadership is a group activity. There is an implied interdependency. Relying on a single person to lead the charge reflects a dysfunctional concept of leadership. It sets up expectations that can’t be met. No one person can do everything. No wise leader would. Leadership is a group activity. There is an implied interdependency.
Everyone has the capacity for leadership. Often what most people lack is the courage—the courage to initiate. Initiative means moving outside your comfort zone. It means seeking out opportunities and being willing to act. Nearly everyone can see a need or see where changes need to be made. What is uncommon though, are people who are willing to take the initiative; to do something about it. Leadership is not always seen in the brightest or the most talented, but it is always found in the courageous. You may not be able to be the CEO but you should think as the CEO. The CEO mindset involves taking the time to think about the forces that are shaping the future of both you and your organization. Managing yourself in this way is important not only to the organization but also to your own personal development.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:35 AM
03.19.07

Looking for Leaders in All the Wrong Places
RECENTLY SOMEONE WAS LAMENTING to me the lack of new leaders in their organization. I replied that perhaps they weren’t really looking for leaders. Maybe they were looking for leaders in all the wrong places. We commonly look for what looks like leadership. We look for people who stand out (self-promoters). We look for clones (people who are just like us). We look for the smartest person in the room (technically competent). We look for people who did a good job for us (promote as a reward). Sometimes we get lucky—often we don’t. Ram Charan begins his book, Know-How, with, “What gets in the way of finding people who can perform is the appearance of leadership. All too often I see people being chosen for leadership jobs on the basis of superficial personal traits and characteristics.” He lists some of the trappings that are often mistaken for leadership: • The seduction of raw intelligence: “He’s extremely bright, incisive, and very analytical. I just feel in my gut he can do the job.”As Charan points out, these attributes are just a small piece of the leadership pie. We need to look deeper. While there may be a shortage of leaders, “there is no shortage of people with the capacity for leadership” as Bill George points out in True North. “The problem is that we have a wrongheaded notion of what constitutes a leader, driven by an obsession with leaders at the top. That misguided standard often results in the wrong people attaining critical leadership roles. … We frequently choose leaders for their charisma instead of their character, their style rather than substance, and their image instead of integrity.” He adds, “There are leaders throughout organizations, just waiting for opportunities to lead. In too many organizations, however, people do not feel empowered to lead, nor are they rewarded for doing so.” There is obviously a problem in the way that we approach leadership development. We are taking the path of least resistance. To put the right people in the right jobs and encourage their leadership potential, we must get to know them to see those things that really count. Our preconceived ideas of what a leader is, is just the thing that is getting in our way of finding great leaders. Our beliefs can set us up for selecting leaders that are dysfunctional. Lists of leadership traits and characteristics can help to educate us, but leadership radiates from who we are. Leadership traits and characteristics are just part of the mix that defines who we really are—our character and attitudes. What else could we be doing to find true leaders?
Posted by Michael McKinney at 10:01 AM
02.23.07

Hardiness: Keep On Breathing Without Letting Go
WINSTON CHURCHILL observed, “The nose of the bulldog has been slanted backwards so that he can breathe without letting go.” In today’s environment, leaders are pulled in all directions. It seems there are more responsibilities and pressures than ever before. Things can easily get out of hand and when they do it’s hard to keep on breathing without letting go. Of course, hardships and stress always accompany accomplishment. It’s important to remember that a strong commitment will carry you forward when nothing else will. Successful people have exceptionally high levels of tenacity and persistence and a general hardiness. Kouzes and Posner find hardiness an important ingredient for leadership success: First, people can’t lead if they aren’t psychologically hardy. No one will follow someone who avoids stressful events and won’t take decisive action. Second, even if their leaders are personally very hardy, they can’t enlist and retain others if they don’t create an atmosphere that promotes psychological hardiness. People won’t remain long with a cause that distresses them. They need to share their leader’s sense of commitment, control, and challenge.Increasing your hardiness has a lot to do with your context setting agility. As Bill Joiner and Stephen Josephs explain, Context setting agility includes scanning your environment, anticipating important changes, deciding what initiatives to take, scoping each initiative, and determining your desired outcomes. Your level of agility in carrying out these tasks depends on how fully you’ve developed two capacities: situational awareness and sense of purpose. Your agility level can also dip temporarily when you’re under high stress. At the same time, increasing your agility level can increase your capacity for dealing with stress.After Steve Jobs separation from Apple in 1985, he recalled, “You‘ve probably had someone punch you in the stomach. It knocks the wind out of you and you can’t breathe, If you relax, you can start breathing again.  That’s how I felt. The thing I had to do was to try to relax. It was hard. But I went for a lot of long walks in the woods and didn’t really talk to a lot of people.” (Steve Jobs: The Journey Is the Reward by Jeffrey Young) That’s how I felt. The thing I had to do was to try to relax. It was hard. But I went for a lot of long walks in the woods and didn’t really talk to a lot of people.” (Steve Jobs: The Journey Is the Reward by Jeffrey Young)
Hardiness. Winston Churchill certainly had it.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 06:35 AM
02.14.07

Simplicity: Focused and On Track Simple Solutions is directed toward getting things done. It’s about being able to “boil things down to their essence” and thereby bring complex issues down to a simple problem statement. To do this you must learn what is important to all stakeholders. Simplified problems are ones that can be acted one through effective, focused communication. Authors, Tom Schmitt and Arnold Perl provide some practical steps to build this skill. They define a continuum of leadership as: clarity of thought leads to simplicity, which leads to focus and powerful communication—the essence of leadership. Here are a few of the ideas found in this book:
Simple Solutions is directed toward getting things done. It’s about being able to “boil things down to their essence” and thereby bring complex issues down to a simple problem statement. To do this you must learn what is important to all stakeholders. Simplified problems are ones that can be acted one through effective, focused communication. Authors, Tom Schmitt and Arnold Perl provide some practical steps to build this skill. They define a continuum of leadership as: clarity of thought leads to simplicity, which leads to focus and powerful communication—the essence of leadership. Here are a few of the ideas found in this book:
Focus on the Amazing Goal, Not the Incremental. The deadly enemy of innovation is incrementalism. By just trying to make problems better a little bit at a time you can lose sight of the possibility of making a quantum leap. A useful question to help you look for amazing goals is, “What would have to be true in order to/for…?” The answer to the question helps you to think differently and make breakthroughs. Be Directionally Correct. “The fact is there will never be enough time or information to help you arrive at the perfect answer. The right answer can be one that is directionally correct. In other words, the solution may not be perfect, but it’s in the ballpark. This paves the way for more action but at least you’re already working with the customer and aren’t stuck back at the starting gate, still refining the model in the search for the non-existent perfect solution.” Determination versus Distractions. Determination is the willingness and ability to overcome obstacles and to avoid distractions. “Determination requires continued focus and commitment to a project. It requires the business savvy to separate the core of an issue from ancillary matters and then to continue plugging away at the core.” It is important to note though, “determination is an art. It requires walking a fine line between passionate focus and blind stubbornness. Use your judgment to determine if the goal needs to be simplified, changed, or even abandoned altogether. Don’t confuse sheer stubbornness with determination. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:26 AM
02.09.07

The Study of LeadershipIn a 1969 keynote address in Tokyo, Peter Drucker made the following observation about an aspect of leadership—management: There are management tools and techniques. There are management concepts and principles. There is a common language of management. And there may be even a universal "discipline" of management. Certainly there is a worldwide generic function which we call management and which serves the same purpose in any and all developed societies. But management is also a culture and a system of values and beliefs. It is also the means through which a given society makes productive its own values and beliefs. Indeed, management may well be considered the bridge between a “civilization” that is rapidly becoming worldwide, and a “culture” which expresses divergent traditions, values, beliefs, and heritages. Of course, along the same lines, leadership encompasses far more than the business or political environment we typically confine it to. From being the act of a few, it has become a personal responsibility. The issues we face today require a multidimensional understanding of leadership that is broader than most academic studies would give it. In fact the study of leadership is not the study of leadership at all, for leadership is the development of an individual’s whole being which is dynamic and ongoing.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 07:41 AM
01.19.07

Six Sigma Leadership Six Sigma expert Peter Pande writes in his book, The Six Sigma Leader, “Studies have repeatedly shown that the high failure rate of many promising leaders is largely due to an over-reliance on a limited set of capabilities. Many times leaders are promoted because of a strong record of achievement, only to derail later because of their inability to adapt. For example, an individual may be good at demanding high performance from his or her followers, or have strong technical ability. However, those strengths are not sufficient when, for example, big-picture thinking or relationship building are also essential to success. To prepare yourself and others for growing challenges, you need the clarity of thought and flexibility to understand your own weaknesses and develop new talents.” Six Sigma expert Peter Pande writes in his book, The Six Sigma Leader, “Studies have repeatedly shown that the high failure rate of many promising leaders is largely due to an over-reliance on a limited set of capabilities. Many times leaders are promoted because of a strong record of achievement, only to derail later because of their inability to adapt. For example, an individual may be good at demanding high performance from his or her followers, or have strong technical ability. However, those strengths are not sufficient when, for example, big-picture thinking or relationship building are also essential to success. To prepare yourself and others for growing challenges, you need the clarity of thought and flexibility to understand your own weaknesses and develop new talents.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:42 AM
01.17.07

Poor Leadership Is Costing UK Business £6+ Billion per YearA new study released this week reveals that UK business is suffering from the poor leadership skills of Britain’s bosses. The survey shows that business leaders fail across the board at setting clear objectives, motivating staff and weeding out poor performers. The study commissioned by Ros Taylor Ltd, a leading firm of Chartered Psychologists, asked over 1500 people from different sized organisations throughout the UK about leadership in the work place. They found:
Taylor went on: “Think about it. Many line managers, heads of department and directors are on a minimum £100K+ pa. These people represent something of the order of a £200K+ investment for the company. As a psychologist, I am intrigued that companies who bend over backwards to “think smart” ignore this area. It’s the “one thing” they could do that would deliver tangible results - and yet the vast majority just don’t do it. They probably think that in the old cliché “leaders are born, not made” and yet in our business we disprove that on an almost daily basis. They can’t leave the innovation and blue sky thinking that comes from truly inspirational leadership to chance – or for that matter to a quirk of genetics – it’s odd to think that multinational companies who factor the canteen subsidy into the cost of a sausage roll don’t have a “leadership development plan.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:37 AM
01.08.07

How to Spot the Future Leaders of Your Business
RAM CHARAN lists in his book, Know How, eleven criteria for spotting future leaders in your organization. He suggests that you repeatedly practice making judgments of other people and reflect on why you might have missed in some cases. Did the individual have the potential you saw in them? How good are your judgments compared to others judgments on the same individual?
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:39 AM
12.22.06

What Drives Our Leadership Impact“Where others see hierarchies, the new leaders see connections” writes Emmanuel Gobillot in his book, The Connected Leader. What differentiates a connected leader is the way in which they impact and influence those around them and this is largely determined by the way in which they view good leadership. More than even our individual skill-set, how we see the role of leadership greatly determines the impact we have on others and the success we will have as leaders.Our impact is the result of a number of factors. Using the iceberg metaphor, above the waterline for all to see, are skills and knowledge. Gobillot writes, “Skills and knowledge are important because they give the leader the ability to take part in the game. On their own, they do not differentiate between average and superior performance…. But it is below the waterline that the real differentiators lie. …Below the waterline, the drivers of impact can be found. Performance will differ depending on how people see their role. If doctors believe that their primary role is solving problems, their behavior is likely to be different from that of surgeons who see their roles as healers.” We need to examine our beliefs if we are to change our impact and effectiveness with those around us. 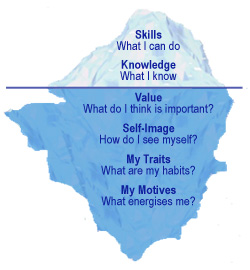 Often we see the "smartest person in the room" or "the leader of all leaders" mind-set to thinking about leadership. With this mentality we won't have the necessary ability to work well with other leaders and developing community. As Jean Lipman-Blumen wrote in Connective Leadership, "leaders cannot just issue orders; instead, they have to join forces, persuade, and negotiate to resolve conflicts." Your ability to do this is largely determined by the "below the waterline" type factors.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:14 AM
12.20.06

The Go PointMen make their own history, but they do not make it as they please; they do not make it under self-selected circumstances, but under circumstances existing already, given and transmitted from the past.  Yet, within those constraints, argues Michael Useem, we have the opportunity to make our own destiny. We all make decisions all the time. Some decisions are in consequential, but often we are called upon to make consequential decisions—those that affect other people. Some people are very good at consistently reaching good decisions in a timely way. Yet, it is surprising how many people are just not great at knowing when to pull the trigger, and how to pull it when they do. The Go Point seeks to address that concern. By taking us into the moment when decisions were made, both good and bad, Useem digs out the principles that emerge from these experiences. From these examples, he constructs templates of fifty principles and tools we can bear in mind when faced with similar types of decisions. He advises us to identify the five or ten lessons that are most salient for the decisions that we most frequently face and then concentrate on just those.
Yet, within those constraints, argues Michael Useem, we have the opportunity to make our own destiny. We all make decisions all the time. Some decisions are in consequential, but often we are called upon to make consequential decisions—those that affect other people. Some people are very good at consistently reaching good decisions in a timely way. Yet, it is surprising how many people are just not great at knowing when to pull the trigger, and how to pull it when they do. The Go Point seeks to address that concern. By taking us into the moment when decisions were made, both good and bad, Useem digs out the principles that emerge from these experiences. From these examples, he constructs templates of fifty principles and tools we can bear in mind when faced with similar types of decisions. He advises us to identify the five or ten lessons that are most salient for the decisions that we most frequently face and then concentrate on just those.
The underlying point in this book is that decision making is a learned skill. You've got to make decisions and then look back on them and mine what lessons you can in order to improve your next decision. Whether it's a long term decision or a split second decision, there is a point when you have to force yourself to make it. That moment is the go point. He writes, “The go point is not always a matter of getting to yes….Rather, the go point is that instant when the choice gets made, whether no or yes, and the commitment moves from consideration to action. How you jump at that moment can make a vast difference, not only for yourself but also for all around you." Below is a template for looking at some of the most commonly encountered problems in reaching a decision.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:49 AM
12.04.06

Leadership Agility
WHAT IS leadership agility? Like agile organizations—organizations that anticipate and respond to rapidly changing conditions by leveraging highly effective internal and external relationships—leadership agility is the ability to take wise and effective action amid complex, rapidly changing conditions. Leadership Agility is an interesting, thorough, and well-written book and one of the best on the topic. Authors Bill Joiner and Stephen Josephs encouragingly tell us that their research “reveals a significant set of findings about the relationship between personal development and leadership effectiveness: As adults grow toward realizing their potential, they develop a constellation of mental and emotional capacities that happen to be the very capacities needed for agile leadership.”Building on the pioneering work of Piaget and Erickson in mapping the stages of human development from infants to adulthood—the pre-conventional stages—the authors identify three more stages they call the conventional stages: Conformer, Expert and Achiever. And finally, there are the post-conventional stages they call: Catalyst, Co-Creator, and Synergist. 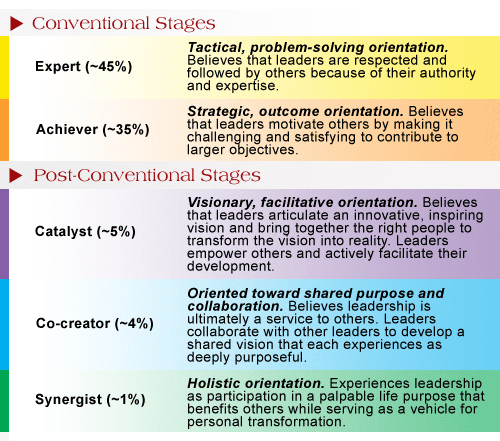 Some people, of course, may never move through all of the stages. Of the 600 managers they studied, most never move beyond the Achiever stage. They write, "Most top executives and administrators, state and national politicians, influential scientists, and other highly successful professionals have stabilized their development at [the Achiever] stage." Only about 10 percent of today’s managers operate at the post-conventional stages of adult development. What does it mean to be at one of the post-conventional stages? Research has shown that people at these post-conventional stages are more deeply purposeful, more visionary in their thinking, and more resilient in responding to change and uncertainty. They’re more welcoming of diverse perspectives and have a greater capacity for resolving differences with other people. They’re also more self-aware, more attuned to their experience, more interested in feedback from others, and better at working through inner conflicts. These stages are sequential and are not personality dependent. In other words, any one can be at any stage but you can move to another stage until you have mastered the one you are at. The question is, “How can we begin to move through these stages of development?” Simply put, you get there by practice—by putting the capacities and traits to work and learning to apply them in various situations. Each stage represents the maturation to a certain point of four competencies and their respective mental and emotional capacities. They state that highly agile leaders orchestrate the four competencies so that they work in concert. They have developed the Leadership Agility Compass to graphically represent these competencies. All eight of the capacities contribute directly to your effectiveness as a leader. 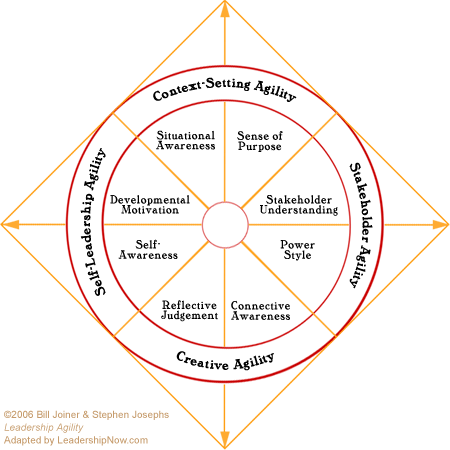 The outer circle on this graphic represents the tasks carried out using the four leadership agility competencies. The middle circle represents the four pairs of capacities that support these competencies. The four mutually reinforcing competencies are: Context-setting agility improves your ability to scan your environment, frame the initiatives you need to take, and clarify the outcomes you need to achieve. It entails stepping back and determining the best initiatives to take, given the changes taking place in your larger environment. Stakeholder agility increases your ability to engage with key stakeholders in ways that build support for your initiative. It requires you to step back from your own views and objectives to consider the needs and perspectives of those who have a stake in your initiatives. Creative agility enables you to transform the problems you encounter into the results you need. It involves stepping back from your habitual assumptions and developing optimal solutions to the often novel and complex issues you face. Self-leadership agility is the ability to use your initiatives as opportunities to develop into the kind of leader you want to be. It entails stepping back; becoming more aware of your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors; and experimenting with new and more effective approaches. After laying this groundwork in far more detail, Leadership Agility provides real life stories to demonstrate what leadership looks like at that level and then clarifies what it takes to move to the next level. You will also learn how to become more effective in your current level of agility. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:02 AM
11.10.06

7 Ways Leaders Handicap Themselves
IN A BOOK that captures the essence of leadership—Great Leadership—author Anthony Bell writes, "For all the importance of great leadership, it doesn’t happen by itself. Without a framework, leaders often handicap themselves in a number of significant ways." He outlines these issues:
Bell writes, "To overcome these obstacles, leaders need some guidelines; they need a framework for understanding and exercising great leadership. Leaders stand or fall not so much by their talent or lack of it as by their understanding or misunderstanding of what great leadership is." In his book he discusses a well presented framework that consists of three dimensions of leadership—organizational, operational, and people leadership. He demonstrates how these three dimensions, when properly integrated and applied, will greatly enhance the quality of your leadership. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:12 AM
11.06.06

Five Hardships Leaders Face and the Lessons They Teach
Adapted from The Center for Creative Leadership Handbook of Leadership Development.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:58 AM
10.24.06

Henry Mintzburg and Frank Brown on Teaching Leadership
THE FINANCIAL TIMES published in a special section on Business Education, a leadership debate between Henry Mintzburg and Frank Brown that has gotten a lot of attention.  At the core of what he takes issue with is the way leadership is portrayed. And rightly so. He has a problem with leaders being presented as “the great one who rides in on a white horse.” It gives the impression that the leader did it all by themselves. He adds: “We have too much of this leadership apart—the hyped-up, individually focused, context-free leadership so popular in the classrooms as well as the press. Courses and MBA programmes that claim to create leaders all too often promote hubris instead. No leader has ever been created in a classroom.” How true. Leadership studies do need to be reconsidered. The current methodology no doubt lead Stanford’s James March to say the following in a recent interview in the Harvard Business Review: I doubt that “leadership” is a useful concept for serious scholarship. The idea of leadership is imposed on our interpretation of history by our human myths, or by the way, we think that history is supposed to be described. As a result, the fact that people talk about leaders and attribute importance to them is neither surprising nor informative. Leadership cannot be taught in the sense that a person can sit in a classroom and walk away a leader any more than one can read a leadership book every week and call themselves a leader. It is possible, however, to teach principles, to lay the groundwork for a way of thinking and to create awareness of traits and characteristics. But until a person combines all of that with their own thinking and character, making it a part of who they are, they are not a leader. And that simply takes time and practice. There is no short-cut to leadership. The leadership journey is an ongoing journey into self-knowledge or awareness. It is a process of reflection to see where you stand in relation to where you should be and determining the steps you need to take in order to get there. Mintzberg’s problem with the conventional MBA classroom is the way it is taught—overemphasizing the science at the expense of its practice and the kinds of “leaders” it tends to generate—MBAs that are too young, and have too little experience to appreciate what they are being taught. That is to say, it tends to produce heroic-type leaders that have no experience to fully understand the world they are charging-in to. As Mark Twain said, "When I was a boy of 14, my father was so ignorant I could hardly stand to have the old man around. But when I got to be 21, I was astonished at how much the old man had learned in seven years." It is astonishing how much these “leaders” find there is to learn after they’ve been out in the workplace for a while that never found a place—or they were never able to make a connection to—in the classroom.  To get the experience and practice necessary to become leaders, Frank Brown, former dean of INSEAD (currently Managing Director & Chief Operating Officer at General Atlantic), writes, “Indeed, true leaders are committed mentors and supporters for training and development initiatives that allow employees to climb the leadership ladder.” He continues: Simply said, the last thing the business world needs is more managers. On the contrary, it is in need of more leaders. On teaching leadership in the classroom you might take a look at Leadership Can Be Taught by Shanon Daloz Parks regarding Ronald Heifetz’s efforts at Harvard. An important book in the area of leadership development is Welter and Egmon’s book, The Prepared Mind of the Leader, for this is where leadership really begins.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:42 AM
10.23.06

The Nature of Leadership
A SURPRISE in this month’s crop of books is The Nature of Leadership by B. Joseph White. Essentially, it is a blueprint for leadership development. He has created a leadership pyramid founded on basics such as a desire to be in charge, and the corresponding ability, strength, and character that all leaders—especially the great ones—must possess.
White cautions, “I make no judgment about the inherent value of Reptiles and Mammals in the workplace. Both are vital and most people are, of course a complex mix of the two. We need task-oriented, no-nonsense Reptiles to ensure the work gets done and done well. We need people-oriented, nurturing Mammals to maintain the human community through which work gets done.” He adds, “I believe organizations falter, fail, or don’t reach their potential both because of leadership that is inadequately Reptilian and because of leadership that is inadequately Mammalian.”
You can read Chapter 1 online: Become a Leader, a Better Leader, a Great Leader 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 05:51 AM
10.05.06

Teaching Leadership
This summer author Paul Taffinder spoke to the Wall Street Journal Online about teaching leadership: I wouldn't say anyone is born a leader. There have been some studies that indicate people who have been exposed to psychologically traumatic experiences are better leaders. They've had to overcome trials and tribulations. So they're more inclined to be challenging and look deep within themselves for what they believe in. Leaders like that learn to be clear about the story they're telling about where they have come from and where they're going.Paul Taffinder’s book The Leadership Crash Course helps to translate lessons learned into practical applications to improve your leadership skills. Looking at the basic personal and emotional components of leadership, the book offers a series of modules that individuals at many levels can study, deploy and refer to from time to time. The lessons are geared toward diagnosing your own behaviors and then applying different techniques to leverage strengths and improve development areas. His web site has interactive tools to further explore your leadership style and preferences. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:58 AM
10.03.06

Leadership in Action is About Dilemmas
Paul Taffinder writes in The Leadership Crash Course that leadership in action is about dilemmas. In an age where we have more choices than ever before, the leader’s job becomes more urgent. The problem isn’t necessarily that we have so many choices, but what we base our selection of choices on. The leader’s job is to guide this process. This might be called imposing context. This speaks to the need we all share for a framework within which to live. Context takes into account where we have been and where we are and where we want to go. The leader must add to the conversation those things that need to be considered to make proper choices. A leader should help to cut through the clutter and help people to consider especially those things beyond the realm of selfish concern. Ironically, getting where we want nearly always means not getting what we want. Leader’s frequently must guide people through behaviors and places they would never choose for themselves if left to their own desires. In a society that wants to achieve the desired ends by simply going straight to the desired ends and short-circuiting the necessary intermediate steps, this can be quite a challenge. At times like these, a leader’s self-knowledge becomes all the more important. 
Posted by Michael McKinney at 08:44 AM
08.21.06

Leading From Within
FROM THE CLASSROOM of Harvard Professor Scott Snook comes an article about leadership styles. It reaffirms the importance of the leader’s self-knowledge. This is not just a cursory overview but an understanding of what we really think on issues we would rather not think about. In Leading from the Maze Jeffrey Patnaude writes, “[T]he leader must be awake and fully alert. Like a nighttime traveler attuned to every sound in the forest, the leader must be aware of all possibilities lurking in the shadows. For we can neither challenge not transform what we cannot see.” Professor Snook said: What you believe about human nature influences your leadership style. If you believe people are fundamentally good—good meaning that they're trying to do their best, they're self-motivated, they want to perform—then your fundamental leadership style will be one way. It will be empowering them, getting obstacles out of the way, and setting high goals while maintaining standards. The better we understand ourselves, the more authentic the contribution we can make—shed the image and do the job.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:59 AM
06.16.06

The Fred Factor for Kids ... Too
I thought I'd pass this along for the Father's Day weekend. This is a timely piece from Mark Sanborn author of The Fred Factor one of our picks for Best Leadership Books of 2004. Mark writes: Proverbs 22:6 says, Train a child in the way he should go, and when he is old he will not turn from it. Check out the Fred Factor Web Site for resources and to subscribe to The Fred Factor eZine.
Posted by Michael McKinney at 01:20 PM
06.15.06

Fathers: Raise A Generation of Outstanding Leaders
THE National Fatherhood Initiative has found that 24-million American children (over a third of all kids in the U.S.) live in homes without their biological father. Additionally, the absence of a dad from so many homes plays a direct role in a number of social ills. Kids in father-deprived homes are more likely to be abused, poor, prone to drug abuse, prone to poor scholastic achievement, and prone to emotional and behavior problems including suicide and crime. A study if violent criminals in U.S. prisons showed that prison populations are overwhelmingly made up of males who grew up without fathers. 60% of convicted rapists, 72% of adolescent murderers, and 70% of all long-term prison inmates came from fatherless homes.  Pat Williams has been going about the country for years stressing the need for fathers and their role in raising leaders. He insists that no child is too young to begin to develop traits that will serve to help them become outstanding leaders. He writes: Kids want to lead. They enjoy setting goals and then taking the steps to achieve those goals. When do kids become bored? When they feel they are being forced to do something they don’t care about. When do they rebel? When they feel they are being told what to do and how to do it. But give them a chance to lead, give them the opportunity and responsibility to make their own decisions, and they will astonish you with their ability to get things done.  You can read an excerpt of The Warrior Within. He is also the author of Coaching Your Kids to Be Leaders.  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:24 PM
05.22.06

Looking for Leaders
WHERE TO FIND good leaders has always been an issue. In our search, we unfortunately, find it easiest to gravitate to the role players— those people who appear to have the qualities we are looking for but really just are good at playing the “game.” They have been around long enough and possess enough ambition to get themselves noticed. These people help to produce the cynicism found in many organizations because they are not effective leaders but effective self-promoters. Once given a title they struggle to keep up because they just don’t have the substance required for the job. General Dwight Eisenhower writes about these people with fake reputations, as he calls them, to his friend General Prichard. This is excerpted from Alan Axelrod’s book, Eisenhower on Leadership: This is a long tough road we have to travel. The men that can do things are going to be sought out just as surely as the sun rises in the morning.In a letter to a friend and fellow commander Vernon E. Prichard, Ike took up the theme of leadership he had discussed in his letter to Scrappy Hartle just two days earlier. “Fake reputations,” he wrote, “habits of glib and clever speech, and glittering surface performance are going to be discovered and kicked overboard.” Those who remain are people capable of “solid, sound leadership,” possessed of “inexhaustible nervous energy to spur on the efforts of lesser men, and iron-clad determination to face discouragement, risk and increasing work without flinching.” Those who remain are the people who also possess “ a darned strong tinge of imagination—I am continuously astounded by the utter lack of imaginative thinking among so many of our people that have reputations for being really good officers.” Finally, those who escape being kicked overboard are those who are most dedicated and “able to forget . . . personal fortunes. I’ve relived two seniors here because they got to worrying about ‘injustice, ‘ ‘unfairness,’ prestige.’” Need will find leaders, but Ike counseled his friend Prichard to get a jump on need by starting to look right now. “While you are doing your stuff from day to day, constantly look and search among your subordinates for the ones that have those priceless qualities in a greater or lesser degree. . . . [Y]ou will find greater and greater need for people upon whom you can depend to take the load off your shoulders.”
Posted by Michael McKinney at 09:51 AM
05.19.06

Leadership Begins at Home
THE Nanaimo News Bulletin reports that Leonard Krog—member of the British Columbia Legislative Assembly—in a speech to the Nanaimo Chamber of Commerce stated, “Community leadership starts at home. The best leadership examples are found in the home by parents who are involved in their communities. People can do small things, like build a community park in their neighborhood, or big things like run for public office or join community groups. Be a leader in your family. That’s how you build a strong and healthy community.” Parents are the earliest and most influential influences on a child. Their examples profoundly affect the kind of leaders they become. Leadership training takes time (think quantity not just "quality") and guidance in every facet of a child’s life from early on. Additionally, leadership needs to be modeled by the parents. It helps if you view all of this in the long-term. The big picture view assists in smoothing out the immature peaks and valleys and helps keep your goals on track. Here are some (not comprehensive) ideas to think on: Take time to know your child. Working with a child’s personality, a parent needs to learn to develop that child’s individual traits and abilities and sometimes temper strengths that left unchecked would become a liability. For example, an assertive, outgoing personality is a great trait in a leader, but without self-control, it can be seen as overly aggressive and controlling.  Take the time to point out where they can learn from the example of others. Use examples and outcomes of decisions of both right and wrong approaches to situations. Teach them cause and effect. Choices have consequences. Take the time to understand what problems and issues your child is dealing with and then guide them to the right decisions by applying the right principles. By instilling principles rather than pat answers to problems, you will give them tools to work with that they can apply over and over again in their life. Take the time to praise them when they make the right choices and gently show them the choice they missed when they go astray. Give them age appropriate responsibilities and let them stand or fall on their choices. (Note: Self-esteem comes from knowing you did do or are doing the right thing and should be praised. It’s not generated from unsupported, manipulative comments designed to make kids—or anyone else for that matter—feel good.) Take the time to involve them in family activities and work. This will help them learn teamwork (sharing and considering others) and a good work ethic. Why do all this? Pat Williams (senior vice president of the Orlando Magic) in his book, Coaching Your Kids to be Leaders, quotes Jackson University football coach Steve Gilbert, I tell young people, "It feels good to be a leader!" Success and failure are part of the adventure of life. Young people need to see that good leaders are important in their community—and there are great rewards for being a good leader. Those rewards include a sense of satisfaction and a feeling that what you are doing is meaningful and significant. You don’t always win when you lead, but that’s okay. Young people should be rewarded and encouraged for stepping up and leading, no matter whether they succeed or fail.Krog added some additional thoughts that apply in any leadership training. “What is negatively affecting leadership across the country is the use of polls to gauge public opinion. Good leadership takes a longer-term view of issues that may or may not be popular. Polls force governments to make popular, short-term decisions to stay in power. And sometimes leadership involves championing ideas that are not so popular.” Of Related Interest:  
Posted by Michael McKinney at 12:08 AM
|
BUILD YOUR KNOWLEDGE
 

How to Do Your Start-Up Right STRAIGHT TALK FOR START-UPS 
Grow Your Leadership Skills NEW AND UPCOMING LEADERSHIP BOOKS 
Leadership Minute BITE-SIZE CONCEPTS YOU CAN CHEW ON 
Classic Leadership Books BOOKS TO READ BEFORE YOU LEAD |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||